A Study on Approach of Historical Townscape Conservation in Urban Area Corresponding to the City Planning System in China
journal or
publication title
福井大学工学部研究報告
volume 50
number 2
page range 273‑281
year 2002‑09
URL http://hdl.handle.net/10098/3257
mi#*'? I $ $ iJf~¥rH5 m 50 ~ m 2 % 2002 if: 9 ~
Mem. Fac. Eng. Fukui Univ., Vol. 50, No.2 (September 2002) 273
A Study on Approach of Historical Townscape Conservation in Urban Area Corresponding to the City Planning System in China
Yongguang ZHOU*, Yiping CHEN**, Shinji NOJIMA *** and Yoshiaki HONDA ****
(Received August 20, 2002)
At first, this research has arranged development ofthe conservation policy of the historical area in China since 1982. Moreover, considering the city planning system in China, the inconsistency of urban renewal and historical townscape conservation is analyzed. At last, the conservation project of Old Street in Huangshan city is taken up as a case study, the approach and the feature of conservation in urban area corresponding to the city planning system in China are clarified.
Key Words: Historical Townscape Conservation, Active Conservation, Historic Cultural City(HCC), Huangshan, China
1. Introduction
1.1 Approach of historical townscape conservation The pioneer of historical townscape conservation in Japan is Kiso Tsumago, connects to tourism development and is making restoration of the historical town successful from the end of the 60s. In recent years, the research on preservation of historical area prospers. Various research results including Eizo Inagaki 1), Shoji Yoshida 2\ and scenery management plan and scenery preservation 3), balance reservation of living standard and historical townscape conservation 4),
community development and decision of scene formation system 5), are mentioned. In this research, there have three values (life value, cultural property value, and scenery value) for historical areas; and the ideal preservation approach can summarize the following features.
1) Harmonize a building and its circumference environment with extension and alteration (height, capacity, material, color tone, etc.) besides restoration of typal buildings, by restriction and guidance.
2) Make the inside ofa building to correspond to present-day life style etc., for reservation of living standard. And 3) Decision of the scene formation system based on citizens'
• Graduate School of Engineering
.. Dept. of City Planning, Zhejiang Univ., China ... Graduate School of Eng., Fiber Amenity Eng.
····Dept. of Architecture and Civil Engineering
participation in municipal affairs, and revival of tradition culture.
That is, the approach and organization for guiding the continuous change of the whole cultural property like
"Active Conservation" 6) or "Conservative Development" 2), which put preservation of the whole cultural property including the sets of a traditional buildings, and environment where people live in the traditional area or peculiar cultural area. Although tourism development which took in historical townscape conservation is the flow in whole-world range in recent years, "Cultural Tourism Charter" 7) lifted by ICOMOS agrees with the main point of this "Active Conservation" .
1.2 Background and purpose of the research
In "Venice charter" 8) which ICOMOS adopted in 1965, "a historical commemoration building is that not only a single architectural work but also the architectural environment of specific civilization, important development or the city that can find out the vestiges of an important incident historically ... " , and the concept of a "historical commemoration building" developed into "the environment as an area" from "the building as a point".
In China, specification of a "Historic Cultural Cities Designation System" (1982), especially conclusion of world heritage preservation treaty since 1987, the recognition of preservation for history culture is deepen, and concern of preservation is increasing in not only point- cultural properties, such as "tangible cultural properties" and
"commemorations", but also historical areas and "intangible cultural properties". However, it can say that the city planning system (land using, city planning and renewal system) has a deep socialistic color, and the suitable historical townscape conservation system corresponding to this system is not hardened yet, and "developmental destruction" is seen in the whole country.
Based on this background, this research has arycmged the development of the preservation policy of the historical area in China since 1982 first. Moreover, the city planning system in urban area in China is considered, and inconsistency of urban renewal and historical townscape conservation is analyzed. At last, the conservation project in Huangshan Old Street is taken up as a case study, and the approach and the feature of conservation corresponding to the city planning system in China are clarified.
2. Related system of historical townscape conservation
2.1 "Historic Cultural Cities Designation System"
In the "Cultural Revolution" in China (1967-1976), there are circumstances of large-scale destruction of cultural properties. It is also indicated to be remarkably destruction of cultural heritages and historical sceneries is progressing in the economic- refonn progress since 1978 9). In 1982, China proclaimed the "The Law of Cultural Property Preservation"
based on the "Cultural Property conservation ordinance"
which fonnulated in 1961. According to "The Law of
Cultural Property Preservation", the whole urban area of a city where the cultural properties contains "tangible cultural properties" and "commemoration", and other cultural properties are rich can be specified to be a "Historic Cultural City" (the following, "HCC") (Fig. 1). In addition, in order to specifY it as a "HCC", it has been a necessary condition to have one or more "Historical Area". According to the "HCC"
designation system --in 1982, 1986, and 1994 - Culture Ministry and Construction Ministry specified 99 cities to be national-class "HCCs". In addition, many provinces (and direct control city, autonomous region) specified 82 province-class "HCCs" until 1995.
According to Yehua's research, it can said that the cultural property preservation system in China developed into
"conservation for an area" from "preservation of a point" by the "Historic Cultural Cities Designation System")O) (the foHowing, "HCCDS"). However, although "HCCDS" has a basis in the " The Law of Cultural Property Preservation "
and the "Town Planning and Zoning Act", it is also pointed out, the law that can specify generally the framework of the preservation system for historic areas has not been formulated yet.
However, inconsistency of historical townscape conservation and urban renewal is deepening with economic growth in the past 20 years. Restricted to the cities specified to be "HCCs", several examples of destruction could be given))). Furthermore, in the historical area of Dinghai City in Zhej iang Province, large-scale clearance is performed
The law basis for Historical Townscape Conservation in urban area in China The Law of Cultural Property Preservation (1991 amendment)
The 8th. The city where cultural property is rich could become a "Historic Cultural City" by examination of the State.
The examination standard for "Historic Cultural City" (Culture Ministry, Construction Ministry, and China Architecture Institution, 1985).
Standard I. One or more historical area in the city.
Standard 2. Deserves a certain city's type in China.
Standard 3. Compared with other cities, it has the peculiar history culture value.
Standard 4. Actually existing, not by history publication.
Standard 5. Emergency.
"Historic Cultural City" protection demand in city planning decision(Culture Ministry, Construction Ministry, 1994). And the extract of "city planning decision detailed rules" (Construction Ministry, 1995).
- Position the protection plan as a special plan of a city master plan.
- The technical standards for "Historic Cultural City" protection plan (the concept of "Historic Cultural City", the examination standard and system, examination / permission system ofa protection plan, etc.).
- The protection measure on city master plan ( the population, industrial structure, and land use in old town, and space composition and scene).
- drawing of the protection range, a protection measure, opinion / plan for repairing and use.
Reference: Yehua et al. ( 1997), " A study on Historic Cultural Cities Conservation System in P.R.China", 1. Archit. Plann. Environ. Eng., AU, No. 494, p195-203, Architectural Institute of Japan.
Fig. 1 "Historic Cultural Cities Designation System" in China
from 1997 - it received a trial which citizens are asking the local government for criminal liability in 2000 (this is exceptional for China). It shows the situation which "HCC"
designation system does not stopped the destruction of the tradition scenery by urban renewal.
Conscious for "Developmental destruction" by urban renewal, the approach to "HCC" preservation is developed from the designation system to conservation master plan (whole city), and from the conservation master plan to the plan of a district level ("historical area") for these 20 years;
moreover, it is pass the process from the designation system of a country to local "HCC" conservation ordinance (Fig. 2).
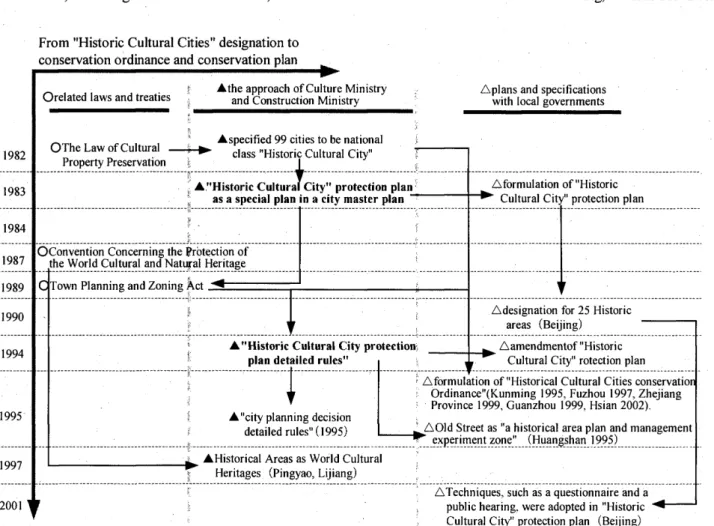
2.2 From "Historic Cultural Cities" designation to conservation ordinan~e and conservation plan
One process is the embodiment to the master plan (for whole city) and the conservation plan at a district level from
"HCC" designation system. Some "HCCDS" designated cities have established the urban conservation plan from 1983. The Construction Ministry and Cultural Ministry established " The demand of conservation plan and decision for Historic Cultural Cities" in 1994; the principle of conservation, drawing of historical areas, and the
From "Historic Cultural Cities" designation to conservation ordinance and conservation plan ....
-
275
preservation measures is needed in "HCC' city master plan (Fig. 1). At the present, the related "HCCDS" system was formulated by Construction Ministry and Culture Ministry, and, execution of the system is not a subsidy system but focusing on the conservation plan by the local government. Moreover, in the 3rd "Historic Cultural Cities"
specification, it deterred the destruction accompanying urban development and decided the view of "preservation is the Lord and urgent from urban redevelopment" 12).
Another process is from "HCCDS" designation system of country to conservation ordinance of provinces and cities.
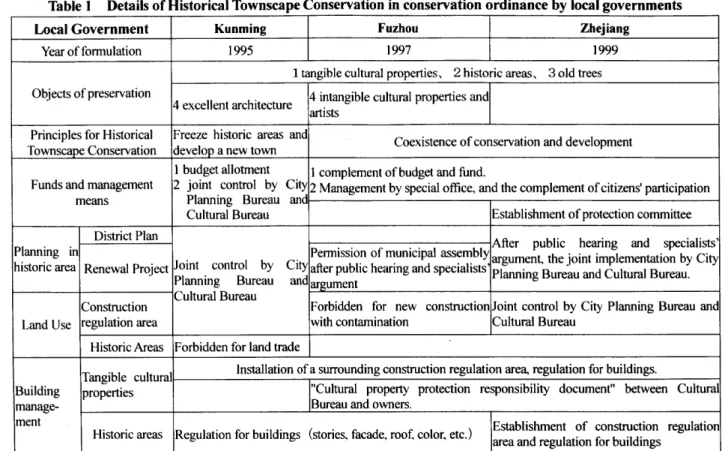
Four cities and one province have formulated "Historical Cultural Cities conservation Ordinance" from 1995 (Kunming 1995, Fuzhou 1997, Zhejiang Province 1999, Guanzhou 1999, Hsian 2002). Table 1 shows the contents of historical townscape conservation in the "conservation ordinance" .
The main candidates for preservation of "Historical Cultural-Cities conservation Ordinance'!' are: 1. designated cultural assets, 2. historical areas, 3. old trees. About the urban planning of historical area, joint examination of city planning bureau and cultural property bureau is needed in the conservation ordinance in Kunming, Yunnan Province.
... the approach of Culture Ministry
Orelated laws and treaties and Construction Ministry b.plans and specifications
with local governments
"
OTh f C I I " "'specified 99 cities to be national ;
1982 P e Law 0 u tur~ ~ class "Historic Cultural C i t y " " " ' - : - - - '
roperty PreservatIon
t
1--~----"'*---f;--- ---.. ---~:.------ .. --.---.---.----,~---.---.------ 1983 .... "Historic Cultura City" protection plan' .. b.formulatlOn of Hlstonc
--- --------;:,:. -------------- -----~'~--------------- ----- ----- --. ----- -- -----------
1990 b.designation for 25 Historic
; , r
areas (Beijing).~---.---.---.---.. ;.---.---.---,---·i·--- --- -
1994 ... "Historic Cultural City protection ... b.amendmentof "Historic
plan detailed rules"
C
r - Cultural City" rotection plan--- --- ---1---+--- --- ---
1 b. formulation of "Historical Cultural Cities conservation Ordinance"(Kunming 1995, Fuzhou 1997, Zhejiang Province 1999, Guanzhou 1999, Hsian 2002).
1995 ... "city planning decision
detailed rules" (1995) . b.Old ~treet as "a historical area plan and management __ _ ______________________________________ -;,______ __ __ __ _________________ __ ______ __ _______ __ _ _ __ _________ __ ___ ___ ~~P_~!.~~_~~! _~~~~~~ ___ ~tI_':I~~g_~~_~!!_ )_?2~~
_____________________ _
1997 L--_ _ _ _ _ _ _ --I.l~ "'Historical Areas as World Cultural
'f
Heritages (Pingyao, Lijiang)f. b. Techniques, such as a questionnaire and a
2001 '
r
public hearing, were adopted in "Historic ... ~I----J_______________________________________________ " _____________________________________________________________________ . ______________
~_~~~~~_~! _~~!~'~_p.~~!~_~~~?_~_ p. !~~___
~~:i:(i,~J?! _________________ _Fig. 2 From "Historic Cultural Cities" specification to conservation ordinance and conservation plan
Table 1 Details of Historical Townscape Conservation in conservation ordinance by local governments
Local Government Kunming Fuzhou Zhejiang
Year of fonnulation 1995 1997 1999
1 tangible cultural properties, 2 historic areas, 3 old trees
O~jects of preservation
4 excellent architecture 4 intangible cultural properties and artists
Principles for Historical Freeze historic areas and
Coexistence of conservation and development Townscape Conservation develop a new town
1 budget allotment I complement of budget and fund.
Funds and management 2 joint control by City
Planning Bureau and 2 Management by special office, and the complement of citizens' participation means
Cultural Bureau Establishment of protection committee
District Plan
After public hearing and specialists'
Planning in Pennission of municipal assembly
Joint control by City argument., the joint implementation by City
historic area Renewal pf(~ject after public hearing and specialists'
Planning Bureau and Planning Bureau and Cultural Bureau.
Cultural Bureau
argument
Construction Forbidden for new construction Joint control by City Planning Bureau and
Land Use regulation area with contamination Cultural Bureau
Historic Areas Forbidden for land trade
Tangible cultural Installation of a surrounding construction regulation area, regulation for buildings.
Building properties "Cultural property protection responsibility document" between Cultural
manage- Bureau and owners.
ment Establishment of construction regulation
Historic areas Regulation for buildings (stories, facade, roof, color, etc.)
area and regulation for buildings
Simultaneously, restnctlons, such as present condition maintenance (repair is possible with a conservation plan) and prohibition of dealings in real estate, are taken for the historical areas, and the feature of "freeze preservation" is strong. Furthermore, urban development installs new town, and develops intensively, called " freeze old town and develop a new town".
Two years after (1997): Fuzhou City also formulated
"Historic Cultural Cities Conservation Ordinance". The candidate for preservation is expanded, includes the large scales of city environment, such as "vision passageway";
intangible cultural heritages, such as "folk-customs, traditional music, art, craft, and meal culture". The conservation plan of historical area changes from the view of
"freeze preservation", to "coexistence of conservation and development". Moreover, it is emphasized management means as "management of a special mechanism, and a complement of citizens' participation in municipal affairs", and is appealing for the citizens' monitoring to illegal acts.
However, although permission of a Cultural Property Office is needed for a cultural property in the case of extension and alteration and demolition, the standard of permission and repair is not clarified. Furthermore, since there is a situation that does not specify many valuable buildings to be cultural properties according to causes, such as financial ability, there is possibly that the cultural property that is not specified can
be pulled down easily.
As mentioned above, although it formulated some related systems for historical townscape conservation in China, the law and regulations for historical townscape conservation are not improved. In many cities, for example, Beijing, Shanghai, Nanjing, and Huangshan, the conservation project precedes from regulations 13). However, the system centering on "freeze preservation" is employed in many cases to historical townscape conservation, and it is thought that a suitable operation standard for historical townscape conservation still hardens, or is not carried out. Therefore, decision of the guideline for historical townscape conservation corresponding to the special feature not only a general principle, for a district not only for the whole city, should be strengthening.
3. Inconsistency of urban renewal and historical townscape conservation
In introduction, we said an improvement of residential environment is improvement, so in this chapter we analyze the city planning system in China, and clarify inconsistency of urban renewal and historical townscape conservation.
Before 1986 in China, an entrepreneur (almost state enterprises) gets the land from the local government by gratis distribution in urban area. After proclaiming "The
Land Act" in 1986, while the country owned the ownership of land, "the right of use" was changed to a system that gratis distribution only for public utilities and onerous for business enterprises. In addition, if an urban area is redeveloped, it applies to "City Renewal Management Regulation" (Fig. 3).
Since the land of urban area is country possession, the local government plays a leading role in renewal in China.
And because the population density in urban area is very high, the view of rational and the saving use for urban land are put into practice. According to the research on land use in urban area and related laws by Zhengjiang Shen's 14), it turns out that local government has legal force to right in disposal of land and building in China. Furthermore, in the case of a renewal project is undertaken in urban area, as the "City Renewal Management Regulation" proclaimed in 1991, if the contractor and the former building owner have not attained compensation deliberations, compulsory develop- ment can be performed by mediation of not a trial but a Construction Bureau (Fig. 3). Moreover, to compensation deliberations of a renewal contractor and a former building owner, and mainly decides a compensation frame with the area of buildings to them, the relation with land is thin.
By the above city planning system (land use, city planning, renewal), it can be said that it has the following characters in urban area in China.
I. The landowner has some rights of the land (a certain period for "using right"), there are very few independent houses in urban area, and it is thought that extension and alteration of the building by the individual are restricted, and renewal in block scale become a usual approach.
2. Although the compensation deliberations at the time of undertaking a renewal project are mainly compensated with building area, the worth of the garden, the area of land, and the worth of the traditional building, etc. is not
277
fully reflected in compensation. Therefore, developers and building owners have the weak volition to beautification and landscaping.
3. Although the government is promoting renewal in block scale strongly, the level of architectural design is low. In various cities, many new housing blocks and new streets without local feature are made. Also in a historical area, there is a tendency for a preservation project as a temporary project. After the project, since residents' preservation consciousness is thin, scenery could not improved continually.
Because of the feature of renewal system in urban area mentioned above, historical townscape conservation has become more difficult in China. Only a "HCCDS"
designation system could not stop the critical phase of the competition from the preservation circumstances for these 20 years. Furthermore, even residents could recognize the
"Active Conservation" approach, since only have the "using right" of the land, residents' participating consciousness is thin than Western and Japan, and applies such as community development approach, is considered to be difficult.
In the following chapter, we study the conservation project in Huangshan Old Street, which specified "a historical area plan and management experiment zone" by Construction Ministry, and the result of joint research by Japanese and Chinese professors, and try to concrete the preservation approach that corresponds to the city planning system In
China.
4. Case study - the conservation project in Huangshan Old Street
4.1 General condition of Huangshan and "Old Street."
Huangshan city is in a position about 350km southwest By City Renewal Management Regulations 199112001 amendment
In the case of deliberation achievement
fonner real estate owners moves into a new building in a fixed period
compulsory move could carried out when exceeding the period
~---~---1 Decision of the market Construction Bureau .---.---~---- .
pnce of real estate
t
admission In the case of deliberationsRedevelopment cannot be attained
entrepreneur
Offer ofa ne\ ddress.
ompensation b building area, etc. should di ussed within one year
former real e.ute ownen
Fig. 3 Renewal system in urban area in China
Mediation by Construction Bureau (less than 30-day detennination).
1
1 f mediation is an objection I. submits to a civil trial.2. the move perfonns compulsorily previously.
near Shanghai, has a local population of 1,370,000 people, and has an area of 9,807 km2. Tourist attractions are mainly constituted by a natural mountains-Huangshan, and some historical cultural resources near her. Huangshan was taken up as a subject matter of Chinese tradition landscape painting· for long history, is deeply concerned with the Chinese culture, and is registered as a "world nature and cultural heritage" in 1990. Moreover, Huangshan city was called "Huizhou" and it prospered to Ming and the Qi period (the 13 to 19th century) as a place in which the famous Huizhou merchants gathered and resided in ancient China.
Many historic spots, such as ancient villages and more than 300 stone guard frames, are remained, and Huizhou ancient villages was specified to be the 2nd "world cultural heritage"
in Huangshan in 2000. When Xiaopin DUN inspected Huangshan and directed tourism development at beginning term of economic-reform in 1979, tourism development is developed promptly from then.
"Old Street" is the historical street in the Huangshan urban area of length 832M. The building from 300 to 50 years before remains mostly, the two-story traditional store faces the both sides of a street, and the ratio ofthe width (5-6m) of the street and the height of a building is suited as human scale. Many Huizhou private houses are built and located in the area of circumference 200ha, and no less than 65 alleys are running from the street. Eaves are put in order, and Matouqiang 15) for fire prevention overlapped several times over irregularly, and the store and the private house were tasted, brewed a deep melody, and show the peculiar scene
12). Since it is still shallow compared with the history of other buildings, the cultural property is not specified, and the resident reach 18,000 is also overcrowded area.
4.2 The conservation of "Old Street"
Since history consciousness of local administration was
strong, cooperation of Qinghua University was obtained in 1985 and established the "Old Street conservation plan"
(excellent planning prize from Construction Ministry of China in 1986) 16). The Old Street and its circumference specified three zones, a "core preservation area", a
"construction regulation area", and an "environmental adjustment area", in the "Old Street conservation plans" (Fig.
4). The range from the Old Street to depth 20M is "core preservation area", the building was specified to be the tradition style of 2 stories, and facade, roof, color tone, indoor finish material, etc. are restricted severely. Around
"core preservation area" about 120ha is "architectural regulation area", and height limits to 15m or less, the color of wall surface limits to thin, the style and the roof limits to local Huizhou style. By close cooperation of specialists and local administration, the Construction Ministry notified specially to city planning section that the planning experiences of Old Street preservation (zoning, architectural regulation approach, etc.) to reference, at the same time Old Street was specified as "a historical area plan and management experiment zone" in 1995, since the result of the conservation project for ten years was large17).
Although the driving force of the conservation project is preservation of a cultural property, in the 90s, the measure of tourism was promoted the historical townscape conservation project greatly. In 1988, "Old Street Management Office"
was installed, penetration of cars and bicycles was forbidden, health administration was strengthened, and attraction of tourists is begun. In the 90s, according to the boom of the Huangshan tourism, tourists continued increasing every year, and 700,000 people have visited to the Old Street in 200118).
The Old Street is becom ing tourists' shopping street of more than 200 shops now. From 1996, Huangshan begins comprehensive management, which called "tourism market synthesis management" 19); include traffic management in
core preservation area the map of Old Street construction regulation area
Fig.4 Old Street in urban area of Huangshan City
urban area, cultivation' of the peace and a contractor's reception soul etc. (Fig. 5). Each section that is perfonning on-site management exceeds a vertical administrative system for the first time, and is taking the positive measure towards tourism development.
4.3 Joint research by Japanese and Chinese specialists 13) Since there is no subsidy system, the conservation project to Old Street is only the range of regulation +a (on-site management). Architectural regulation zone (back alley around an Old Street) is the residential section of the tradition private houses. When regulation of extension and alteration is severe, the. diversion to commerce is difficult, and superannuating has already progressed, and overcrowded residents is also severe, residents are moving out now.
The intentionof old town protection in
279
Eastern area of Old Street perfonned thorough renewal from 1994 in consideration of the style of building and height to the comparatively low property value. Photograph 1 and photograph 2 are contrast of two areas in Fig. 4. This development approach can be called ordinary view in China.
However, eastern area became a new shopping center, the chann of a tradition private house that overlapped with the thin alley at irregularity, and residents' networks were lost.
In order to save historical area, the height of the public consciousness or'resident is required. However, by the land system and renewal system in urban area that were pointed . out in Chapter 3, residents' participating consciousness is thin and the suitable preservation approach is difficult to fmd.
From 1996, the group of Zixuan ZHU from Qinghua University (Beijing, China), and the group of Onishi from Kyoto College of Art (present Kyoto University of Art and
n-site managemen
1979 urban area master plan (Qmghua
____________
~n_i_~~r~itx:_flullO~~~anJrfl1f1\entL------ --t---:---
---~------, ---
Rcgula(I(111 (11 II1,talldtlllll lllllll1ll1g ,(~ Ie III huJidlllg I 1985 uliol. al1d l11atcllal(<)lIlghua I I1I\CI,I(\) •
--- ---t---:-.. --- ---
---~----.. ---
1987
; r :
--- ---
----!-~~~~~~p-~ -p-~!~-~~~:!-~~?-~~~! ~~-----
_1 ____ --- --- ---- -- -- --- ---.. -- --- --- --- --c ---- - - ---1988 (Huangshan government) : garbage collection, outdoor advertising management, no enter for .
• cars and bicyc1es(old town management office) ,
~~~~~ ~~~~~~~ ~ ~ ~~~~~~ ~ ~ ~~~~~~ ~~ ~~~~~ ~ ~ ~~~~~~ ~ ~ ~~~~~~~ ~~ ~~~~~~ ~ ~ ~~~~~~~ ~~ ~~~~~~~ ~~~~I ~ ~~~;~~~;~~;i};~~M~lfl~~~~~~~.~ ~ ~~~~~~ ~ ~ ~~~~~~~: ~ ~~~~~~ ~: ~ ~~~~: ~ ~: I~~~:.:: :~~~:: : ~:
1992 I ! Instruction of environmental hygiene !
;~;~---~~~~:;;ii-~~~,u~i~~i:;:~o[;~-r~~~?t~ fy-zoiies -(CiiY---I --- t--- ----mi\l)~g~-"!~!!trJ'gl~D~-!!~!!l~Ml
______ ---- ------j---
--- _ .. --- ---_ ... ---... --t----
---t-_ .. ---... ---_ ... ---
-1-'" ---_ .. ---... ---... ----_ ... ---... -1---.. ---1995
1996
I :
i :I i ! i
I ' , ~
• i i i
--- ---.J. ---, --- ---,--- ---- --- --
--t---
.!lllilt Ic,carch bl thc rCI1C\\ dllli hurldrl1g, ()lIlgl11ld lirmcr,l1\ (hHlhllrol11 1\.\ (1(ll)
I I I I I
1l1UII'111 111,11kc( '~I1(hc'h mal1,lgCIl1CI1(
(//ual1g,hal1 gll\CII1IllCllt lilHll/9l )(])
PR (civilization committee) I Management strengthening on
F.orbidden occupancy of public space (Hygiene Bureau).
Management strengthening to companies (commerce-and- I accident, peace(Public Peace
• Bureau, Cultural Bureau) . industry office)
__________________ ____________________________________________________________ _ ____ : __ .1:-: __
= __ = __ -:-:: __ -:-:: __ -:-:: __ = __
-1-:-__= __ = __
= __= __ = __ = __
= __ -:-:: __= __ = ___ = __ = __ = __
= __ :-:T._= __= __
= __ = __ -:-:: __ C __= __ = __
= __ =-=-= __= __ = __ = __ = __ = __ -:-:: __ = ___ = __ = __ = __
~___ _
•
IInstallation of pol ice boxes, peace• strengthening (Public Peace Bureau) because of tourists' opposition
1997 failure of admission ticket sale
--- --- --- --- --- -.--- --- --- ---+-----1._--_.- -.-"----." ---- --- ---- ""-- -- -- --- -- --.. ---"-- ---j- --- - - -- --.-- - - --- -- - - .---- - - - -- ---- - - - ---
998 Announcement for planning management in
;~~::-:-~n_~ar~-~:a(:u:an:gS~~~~;~~~:;~~t~;~~~~~~~~t::----: __ :--::-::::-::: _::--:-:: __ ::::: :-: -::::_-_-:: ::_:: ::::-:-:::_::::::_:----_:
Announcement building management in core I 2000 preservation area (City Planning Bureau) •
--- -- --- --- --- --- --- ---1- ---, --- ---."- --- --- -- -- --- --- ---" --- --- ---"--
2002 environmental hygiene management regulation (Tunxi government)
Fig.5 Circumstances of the plan measure and on-site management in old town protection project
Design) started the joint research.
At first, to the typal residential section in central Old Street, based on detailed investigation of site unit, joint research by Japanese and Chinese professors divides up preservation construction and rebuilt construction. Moreover, the questionnaire was performed and the different scale and different form of the existing building were corresponded based on the intention to continue living and using of residents' life space, the new "Huizhou apartment" was planned and the preservation reproduction plan was stood.
Furthermore, paying attention to the small open space, the half-public space called "the ceiling20)" and the thin alley, it was substantial in the further communicational space, for corresponding the life style of the next generation.
Joint research by Japanese and Chinese professors has an important meaning. First, the clearance in arrangement of an orderly building and a large-scale unit is improved in China, the existing space in historical area is saved, and the foundation of traditional scenery is built. Moreover, annex landscape-elements, such as small open space, wells and drawing water space are probed, and "Active Conservation"
which creates a model area and guides the continuous change, finally raises the preservation possibility and the quality of the whole area. Furthermore, the development approach of residents' absence is improved, by preservation reproduction on condition of residents and continuing living, the existing social network can be saved and it is thought that it is helpful also to revival of tradition culture.
In order to strengthen regulation and guidance for the buildings in "architectural regulation area", Huangshan government issued "announcement for planning management in central urban area" in 1998 21). In the "core preservation area", to the . new reconstruction within historical area, and demolition of a building, the City Planning Bureau is concerned at the monitoring under construction, and all the process of inspection after completion, and is aiming at thorough regulation guidance from the first design to announcement. Moreover, architects and consultants are specified and it is asking for better new reconstruction.
As mentioned above, about the reproduction approach which creates a model area and guides the continuous change, and the cooperation organization of vertical administrative system towards tourism, and architectural management such as monitoring of all the process of extension and alteration and contractor specification, it can be called advanced experience of historical townscape conservation in China.
5. Conclusion
This research is a study for historical townscape conservation in China that just started. The following , summaries could be made.
1. Although "freeze preservation of point-cultural properties, such as "tangible cultural properties" and a
"commemoration", is a popular approach, historical townscape conservation is conservation for an area, and since the improvement of residential environment is also important, it is asking for" Active Conservation".
2. China formulated the "Historic Cultural Cities Designation System", and cultural property preservation developed from "preservation of a point" to . "conservation for an area" in 1982. However, the application of "freeze preservation" from cultural property preservation system to historical townscape conservation happened in many cases, and it is thought that suitable historical townscape conservation plan or concrete operation standard is still hardens, or not carried out.
3. The research on city planning system (land, city planning, renewal system) in China showed, there is legal force of right of Chinese local government in disposal for and building. And in compensation deliberations of redevelopment contractors and former building owners, the compensation frame is mainly decided with the area of construction. Therefore in China, developers and building owners apply the weak volition to beautification and landscaping, so the approaches such as community development are used difficultly, and it is thought that selection of the preservation approach is narrow.
4. The concrete approach and the feature were viewed in case study of Huangshan Old Street, which specified to be the only ""historical area plan and management experiment zone" in China. In historical townscape conservation, it turns out that regulation guidance, cooperation organization of the vertical administrative system towards tourism, monitoring of the process of the extension and alteration in architectural management, architects and consultants' specification, and the specialist s ' role are large.
5. In joint research by Japanese and Chinese professors, as a concrete approach which can be adapted for city planning system in China, the preservation reproduction which thought the intention for the existing space of a site unit, not a independent house but a low layer
apartment, and continue living for residents are important, and a model area are created at Old Street in Huangshan, and it can be called the experience that turned to "Active Conservation".
Notes
1) E Inagaki, "preservation of historical environment the meaning and the hand", JURISUTO, a special number, development and preservation (1976).
2) S Yoshida's research, (j)"preservation of the direction-historical environment of a new cultural aid of Japan", "international cooperation research", total No.22 (1995) , pI6-21, Japan International Cooperation Agency. (2) "preservation of historical environment in Sanaa, Yemen ",1. Archit. Plann. Environ. Eng., AU, Architectural Institute of Japan, No.500, pI85-190(October, 1997). @ "preservation of historical environment in Fezu, Morocco", 1. Archit. Plann. Environ. Eng., AU, Architectural Institute of Japan, No.520 , p247-252 (June, 1999).
3) Nishiyama et al. (1990, 1995), Saito et al. (1996), Omori et al.
(1997,2000), papers of the Annual Conference on City Planning, The City Planning Institute of Japan.
4) Fujisaki (1994), Kobayashi et al. (1999, 20(0), papers of the Annual Conference on City Planning, The City Planning Institute of Japan.
5) Research of Okazaki and others, (1994, 1995), papers of the Annual Conference on City Planning, The City Planning Institute of Japan.And, 1. Archit. Plann. Environ. Eng., AU, Architectural Institute of Japan, No.531, p 179-185 (May, 2000).
6) Koroda and Shimomura, "The current situation oftourism and its outlook in the historic village of Shirakawa-go, the world heritage", papers of the 36th Annual Conference on City Planning, The City Planning Institute of Japan, p253-258, (2001).
7) ICOMOS (International Council on Monuments and Sites) is international NGO for preservation for the cultural property, founded in 1965, and is the main advisers to world heritage committee about specification of the new site of world heritage.
International Cultural Tourism Charter (1999) has appeared in http://www.icomos.orgitourismlcharter.html.
8) The Venice Charter: http://www.icomos.orgiicahml.
9) Akemi, Onishi and Nishio, "A study of the changes of living spaces and townscape at the area of traditional courtyard houses in China ", papers of the 30th Annual Conference on City Planning, The City Planning Institute of Japan, p457-462.
(1995)
281
10) Yehua et aI., " A study on Historic Cultural Cities Conservation System in PR.China", 1. Archit. Plann. Environ. Eng., AU, Architectural Institute of Japan, No. 494, p 195-203. ( 1997) 11) For example, the castle from Yuan time in Yibin in 1993, the
100m' wall of castle from Ming time in Chengdu in 1995, the castle from Song period in Xiangfan in 1999 all broke completely (cultural property with not specifies, all 400 years before).
12) Wenlang Wang, "Tourism business detailed explanation in China ", Japanese Qiaobao Co. p366, (2001)
13) Onishi and Zixuan ZHU, "Historal cities in China - Reproduction of scenery preservation", K3:.iima Publishing Co.
Ltd. (2002)
14) Zhenjiang Shen and Norioki Ishimaru, "A study on urban plan project and related law system in China -in the case of Chengdu city ", papers of the 34th Annual Conference on City Planning, The City Planning Institute of Japan, p871-876.
( 1999)
15) A kind of firewall, the decorative wall that the wall by the side rises more highly than the roof, and gradually in the shape of stairs.
16) Zixuan ZHU, "Huangshan Old Street conservation plan", China scholarly journal "city planning". (Jan 1994)
17) City Planning Division of Construction Ministry, China,
"Huangshan Old Street historical area management trial valve method." ( 1995)
18) The 2001 data, Huangshan Old Street management offtce.(2001)
19) Huangshan government (1996-2000), "Notification of synthesis management for Huangshan tourism", 1996-2000.
20) An open courtyard style.
21) Huangshan government, "Announcement about planning management of central urban area", 1998 / No.3 announcement.
And Huangshan City Planning Bureau, "Announcement about the extension-and-alteration planned management in Old Street core preservation area", 2000, 03, 22.
References
[1] Onishi and Zixuan ZHU, "Historal cities in China - Reproduction of scenery preservation", K3:.iima Publishing Co.
Ltd. (2002)
[2] Yehua et aI., " A study on Historic Cultural Cities Conservation System in P.R.China", 1. Archit. Plann. Environ. Eng., AU, Architectural Institute of Japan, No. 494, p 195-203. (1997)