アーゼラ点滴静注液 100㎎
アーゼラ点滴静注液 1000㎎
に関する資料
本資料に記載された情報に係る権利及び内容の責任はグラクソ・スミ
スクライン株式会社に帰属するものであり、当該情報を適正使用以外
の営利目的に利用することはできません。
グラクソ・スミスクライン株式会社
第 1 部の略号等一覧 略語(略称) 内容 AUC 血漿中濃度-時間曲線下面積 AUC0-∞ 投与後無限時間までの血漿中濃度-時間曲線下面積 ADCC 抗体依存性細胞介在性細胞傷害(作用) BAV ウシアデノウイルス BFR フルダラビン抵抗性で巨大リンパ節腫大(>5 cm)により alemtuzumab 治療 が適切でない CCDS 企業中核データシート CDC 補体依存性細胞傷害(作用) CI 信頼区間 CL クリアランス CLL 慢性リンパ性白血病 Cmax 最高血中濃度 Cmin 最低血中濃度 CYP チトクローム P450 DLT 用量制限毒性 DLBCL びまん性大細胞型 B 細胞性リンパ腫 DR フルダラビンおよび alemtuzumab に抵抗性 FL 濾胞性リンパ腫 HBV B 型肝炎ウイルス HSV 単純ヘルペスウイルス Ig 免疫グロブリン LD50 50%致死量 MLV マウス白血病ウイルス MMV マウス微小ウイルス MTD 最大耐量 NCI 米国国立がん研究所 PFS 無増悪生存期間 PK 薬物動態 PR 部分寛解 SCID 重症複合型免疫不全 SD 安定 SPD (標的病変の)二方向積和 t1/2 消失半減期 Apr 24 2012 13:15:15
1.4. 特許状況 、 ( )、 ( )。 1.4. 特許状況 1.4 - p. 1
1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 オファツムマブ(遺伝子組換え)(以下、オファツムマブ)は、Genmab 社により開発さ れたCD20 分子エピトープを特異的に認識する新規のヒト型 IgG1κ モノクローナル抗体であ る。オファツムマブはB リンパ球表面に発現したヒト CD20 分子上の大小の細胞外ループに 局在する、リツキシマブ(遺伝子組換え)(以下、リツキシマブ)とは異なるエピトープを 特異的に認識し、CD20 エピトープに高い親和性で結合することおよび結合後の解離速度が 遅いことを特徴とする。In vitro において、特に CD20 低発現細胞に対してリツキシマブより 高い補体依存性細胞傷害作用(CDC)を示し、より高い細胞溶解性を誘発することが示され た。 オファツムマブは、in vitro において CDC および抗体依存性細胞介在性細胞傷害作用 (ADCC)を誘発することにより、抗腫瘍効果を発揮することが確認された。特に、オファ ツムマブは補体C1q との結合が増強されているため、CD20 低発現細胞に対しても、リツキ シマブより強力なCDC を誘発することが確認された(2.6.2)。 慢性リンパ性白血病(CLL)は治癒し難い疾患であり、疾患の進行に伴い治療の選択肢は 少なくなるため、CLL 患者の医療ニーズは満たされていない。これらのことから、比較的 CD20 分子の発現量の少ない CLL に対するオファツムマブの臨床効果が期待され、欧米にお いてCLL に対するオファツムマブ単剤療法の臨床開発計画を立案するに至った。欧米では フルダラビンおよびalemtuzumab に抵抗性の CLL 患者またはフルダラビン抵抗性で巨大リ ンパ節腫大によりalemtuzumab 治療が適切でない CLL 患者を対象として臨床試験が実施さ れ、オファツムマブの有効性および安全性が確認されたことから、米国では2009 年 10 月に、 また欧州では2010 年 4 月にフルダラビンおよび alemtuzumab に抵抗性の CLL を適応症とし て承認を取得した。 本邦においてCLL 治療に対する治療選択肢は欧米に比べさらに少なく、医療ニーズは十 分に満たされておらず、オファツムマブは医療上の必要性が高い薬剤であると考えられたこ とから、2008 年より CLL 患者を対象として臨床試験を開始した。 1.5.1. 慢性リンパ性白血病(CLL) CLL は、成熟した末梢 B 細胞性新生物の亜型であり、B 細胞由来のリンパ球が末梢血、 骨髄、リンパ節、脾臓および肝臓に蓄積し、腫瘍細胞表面にCD5 抗原、CD20 抗原、CD23 抗原が発現することを特徴とする。欧米では全白血病の約3 割を占める頻度の高い白血病で ある[Müller-Hermalink, 2008]が、本邦では全白血病の 5%であり、罹患率は 10 万人に約 0.5 人とされている。CLL の初期は自覚症状に乏しく、多くの患者は無症候性のリンパ球増加症 を示し、健康診断などの血液検査で偶然に診断されることが多い[薄井, 2011]。 診断は、CLL の改訂ガイドラインによる診断基準[米国国立がん研究所(NCI)ワーキン ググループ][Hallek, 2008]を用いて行われ[薄井, 2011]、病期分類には Rai 分類[Rai , 1975]お よびBinet 分類[Binet, 1981]が使用されている[日本血液学会, 2010]。診断時の年齢(中央 値)は 67 歳、男性の発症率は女性の 2 倍であり、診断時には約 8 割の患者でリンパ節腫大、 約5 割の患者で脾腫を認める[薄井, 2011]。脾腫により、早期満腹感や腹部膨満といった症 状が生じることがある[Kipps, 2010]。疾患の進行とともに、易疲労感、リンパ節腫脹、盗汗、 1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 1.5 - p. 1 Apr 18 2012 11:56:36
発熱、体重減少、易感染性、貧血、血小板減少などの症状・所見を認め、生活の質に著しく 影響することがある。また、活動性の患者ではリンパ球の倍加時間が6 ヵ月以内であり、進 行が速いことを特徴とする[薄井, 2011]。 表 1.5.1-1 NCI ワーキンググループによる CLL の診断基準(2008 年) 1. 末梢血でリンパ球が 5000 /µL 以上 3 ヵ月持続する 2. 細胞形態 小型、成熟リンパ球(狭い細胞質、核小体不明瞭の濃染核、部分的に凝集したクロマチンを有する) 大型もしくは異型リンパ球や前リンパ球の占める比率は55%、標本作製時に壊れたリンパ球(smudge cell)を認める 3. 免疫形質 CD5 と B 細胞表面抗原(CD19、CD20、CD23)が発現 免疫グロブリン(Ig)軽鎖のクロナリティ(κ 鎖か λ 鎖のいずれか)が認められる 細胞surface(表面)Ig や CD20 発現は正常 B 細胞より弱い 4. 骨髄検査(診断に必須ではないが、治療前に実施が望ましい) リンパ球様細胞が骨髄中の有核細胞の30%超
付記 小リンパ球性リンパ腫small lymphocytic lymphoma の診断(鑑別診断に用いられる) 1. リンパ節腫脹が認められる 2. 骨髄浸潤による血液減少は認められない 3. 末梢血の B リンパ球数は 5000 /µL 未満 4. 可能な限りリンパ節生検標本で診断する [Hallek, 2008] 表 1.5.1-2 CLL の病期分類 Rai の病期分類 Binet の病期分類 病期 リ ス ク 分類基準 生存期間 中央値 (年) 病期 リ ス ク 分類基準 生存期間 中央値 (年) 0 低 リンパ球増加 (≥15,000 /µL)かつ骨髄リ ンパ球40%以上 >10 Ⅰ 病期0+リンパ節腫脹 A 低 リンパ球増加(末梢血リン パ球≥4,000 /µL かつ骨髄リ ンパ球≥40%)+リンパ領 域腫大が2 ヵ所以下 >10 Ⅱ 中 病期0+肝腫+脾腫(どち らか、または両方)±リン パ節腫脹 7 B 中 病期A+リンパ領域腫大が 3 ヵ所以上 5 Ⅲ 病期0+貧血(Hb<11 g/dL またはHt<33%)± リンパ節 腫脹 ± 肝腫 ± 脾腫 C Ⅳ 高 病期0+血小板減少(Plt<10 万 /µL)± リンパ節腫脹 ± 肝腫 ± 脾腫 ± 貧血 1.5 D 高 リンパ球増加+貧血 (Hb<10 g/dL)または血小 板減少(Plt<10 万 /µL) 1.5 Hb:血色素量、Ht:ヘマトクリット値、Plt:血小板数 [日本血液学会, 2010] 合併症としては、自己免疫性溶血性貧血、自己免疫性血小板減少症などの自己免疫疾患、 低γ グロブリン血症を伴い重篤となる感染症、固形がんや他のリンパ系腫瘍の発症などが報 告されている[薄井, 2011; Cheson, 1996]。CLL 患者では、免疫力が低下しているために、自 己免疫性疾患やCLL 患者でのおもな死因である感染症を合併するリスクが増加することが あり、CLL の治療は原疾患への治療と合併症に対する治療が必要である。診断時の生存期間 (中央値)は5~20 年間だが、抗悪性腫瘍薬が効き難い難治性 CLL では 6~14 ヵ月と生存 期間が短い[Tam, 2007]。 なお、CLL に対する治療の現状と問題点については 2.5.1.3.に詳述した。 1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 1.5 - p. 2 Apr 18 2012 11:56:36
1.5.2. 開発の経緯 非臨床試験は海外において20 年から開始され、品質、薬理、薬物動態および毒性に関 する検討が行われた。また、臨床的検討は海外において20 年より、本邦においては2008 年より開始された。 1.5.2.1. 品質に関する試験 オファツムマブの製造工程は、工程開発に伴い、何度か変更され、実生産工程へとスケー ルアップされている。 初期の非臨床試験に使用した原薬ロット(ロット番号L08131/15、L08131/27、L09136/10 およびL09167/15)は、ASM26 細胞株を用いて、 スケール、 L スケール および L パイロットスケールの開発工程で製造された。その後、ASM26 細胞株を用い た L スケール(製造工程 A)による製造が開始された。次に、 L にスケールアップ された(製造工程B)。なお、製造工程 A および製造工程 B で製造された原薬ロットは、 非臨床試験や初期の臨床試験に使用された。開発をさらに進めるため、別の遺伝子発現構成 体導入細胞株からクローニングされたSJT26 細胞株が調製され、 L スケール(製造工 程C)での原薬ロットの製造に使用された。製造工程 C で製造された原薬ロットは、臨床試 験および非臨床試験に使用された。その後、臨床試験に使用する原薬量の増大に対応するた め、また商業生産に準備するために、製造所がLonza Biologics 社の 州 工場に変更となり、製造工程は L までスケールアップされた。その際に、原 薬および製剤の処方も変更され(製造工程D:本剤で申請する原薬製造工程)、原薬中およ び製剤中の緩衝液がクエン酸緩衝液から酢酸緩衝液に変更された。 なお、国内第Ⅰ相臨床試験[OMB111148 試験(148 試験)]および海外第Ⅱ相試験 [OMB111773 試験(773 試験)、旧試験番号:Hx-CD20-406 試験]では、旧処方製剤(原 薬:製造工程C、クエン酸製剤)が使用された。一方、日本および韓国で実施した第Ⅰ/Ⅱ 相試験[OMB112758 試験(758 試験)]では、本剤(原薬:製造工程 D、酢酸製剤)が使 用された。 本剤の安定性試験については100 mg 製剤および 1000 mg 製剤ともに長期保存試験、加速 試験および苛酷試験を実施した。安定性試験の結果から100 mg 製剤および 1000 mg 製剤の 有効期間は保存条件5±3°C、遮光で 24 箇月と設定した。なお、長期保存試験は継続中であ る。 1.5.2.2. 非臨床試験 20 年より薬理試験、薬物動態試験および毒性試験を実施した。なお、本薬は抗体医薬 であり、その代謝経路は一般によく分かっていることから、代謝に関する試験は実施しなか った。また、本薬(分子量149 kDa)は、糸球体ろ過される分子量(約 60 kDa 以下)よりも 大きいことから、腎排泄される可能性は低いと考え、排泄に関する試験は実施しなかった。 さらに、本薬はCD20 以外の蛋白質や高分子には結合しないこと、CD20 が CYP やトランス ポーターの発現を調節するとの報告がないこと、および本薬はCYP などによる代謝を受け 1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 1.5 - p. 3 Apr 18 2012 11:56:36
ないことから、CYP の基質、誘導薬または阻害薬との併用により、薬物動態学的薬物相互 作用を引き起こす可能性はないと考え、薬物動態学的薬物相互作用に関する試験は実施しな かった。また、本薬は抗体医薬品であることから、遺伝毒性試験およびがん原性に関する試 験は実施しなかった。 効力を裏付ける試験成績において、本薬は in vitro で CD20+B 細胞に特異的な CDC および ADCC の誘発作用を示したこと、および in vivo の異種移植重症複合型免疫不全マウスモデ ルで、おそらくそれらの作用を介して抗B 細胞性腫瘍活性を示し、リツキシマブよりも高 い生存率延長作用を示したことから、ヒトのB 細胞性慢性リンパ性白血病に対する有効な 治療薬である可能性が示された。 サルの胚・胎児発生に関する試験で投薬群の臍帯血より本薬が検出され、胎盤通過性が確 認された。ヒトにおける妊娠への影響は不明であることから、妊婦への投与禁止に関する注 意喚起および適切な避妊が必要であると考えられる。 1.5.2.3. 臨床試験 1.5.2.3.1. 海外における臨床開発 オファツムマブ単剤療法の臨床試験として、20 年より濾胞性リンパ腫(FL)患者を対 象とした第Ⅰ/Ⅱ相試験[Hx-CD20-001 試験(001 試験)]および CLL 患者を対象とした第 Ⅰ/Ⅱ相試験[Hx-CD20-402 試験(402 試験)]が開始された。 2006 年には GlaxoSmithKline 社は Genmab 社と共同開発に関する契約を締結し、同年より 開始したフルダラビンおよびalemtuzumab に抵抗性(DR)、またはフルダラビン抵抗性で 巨大リンパ節腫大(>5 cm)により alemtuzumab 治療が適切でない(BFR)CLL 患者を対象 としたオファツムマブ単剤療法による第Ⅱ相試験(773 試験)の中間解析の結果からオファ ツムマブ単剤療法時の良好な有効性および安全性が確認された。また、CLL 患者を対象とし たHx-CD20-402 試験(402 試験)および Hx-CD20-407 試験(407 試験)、濾胞性リンパ腫 (FL)患者を対象とした臨床試験[Hx-CD20-001 試験(001 試験)、Hx-CD20-405 試験 (405 試験)、Hx-CD20-409 試験(409 試験)]、びまん性大細胞型 B 細胞性リンパ腫 (DLBCL)患者を対象とした臨床試験[OMB111776/GEN415 試験(776 試験)]の結果か らも、オファツムマブの良好な安全性が確認された。これらのことから、米国では2009 年 1 月、欧州では 2009 年 2 月に DR または BFR の CLL を申請効能・効果として承認申請を行 い、米国では2009 年 10 月に、また欧州でも 2010 年 4 月に DR の CLL を効能・効果として 承認された。 1.5.2.3.2. 本邦における臨床開発 本邦においては2008 年 9 月より再発・難治性の CLL または FL 患者を対象とした第Ⅰ相 試験(148 試験)を開始し、オファツムマブ 1000 mg までの良好な忍容性が確認された。本 試験は2009 年 11 月に完了した。 海外での402 試験および 773 試験において、再発・難治性の CLL 患者を対象にオファツ ムマブ2000 mg までの良好な忍容性および有効性が確認されたこと、および 402 試験の結果 から、臨床効果と薬物動態(PK)パラメータに有意な関連性が認められたことから、日本 1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 1.5 - p. 4 Apr 18 2012 11:56:36
人CLL 患者における 2000 mg 投与時の忍容性を確立し、有効性を確認することを目的とし て第Ⅰ/Ⅱ相試験(758 試験)を実施した。 758 試験では、初回用量としてオファツムマブ 300 mg を点滴静注した後、1 週間間隔で 2000 mg を 7 回(計 8 回)点滴静注し、さらにオファツムマブの効果を確実なものとし、長 期間持続させるために、2000 mg を 4 週間間隔で 4 回点滴静注した。 1.5.2.3.3. 本邦における承認申請の経緯 本邦においてCLL を申請効能・効果とした臨床開発を進めるために、20 年 月 日に 本邦での ( ) などについて医薬品 相談 を実施した(1.13.2.1)。 その後、 ・ を行うために、20 年 月 日 に ( )の 医薬品 相談を実施し(1.13.2.2)、 年 9 月より758 試験を開始した。本試験が 2011 年 4 月に完了した後、 ・ などについて 年 月 日に医薬品 ( )を実施し(1.13.2.3)、以下の助言が得られた。 • 提示された と考える。 • であることを考慮すると、本剤 と考える。ただし、 、 、 を説明する であるため、 を 、 があると考える。 これらの結果を踏まえ、以下の効能・効果および用法・用量にて承認申請を行うこととし た。 効能・効果 既治療の慢性リンパ性白血病 用法・用量 通常、成人には、オファツムマブ(遺伝子組換え)として 1 回目の投与時には 300 mg を、 2~8 回目の投与時には 2000 mg を 1 週間間隔で点滴静注する。8 回目の投与 4~5 週後、 2000 mg を 4 週間間隔で点滴静注する(9~12 回目)。 1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 1.5 - p. 5 Apr 18 2012 11:56:36
なお、本承認申請で評価資料とした臨床試験の一覧を表 1.5.2-1 に示す。 表 1.5.2-1 評価資料とした臨床試験の一覧 試験番号 主要目的 対象 1 デザイン 用法・用量 症例数 国内 OMB111148 忍容性 CLL 2 再発・難治性 非盲検 用量漸増 300 mg を 1 回、500 mg を 1 週間間隔 で7 回 300 mg を 1 回、1000 mg を 1 週間間隔 で7 回 500 mg: 3 例 1000 mg: 3 例 OMB112758 (日本およ び韓国) 忍容性 有効性 CLL 既治療 単群 非盲検 300 mg を 1 回、2000 mg を 1 週間間隔 で7 回、さらに 4 週間間隔で 4 回投与 2000 mg: 10 例 海外 OMB111773/ Hx-CD20-406 有効性 CLL 難治性 単群 非盲検 300 mg を 1 回、2000 mg を 1 週間間隔 で7 回、さらに 4 週間間隔で 4 回投与 2000 mg: 223 例 1. CLL:慢性リンパ性白血病 2. 計画では CLL または FL を対象としたが、実際に組み入れられたのは CLL のみであった。 以上の開発の経緯を図 1.5.2-1 に示す。 なお、CLL は本邦において極めて症例数が少ない疾患であることから、希少疾病用医薬品 の指定申請を行い、2011 年 9 月に指定を受けた。 1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 1.5 - p. 6 Apr 18 2012 11:56:36
試験項目 国内 海外 品質に関する試験 ○ 効力を裏付ける試験 ○ 薬理 副次的薬理試験 ○ ADME 薬物動態試験(動物) ○ 反復投与毒性試験 ○ 生殖発生毒性試験 ○ 毒性 その他の毒性試験 ○ OMB111148 試験 ○ OMB112758 試験 ○ ○ OMB111773 試験 ○ Hx-CD20-402 試験(ref) ○ Hx-CD20-001 試験(ref) ○ Hx-CD20-407 試験(ref) ○ Hx-CD20-405 試験(ref) ○ Hx-CD20-409 試験(ref) ○ 臨床試験 OMB111776/GEN415 試験(ref) ○ 図 1.5.2-1 開発の経緯図 1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 1.5 - p. 7 Apr 18 2012 11:56:36
1.5.3. 海外および本邦において現在実施中のおもな臨床試験 1.5.3.1. 悪性腫瘍領域 海外においてCLL、非ホジキンリンパ腫などを対象としたオファツムマブ単剤療法または 他の抗悪性腫瘍薬との併用療法の臨床試験が進行中である。また、本邦においてもFL また はDLBCL を対象としたオファツムマブ単剤療法または他の抗悪性腫瘍薬との併用療法の臨 床試験が進行中である。 1.5.3.2. 悪性腫瘍領域以外 悪性腫瘍領域以外の疾患に対する開発として、海外では関節リウマチおよび多発性硬化症 の臨床試験が進行中である。 参考文献
Binet JL, Auquier A, Dighiero G, et al. A New Prognostic Classification of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Derived from a Multivariate Survival Analysis. Cancer. 1981;48:198-206.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Grever M, et al. National Cancer Institute-Sponsored Working Group Guidelines for Chronic Lymphocytic Lymphoma: Revised Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment. Blood. 1996;87:4990-7.
Hallek M, Bruce D, Cheson BD, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic
lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute- Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood. 2008;111:5446-56.
Kipps TJ. Williams Hematology: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related diseases. Eighth ed. :McGraw-Hill; 2010.
Müller-Hermalink HK, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/ small lymphocytic lymphom. Precursor lymphoid neoplasm. Swerdlow SH, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Heamatopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. LARCPress, Lyon. 2008:180-2.
Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, et al. Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1975;46:219-34.
Tam CS, O'Brien S, Lerner S, et al. The natural history of fludarabine-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients who fail alemtuzumab or have bulky lymphadenopathy. Leuk Lymphoma.
2007;48:1931-9. 日本血液学会, 日本リンパ網内系学会. 造血器腫瘍取扱い規約. 第 1 版 ed. 東京:金原出版株 式会社; 2010. 薄井 紀子. 急性および慢性リンパ性白血病. 日内会誌. 2011;100:1817-24. 1.5. 起原又は発見の経緯及び開発の経緯 1.5 - p. 8 Apr 18 2012 11:56:37
1.6. 外国における使用状況等に関する資料 本剤は、フルダラビンおよび alemtuzumab に抵抗性の慢性リンパ性白血病(chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: CLL)の治療薬として 2009 年 10 月 26 日に米国で迅速承認を取得し、 欧州(EU 加盟 27 ヵ国)でも 2010 年 4 月 19 日に条件付で承認を取得した。現在、米国、欧 州をはじめカナダ、オーストラリアなど 39 ヵ国で承認されている(2012 年 10 月現在)。 米国および英国における承認状況を表 1.6-1 に示す。 また本項では、以下の資料を添付した。 1.6.1 米国における添付文書の原文および和訳 1.6.2 英国における添付文書の原文および和訳
1.6.3 企業中核データシート(COMPANY CORE DATASHEET)の原文
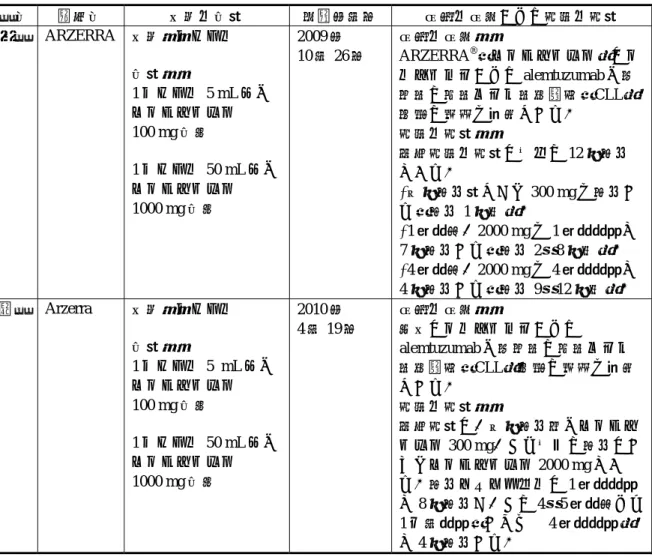
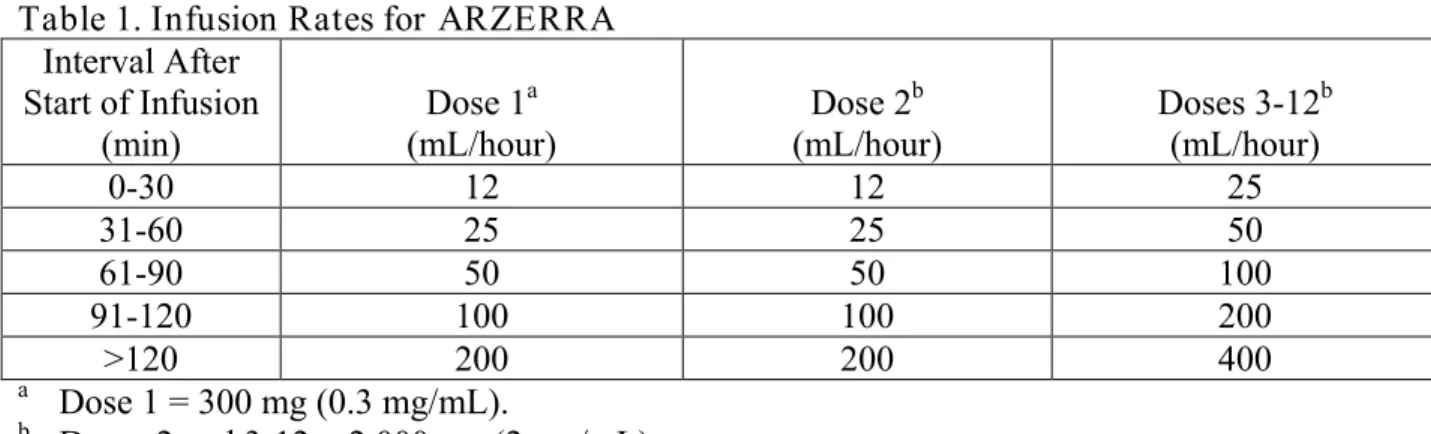
表 1.6-1 米国および英国における承認状況(2012 年 10 月現在) 国名 販売名 剤型・含量 承認年月日 効能・効果および用法・用量 米国 ARZERRA 剤型:バイアル 含量: 1 バイアル 5 mL 中に オファツムマブ 100 mg 含有 1 バイアル 50 mL 中に オファツムマブ 1000 mg 含有 2009 年 10 月 26 日 効能・効果: ARZERRA®(オファツムマブ)はフ ルダラビンおよび alemtuzumab に抵 抗性の慢性リンパ性白血病(CLL) 患者の治療を適応とする。 用法・用量: 推奨用法・用量は以下の 12 回投与 である。 •初回投与量として 300 mg を投与す る(投与 1 回目)。 •1 週間後、2000 mg を 1 週間間隔で 7 回投与する(投与 2~8 回目)。 •4 週間後、2000 mg を 4 週間間隔で 4 回投与する(投与 9~12 回目)。 英国 Arzerra 剤型:バイアル 含量: 1 バイアル 5 mL 中に オファツムマブ 100 mg 含有 1 バイアル 50 mL 中に オファツムマブ 1000 mg 含有 2010 年 4 月 19 日 効能・効果: 本剤はフルダラビンおよび alemtuzumab に抵抗性の慢性リンパ 性白血病(CLL)患者の治療を適応 とする。 用法・用量: 推奨用量は、初回投与時にオファツ ムマブ 300 mg、それ以降の投与はす べてオファツムマブ 2000 mg であ る。投与スケジュールは 1 週間間隔 で 8 回投与し、その 4~5 週間後より 1 ヵ月間隔(すなわち 4 週間間隔) で 4 回投与する。 1.6. 外国における使用状況等に関する資料 1.6 - p. 1 Jan 16 2013 10:31:58
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ARZERRA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ARZERRA.
ARZERRA (ofatumumab) Injection, for intravenous infusion Initial U.S. Approval: 2009
--- RECENT MAJOR CHANGES ---
Dosage and Administration, Preparation and
Administration (2.5) 04/2011 Warnings and Precautions, Hepatitis B Infection and
Reactivation (5.4) 09/2011
---INDICATIONS AND USAGE ---
ARZERRA (ofatumumab) is a CD20-directed cytolytic monoclonal antibody indicated for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab. The effectiveness of ARZERRA is based on the demonstration of durable objective responses. No data demonstrate an improvement in disease-related symptoms or increased survival with ARZERRA. (1, 14)
--- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ---
• Dilute and administer as an intravenous infusion. Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. (2.1)
• Recommended dosage and schedule is 12 doses administered as follows: • 300 mg initial dose, followed 1 week later by
• 2,000 mg weekly for 7 doses, followed 4 weeks later by • 2,000 mg every 4 weeks for 4 doses. (2.1)
• Premedicate with oral acetaminophen, oral or intravenous antihistamine, and intravenous corticosteroid. (2.4)
--- DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS ---
• 100 mg/5 mL single-use vial. (3) • 1,000 mg/50 mL single-use vial. (3)
--- CONTRAINDICATIONS ---
None. (4)
--- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ---
• Infusion Reactions: Premedicate with an intravenous corticosteroid (as appropriate), an oral analgesic, and an oral or intravenous antihistamine. Monitor patients closely during infusions. Interrupt infusion if infusion reactions occur. (2.3, 2.4, 5.1)
• Cytopenias: Monitor blood counts at regular intervals for neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. (5.2)
• Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML): Monitor neurologic function and discontinue ARZERRA if PML is suspected. (5.3) • Hepatitis B Infection and Reactivation: Screen high-risk patients.
Discontinue ARZERRA in patients who develop viral hepatitis or reactivation of viral hepatitis. (5.4)
--- ADVERSE REACTIONS ---
Most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were neutropenia, pneumonia, pyrexia, cough, diarrhea, anemia, fatigue, dyspnea, rash, nausea, bronchitis, and upper respiratory tract infections. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GlaxoSmithKline at 1-888-825-5249 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
--- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS ---
• Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
• Nursing mothers: Published data suggest that consumption of breast milk does not result in substantial absorption of maternal antibodies into circulation. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Revised: 09/2011
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS* 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage Regimen 2.2 Administration
2.3 Dose Modification 2.4 Premedication
2.5 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion Reactions 5.2 Cytopenias
5.3 Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy 5.4 Hepatitis B Infection and Reactivation 5.5 Intestinal Obstruction
5.6 Immunizations
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience 6.2 Immunogenicity
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy 8.3 Nursing Mothers 8.4 Pediatric Use 8.5 Geriatric Use 8.6 Renal Impairment 8.7 Hepatic Impairment 10 OVERDOSAGE 11 DESCRIPTION 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action 12.2 Pharmacodynamics 12.3 Pharmacokinetics 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility 13.3 Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not
listed.
p. 1 Apr 19 2012 11:24:05
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ARZERRA
®(ofatumumab) is indicated for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic
leukemia (CLL) refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab.
The effectiveness of ARZERRA is based on the demonstration of durable objective responses
[see Clinical Studies (14)]. No data demonstrate an improvement in disease-related symptoms or
increased survival with ARZERRA.
2
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage Regimen
•
Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus.
•
Premedicate before each infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
•
Administer with an in-line filter set supplied with product.
The recommended dosage and schedule is 12 doses administered as follows:
•
300 mg initial dose (Dose 1), followed 1 week later by
•
2,000 mg weekly for 7 doses (Doses 2 through 8), followed 4 weeks later by
•
2,000 mg every 4 weeks for 4 doses (Doses 9 through 12)
2.2 Administration
Prepare all doses in 1,000 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP [see Dosage and
Administration (2.5)].
•
Dose 1: Initiate infusion at a rate of 3.6 mg/hour (12 mL/hour).
•
Dose 2: Initiate infusion at a rate of 24 mg/hour (12 mL/hour).
•
Doses 3 through 12: Initiate infusion at a rate of 50 mg/hour (25 mL/hour).
In the absence of infusional toxicity, the rate of infusion may be increased every 30 minutes as
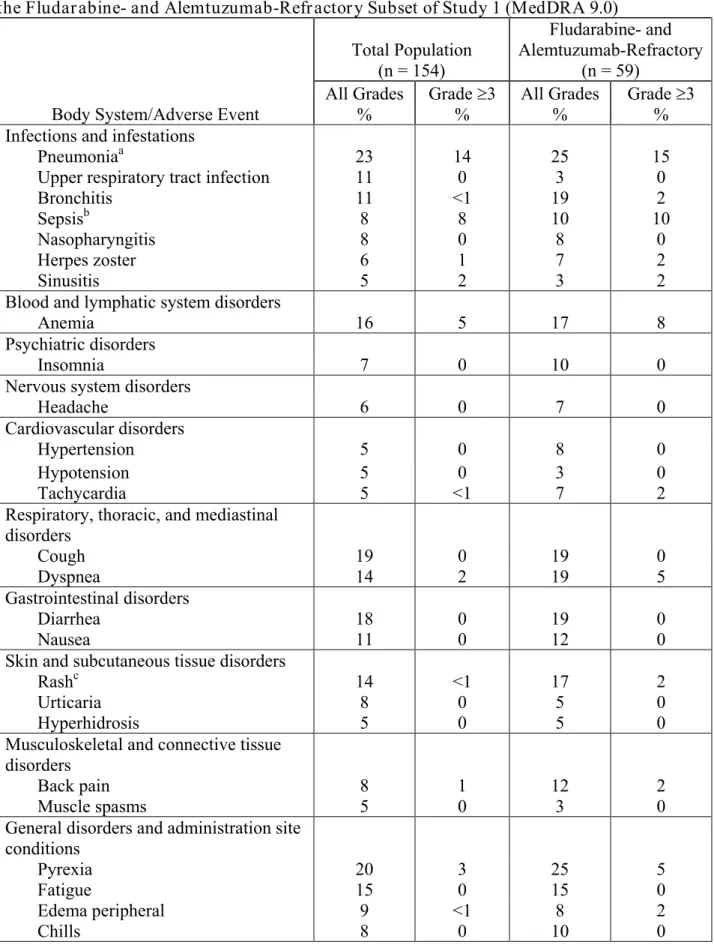
described in Table 1. Do not exceed the infusion rates in Table 1.
Table 1. Infusion Rates for ARZERRA
Interval After
Start of Infusion
(min)
Dose 1
a(mL/hour)
Dose 2
b(mL/hour)
Doses 3-12
b(mL/hour)
0-30
12
12
25
31-60
25
25
50
61-90
50
50
100
91-120
100
100
200
>120
200
200
400
aDose 1 = 300 mg (0.3 mg/mL).
bDoses 2 and 3-12 = 2,000 mg (2 mg/mL).
p. 2 Apr 19 2012 11:24:052.3 Dose Modification
•
Interrupt infusion for infusion reactions of any severity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
•
For Grade 4 infusion reactions, do not resume the infusion.
•
For Grade 1, 2, or 3 infusion reaction, if the infusion reaction resolves or remains less than or
equal to Grade 2, resume infusion with the following modifications according to the initial
Grade of the infusion reaction.
Grade 1 or 2: Infuse at one-half of the previous infusion rate.
Grade 3: Infuse at a rate of 12 mL/hour.
•
After resuming the infusion, the infusion rate may be increased according to Table 1 above,
based on patient tolerance.
2.4 Premedication
•
Premedicate 30 minutes to 2 hours prior to each dose with oral acetaminophen 1,000 mg (or
equivalent), oral or intravenous antihistamine (cetirizine 10 mg or equivalent), and
intravenous corticosteroid (prednisolone 100 mg or equivalent).
•
Do not reduce corticosteroid dose for Doses 1, 2, and 9.
•
Corticosteroid dose may be reduced as follows for Doses 3 through 8 and 10 through 12:
•
Doses 3 through 8: Gradually reduce corticosteroid dose with successive infusions if a
Grade 3 or greater infusion reaction did not occur with the preceding dose.
•
Doses 10 through 12: Administer prednisolone 50 mg to 100 mg or equivalent if a
Grade 3 or greater infusion reaction did not occur with Dose 9.
2.5 Preparation and Administration
•
Do not shake product.
•
Inspect parenteral drug products visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to
administration. ARZERRA should be a clear to opalescent, colorless solution and may
contain a small amount of visible translucent-to-white, amorphous, ofatumumab particles.
The solution should not be used if discolored or cloudy, or if foreign particulate matter is
present.
•
300-mg dose: Withdraw and discard 15 mL from a 1,000-mL bag of 0.9% Sodium Chloride
Injection, USP. Withdraw 5 mL from each of 3 single-use 100 mg vials of ARZERRA and
add to the bag. Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion.
Preparation of Solution:
•
2,000-mg dose: Withdraw and discard 100 mL from a 1,000-mL bag of 0.9% Sodium
Chloride Injection, USP. Withdraw 50 mL from each of 2 single-use 1,000 mg vials of
ARZERRA and add to the bag. Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion.
•
Store diluted solution between 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F).
•
No incompatibilities between ARZERRA and polyvinylchloride or polyolefin bags and
administration sets have been observed.
p. 3 Apr 19 2012 11:24:05
•
Do not mix ARZERRA with, or administer as an infusion with, other medicinal products.
Administration Instructions:
•
Administer using an infusion pump with an administration set and the provided in-line filter
set.
•
Flush the intravenous line with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP before and after each
dose.
•
Start infusion within 12 hours of preparation.
•
Discard prepared solution after 24 hours.
3
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
•
100 mg/5 mL single-use vial.
•
1,000 mg/50 mL single-use vial.
4
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion Reactions
ARZERRA can cause serious infusion reactions manifesting as bronchospasm, dyspnea,
laryngeal edema, pulmonary edema, flushing, hypertension, hypotension, syncope, cardiac
ischemia/infarction, back pain, abdominal pain, pyrexia, rash, urticaria, and angioedema.
Infusion reactions occur more frequently with the first 2 infusions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Premedicate with acetaminophen, an antihistamine, and a corticosteroid [see Dosage and
Administration (2.1, 2.4)]. Interrupt infusion for infusion reactions of any severity. Institute
medical management for severe infusion reactions including angina or other signs and symptoms
of myocardial ischemia [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
In a study of patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, an
indication for which ARZERRA is not approved, 2 of 5 patients developed Grade 3
bronchospasm during infusion.
5.2 Cytopenias
Prolonged (≥1 week) severe neutropenia and thrombocytopenia can occur with ARZERRA.
Monitor complete blood counts (CBC) and platelet counts at regular intervals during therapy,
and increase the frequency of monitoring in patients who develop Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias.
5.3 Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), including fatal PML, can occur with
ARZERRA. Consider PML in any patient with new onset of or changes in pre-existing
p. 4 Apr 19 2012 11:24:05
neurological signs or symptoms. Discontinue ARZERRA if PML is suspected, and initiate
evaluation for PML including consultation with a neurologist, brain MRI, and lumbar puncture.
5.4 Hepatitis B Infection and Reactivation
Fulminant and fatal hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and reactivation can occur in patients
following treatment with ARZERRA. Screen patients at high risk of HBV infection before
initiation of ARZERRA. Closely monitor carriers of hepatitis B for clinical and laboratory signs
of active HBV infection during treatment with ARZERRA and for 6 to 12 months following the
last infusion of ARZERRA. Discontinue ARZERRA in patients who develop viral hepatitis or
reactivation of viral hepatitis, and institute appropriate treatment. Insufficient data exist
regarding the safety of administration of ARZERRA in patients with active hepatitis.
5.5 Intestinal Obstruction
Obstruction of the small intestine can occur in patients receiving ARZERRA. Perform a
diagnostic evaluation if obstruction is suspected.
5.6 Immunizations
The safety of immunization with live viral vaccines during or following administration of
ARZERRA has not been studied. Do not administer live viral vaccines to patients who have
recently received ARZERRA. The ability to generate an immune response to any vaccine
following administration of ARZERRA has not been studied.
6
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the
labeling:
•
Infusion Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Hepatitis B Reactivation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Intestinal Obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) in Study 1 were neutropenia, pneumonia, pyrexia,
cough, diarrhea, anemia, fatigue, dyspnea, rash, nausea, bronchitis, and upper respiratory tract
infections.
The most common serious adverse reactions in Study 1 were infections (including pneumonia
and sepsis), neutropenia, and pyrexia. Infections were the most common adverse reactions
leading to drug discontinuation in Study 1.
p. 5 Apr 19 2012 11:24:05
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates
observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials
of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of monotherapy with ARZERRA was evaluated in 181 patients with relapsed or
refractory CLL in 2 open-label, non-randomized, single-arm studies. In these studies,
ARZERRA was administered at 2,000 mg beginning with the second dose for 11 doses (Study 1
[n = 154]) or 3 doses (Study 2 [n = 27]).
The data described in Table 2 and other sections below are derived from 154 patients in Study 1.
All patients received 2,000 mg weekly from the second dose onward. Ninety percent of patients
received at least 8 infusions of ARZERRA and 55% received all 12 infusions. The median age
was 63 years (range: 41 to 86 years), 72% were male, and 97% were White.
p. 6 Apr 19 2012 11:24:05
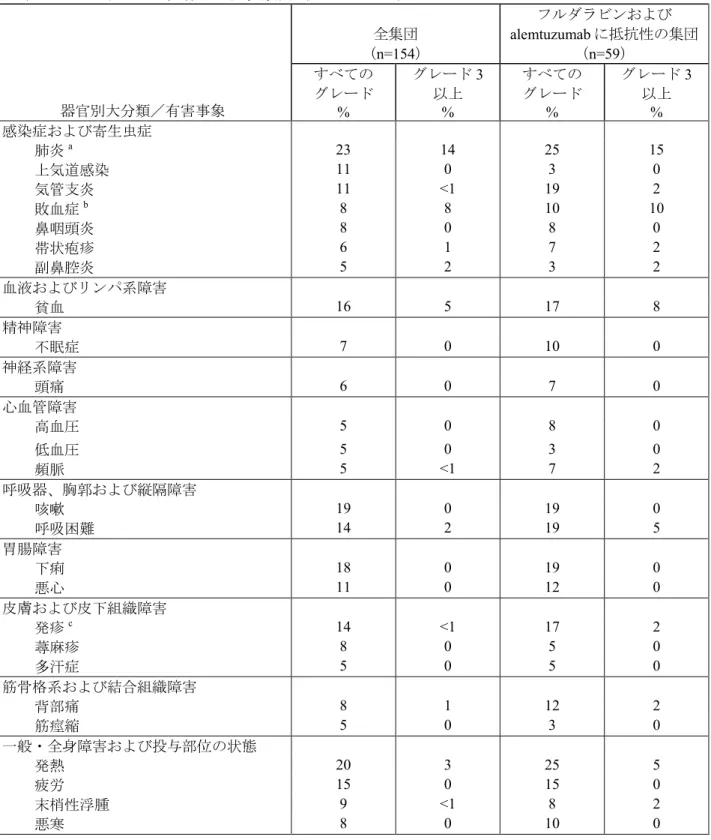
Table 2. Incidence of All Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥5% of Patients in Study 1 and in
the Fludarabine- and Alemtuzumab-Refractory Subset of Study 1 (MedDRA 9.0)
Body System/Adverse Event
Total Population
(n = 154)
Fludarabine- and
Alemtuzumab-Refractory
(n = 59)
All Grades
%
Grade ≥3
%
All Grades
%
Grade ≥3
%
Infections and infestations
Pneumonia
a23
14
25
15
Upper respiratory tract infection
11
0
3
0
Bronchitis
11
<1
19
2
Sepsis
b8
8
10
10
Nasopharyngitis
8
0
8
0
Herpes zoster
6
1
7
2
Sinusitis
5
2
3
2
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Anemia
16
5
17
8
Psychiatric disorders
Insomnia
7
0
10
0
Nervous system disorders
Headache
6
0
7
0
Cardiovascular disorders
Hypertension
5
0
8
0
Hypotension
5
0
3
0
Tachycardia
5
<1
7
2
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal
disorders
Cough
19
0
19
0
Dyspnea
14
2
19
5
Gastrointestinal disorders
Diarrhea
18
0
19
0
Nausea
11
0
12
0
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rash
c14
<1
17
2
Urticaria
8
0
5
0
Hyperhidrosis
5
0
5
0
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue
disorders
Back pain
8
1
12
2
Muscle spasms
5
0
3
0
General disorders and administration site
conditions
Pyrexia
20
3
25
5
Fatigue
15
0
15
0
Edema peripheral
9
<1
8
2
Chills
8
0
10
0
p. 7 Apr 19 2012 11:24:05a
Pneumonia includes pneumonia, lung infection, lobar pneumonia, and bronchopneumonia.
bSepsis includes sepsis, neutropenic sepsis, bacteremia, and septic shock.
c
Rash includes rash, rash macular, and rash vesicular.
Infusion Reactions:
Infusion reactions occurred in 44% of patients on the day of the first
infusion (300 mg), 29% on the day of the second infusion (2,000 mg), and less frequently during
subsequent infusions.
Infections:
A total of 108 patients (70%) experienced bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. A
total of 45 patients (29%) experienced ≥Grade 3 infections, of which 19 (12%) were fatal. The
proportion of fatal infections in the fludarabine- and alemtuzumab-refractory group was 17%.
Neutropenia:
Of 108 patients with normal neutrophil counts at baseline, 45 (42%) developed
≥
Grade 3 neutropenia. Nineteen (18%) developed Grade 4 neutropenia. Some patients
experienced new onset Grade 4 neutropenia >2 weeks in duration.
6.2 Immunogenicity
There is a potential for immunogenicity with therapeutic proteins such as ofatumumab. Serum
samples from patients with CLL in Study 1 were tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
(ELISA) for anti-ofatumumab antibodies during and after the 24-week treatment period. Results
were negative in 46 patients after the 8
thinfusion and in 33 patients after the 12
thinfusion.
Immunogenicity assay results are highly dependent on several factors including assay sensitivity
and specificity, assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant
medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of incidence of antibodies to
ARZERRA with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
7
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No formal drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with ARZERRA.
8
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C:
There are no adequate or well-controlled studies of ofatumumab in
pregnant women. A reproductive study in pregnant cynomolgus monkeys that received
ofatumumab at doses up to 3.5 times the recommended human dose of ofatumumab did not
demonstrate maternal toxicity or teratogenicity. Ofatumumab crossed the placental barrier, and
fetuses exhibited depletion of peripheral B cells and decreased spleen and placental weights.
ARZERRA should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies
the potential risk to the fetus.
p. 8 Apr 19 2012 11:24:05
There are no human or animal data on the potential short- and long-term effects of perinatal
B-cell depletion in offspring following in utero exposure to ofatumumab. Ofatumumab does not
bind normal human tissues other than B lymphocytes. It is not known if binding occurs to unique
embryonic or fetal tissue targets. In addition, the kinetics of B-lymphocyte recovery are
unknown in offspring with B-cell depletion [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.3)].
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether ofatumumab is secreted in human milk; however, human IgG is secreted
in human milk. Published data suggest that neonatal and infant consumption of breast milk does
not result in substantial absorption of these maternal antibodies into circulation. Because the
effects of local gastrointestinal and limited systemic exposure to ofatumumab are unknown,
caution should be exercised when ARZERRA is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ARZERRA have not been established in children.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ARZERRA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to
determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology
(12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No formal studies of ARZERRA in patients with renal impairment have been conducted [see
Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No formal studies of ARZERRA in patients with hepatic impairment have been conducted.
10
OVERDOSAGE
No data are available regarding overdosage with ARZERRA.
11
DESCRIPTION
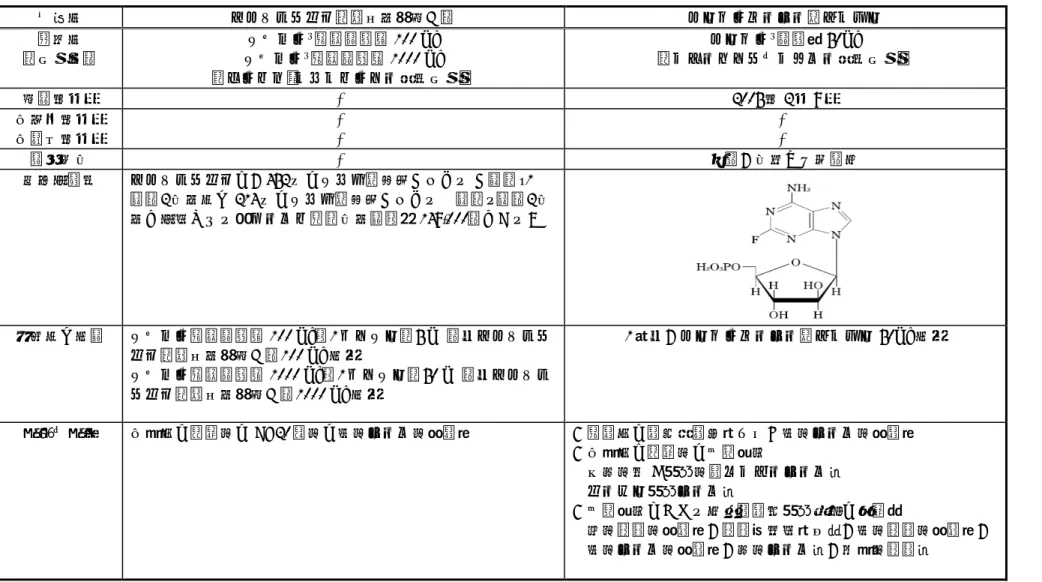
ARZERRA (ofatumumab) is an IgG1κ human monoclonal antibody with a molecular weight of
approximately 149 kDa. The antibody was generated via transgenic mouse and hybridoma
technology and is produced in a recombinant murine cell line (NS0) using standard mammalian
cell cultivation and purification technologies.
ARZERRA is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless, preservative-free liquid concentrate for
intravenous administration. ARZERRA is supplied at a concentration of 20 mg/mL in single-use
vials. Each single-use vial contains either 100 mg ofatumumab in 5 mL of solution or 1,000 mg
ofatumumab in 50 mL of solution.
p. 9 Apr 19 2012 11:24:05
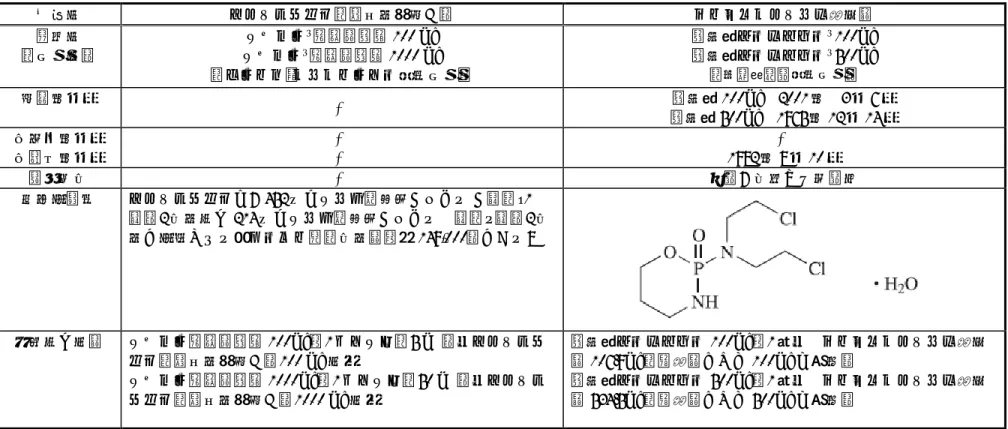
Inactive ingredients include: 10 mg/mL arginine, diluted hydrochloric acid, 0.019 mg/mL edetate
disodium, 0.2 mg/mL polysorbate 80, 6.8 mg/mL sodium acetate, 2.98 mg/mL sodium chloride,
and Water for Injection, USP. The pH is 5.5.
12
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ofatumumab binds specifically to both the small and large extracellular loops of the CD20
molecule. The CD20 molecule is expressed on normal B lymphocytes (pre-B- to mature
B-lymphocyte) and on B-cell CLL. The CD20 molecule is not shed from the cell surface and is
not internalized following antibody binding.
The Fab domain of ofatumumab binds to the CD20 molecule and the Fc domain mediates
immune effector functions to result in B-cell lysis in vitro. Data suggest that possible
mechanisms of cell lysis include complement-dependent cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent,
cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In patients with CLL refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab, the median decrease in
circulating CD19-positive B cells was 91% (n = 50) with the 8
thinfusion and 85% (n = 32) with
the 12
thinfusion. The time to recovery of lymphocytes, including CD19-positive B cells, to
normal levels has not been determined.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic data were obtained from 146 patients with refractory CLL who received a
300-mg initial dose followed by 7 weekly and 4 monthly infusions of 2,000 mg. The C
maxand
AUC
(0-∞)after the 8
thinfusion in Study 1 were approximately 40% and 60% higher than after the
4
thinfusion in Study 2. The mean volume of distribution at steady-state (V
ss
) values ranged from
1.7 to 5.1 L. Ofatumumab is eliminated through both a target-independent route and a
B cell-mediated route. Ofatumumab exhibited dose-dependent clearance in the dose range of 100
to 2,000 mg. Due to the depletion of B cells, the clearance of ofatumumab decreased
substantially after subsequent infusions compared to the first infusion. The mean clearance
between the 4
thand 12
thinfusions was approximately 0.01 L/hr and exhibited large inter-subject
variability with CV% greater than 50%. The mean t
1/2between the 4
thand 12
thinfusions was
approximately 14 days (range: 2.3 to 61.5 days).
Special Populations: Cross-study analyses were performed on data from patients with a variety
of conditions, including 162 patients with CLL, who received multiple infusions of ARZERRA
as a single agent at doses ranging from 100 to 2,000 mg. The effects of various covariates (e.g.,
p. 10 Apr 19 2012 11:24:06
body size [weight, height, body surface area], age, gender, baseline creatinine clearance) on
ofatumumab pharmacokinetics were assessed in a population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Body Weight: Volume of distribution and clearance increased with body weight. However, this
increase was not clinically significant. No dosage adjustment is recommended based on body
weight.
Age: Age did not significantly influence ofatumumab pharmacokinetics in patients ranging from
21 to 86 years of age. No pharmacokinetic data are available in pediatric patients.
Gender: Gender had a modest effect on ofatumumab pharmacokinetics (14% to 25% lower
clearance and volume of distribution in female patients compared to male patients) in a
cross-study population analysis (41% of the patients in this analysis were male and 59% were
female). These effects are not considered clinically important, and no dosage adjustment is
recommended.
Renal Impairment: Creatinine clearance at baseline did not have a clinically important effect on
ofatumumab pharmacokinetics in patients with calculated creatinine clearance values ranging
from 33 to 287 mL/min.
13
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity or mutagenicity studies of ofatumumab have been conducted. In a
repeat-dose toxicity study, no tumorigenic or unexpected mitogenic responses were noted in
cynomolgus monkeys treated for 7 months with up to 3.5 times the human dose of ofatumumab.
Effects on male and female fertility have not been evaluated in animal studies.
13.3 Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology
Pregnant cynomolgus monkeys dosed with 0.7 or 3.5 times the human dose of ofatumumab
weekly during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 20 to 50) had no maternal toxicity or
teratogenicity. Both dose levels of ofatumumab depleted circulating B cells in the dams, with
signs of initial B cell recovery 50 days after the final dose. Following Caesarean section at
gestational day 100, fetuses from ofatumumab-treated dams exhibited decreases in mean
peripheral B-cell counts (decreased to approximately 10% of control values), splenic B-cell
counts (decreased to approximately 15 to 20% of control values), and spleen weights (decreased
by 15% for the low-dose and by 30% for the high-dose group, compared to control values).
Fetuses from treated dams exhibiting anti-ofatumumab antibody responses had higher B cell
counts and higher spleen weights compared to the fetuses from other treated dams, indicating
partial recovery in those animals developing anti-ofatumumab antibodies. When compared to
control animals, fetuses from treated dams in both dose groups had a 10% decrease in mean
p. 11 Apr 19 2012 11:24:06
placental weights. A 15% decrease in mean thymus weight compared to the controls was also
observed in fetuses from dams treated with 3.5 times the human dose of ofatumumab. The
biological significance of decreased placental and thymic weights is unknown.
The kinetics of B-lymphocyte recovery and the potential long-term effects of perinatal B-cell
depletion in offspring from ofatumumab-treated dams have not been studied in animals.
14
CLINICAL STUDIES
Study 1 was a single-arm, multicenter study in 154 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL.
ARZERRA was administered by intravenous infusion according to the following schedule:
300 mg (Week 0), 2,000 mg weekly for 7 infusions (Weeks 1 through 7), and 2,000 mg every
4 weeks for 4 infusions (Weeks 12 through 24). Patients with CLL refractory to fludarabine and
alemtuzumab (n = 59) comprised the efficacy population. Drug refractoriness was defined as
failure to achieve at least a partial response to, or disease progression within 6 months of, the last
dose of fludarabine or alemtuzumab. The main efficacy outcome was durable objective tumor
response rate. Objective tumor responses were determined using the 1996 National Cancer
Institute Working Group (NCIWG) Guidelines for CLL.
In patients with CLL refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab, the median age was 64 years
(range: 41 to 86 years), 75% were male, and 95% were White. The median number of prior
therapies was 5; 93% received prior alkylating agents, 59% received prior rituximab, and all
received prior fludarabine and alemtuzumab. Eighty-eight percent of patients received at least
8 infusions of ARZERRA and 54% received 12 infusions.
The investigator-determined overall response rate in patients with CLL refractory to fludarabine
and alemtuzumab was 42% (99% CI: 26, 60) with a median duration of response of 6.5 months
(95% CI: 5.8, 8.3). There were no complete responses. Anti-tumor activity was also observed in
additional patients in Study 1 and in a multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation study (Study 2)
conducted in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL.
16
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ARZERRA (ofatumumab) is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless, preservative-free liquid
concentrate (20 mg/mL) for dilution and intravenous administration provided in single-use glass
vials with a latex-free rubber stopper and an aluminum overseal. Each vial contains either
100 mg ofatumumab in 5 mL of solution or 1,000 mg ofatumumab in 50 mL of solution.
ARZERRA is available as follows:
Carton Contents
NDC
3 single-use 100 mg/5 mL vials with 2 in-line filter sets
Vial: NDC 0173-0821-02
Carton of 3 vials: NDC 0173-0821-33
1 single-use 1,000 mg/50 mL vial with 2 in-line filter sets Vial and Carton: NDC 0173-0821-01
p. 12 Apr 19 2012 11:24:06
Store ARZERRA refrigerated between 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F). Do not freeze. Vials should be
protected from light.
17
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients to contact a healthcare professional for any of the following:
•
Signs and symptoms of infusion reactions including fever, chills, rash, or breathing problems
within 24 hours of infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions
(6.1)]
•
Bleeding, easy bruising, petechiae, pallor, worsening weakness, or fatigue [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.2)]
•
Signs of infections including fever and cough [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and
Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
•
New neurological symptoms such as confusion, dizziness or loss of balance, difficulty
talking or walking, or vision problems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Symptoms of hepatitis including worsening fatigue or yellow discoloration of skin or eyes
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
New or worsening abdominal pain or nausea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Pregnancy or nursing [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)]
Advise patients of the need for:
•
Periodic monitoring for blood counts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Avoiding vaccination with live viral vaccines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Manufactured by:
GLAXO GROUP LIMITED
Greenford, Middlesex, UB6 0NN, United Kingdom
U.S. Lic. 1809
Distributed by:
GlaxoSmithKline
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
©2011, GlaxoSmithKline. All rights reserved.
September 2011
ARZ:6PI
p. 13 Apr 19 2012 11:24:06
添付文書の重要点(ハイライト) これらの重要点(ハイライト)には、ARZERRA を安全かつ有 効に使用するために必要とされるすべての情報が含まれているわ けではない。ARZERRA に関する添付文書(全文)も参照のこと。 ARZERRA(オファツムマブ) 注射剤-静脈内投与 米国での初回承認:2009 年 --- 最近の主要な変更箇所 --- 「用法・用量」の「調製および投与」(2.5 項) 2011 年 4 月改訂 「警告および使用上の注意」の「B 型肝炎の感 染と再活性化」(5.4 項) 9 月改訂 2011 年 --- 効能・効果--- ARZERRA(オファツムマブ)は CD20 に対する細胞傷害性モノ クローナル抗体であり、フルダラビンおよび alemtuzumab に抵抗 性の慢性リンパ性白血病(CLL)患者の治療を適応とする。本剤 の有効性は持続的な客観的奏効の実証に基づいており、本剤によ る疾患に関連した症状の改善や生存期間の延長を証明したデータ はない(1 項、14 項)。 --- 用法・用量--- • 希釈し、点滴静注する。プッシュまたはボーラスで静脈内投 与してはならない(2.1 項)。 • 推奨用法・用量は以下の 12 回投与である。 • 初回投与量として 300mg を投与する。 • 1 週間後、2000mg を 1 週間間隔で 7 回投与する。 • 4 週間後、2000mg を 4 週間間隔で 4 回投与する(2.1 項)。 • 経口用アセトアミノフェン、経口用または静注用抗ヒスタミ ン薬および静注用コルチコステロイドを前投与する(2.4 項)。 --- 剤形および含量 --- • 100mg/5mL の single-use(1 回使い切り)バイアル(3 項) • 1000mg/50mL の single-use(1 回使い切り)バイアル(3 項) --- 禁忌 --- なし(4 項)。 --- 警告および使用上の注意--- • Infusion Reaction:前投薬として、静注用コルチコステロイド (必要に応じて)、経口用鎮痛薬および経口用または静注用 抗ヒスタミン薬を前投与する。本剤投与中は患者を注意深く 観察すること。Infusion reaction が発現した場合には投与を中 断すること(2.3 項、2.4 項、5.1 項)。 • 血球減少症:定期的に血球数を測定して好中球減少および血 小板減少の有無を確認すること(5.2 項)。 • 進行性多巣性白質脳症(PML):神経機能をモニターし、PML が疑われる場合には本剤の投与を中止すること(5.3 項)。 • B 型肝炎の感染および再活性化:リスクの高い患者をスクリー ニングすること。ウイルス性肝炎を発症した場合やウイルス 性肝炎が再活性化した場合は本剤の投与を中止すること(5.4 項)。 --- 副作用 --- もっとも多くみられた副作用(≧10%)は好中球減少症、肺炎、 発熱、咳嗽、下痢、貧血、疲労、呼吸困難、発疹、悪心、気管支 炎および上気道感染であった(6 項)。 副作用が疑われる場合は、GlaxoSmithKline(1-888-825-5249) またはFDA(1-800-FDA-1088 もしくはwww.fda.gov/medwatch)に 報告すること。 ---特別な集団への投与 --- • 妊婦:動物データに基づくと、胎児に害を及ぼすおそれがあ る(8.1 項)。 • 授乳婦:公表データに基づくと、母乳による授乳を行っても、 母親の抗体が乳児の体内に実質的に吸収されることはないと 考えられる(8.3 項)。 患者に伝えるべき情報については17 項を参照。 2011 年 9 月改訂 添付文書(全文):目次* 1 効能・効果 2 用法・用量 2.1 推奨用法・用量 2.2 投与方法 2.3 用量の調整 2.4 前投薬 2.5 調製および投与 3 剤形および含量 4 禁忌 5 警告および使用上の注意 5.1 Infusion Reaction 5.2 血球減少症 5.3 進行性多巣性白質脳症 5.4 B型肝炎の感染および再活性化 5.5 腸閉塞 5.6 予防接種 6 副作用 6.1 臨床試験成績 6.2 免疫原性 7 薬物相互作用 8 特別な集団への投与 8.1 妊婦 8.3 授乳婦 8.4 小児への投与 8.5 高齢者への投与 8.6 腎機能障害 8.7 肝機能障害 10 過量投与 11 組成・性状 12 臨床薬理 12.1 作用機序 12.2 薬力学 12.3 薬物動態 13 非臨床毒性 13.1 がん原性、遺伝毒性、受胎能障害 13.3 生殖発生毒性 14 臨床試験 16 包装/保管および取扱い方法 17 患者に伝えるべき情報 * 添付文書(全文)から省略されたセクションおよびサブセク ションは記載していない。 p. 1 Apr 19 2012 11:24:06
添付文書(全文)
1
効能・効果
ARZERRA®(オファツムマブ)はフルダラビンおよび alemtuzumab に抵抗性の慢性リンパ性白血 病(CLL)患者の治療を適応とする。 本剤の有効性は持続的な客観的奏効の実証に基づいている[「臨床試験」(14項)参照]。本剤 による疾患に関連した症状の改善や生存期間の延長を証明したデータはない。2
用法・用量
2.1 推奨用法・用量•
プッシュまたはボーラスで静脈内投与してはならない。•
各回の点滴静注前に前投薬を行うこと[「用法・用量」(2.4項)参照]。•
本剤に添付されているインラインフィルターセットを用いて投与すること。 推奨用法・用量は以下の12 回投与である。•
初回投与量として300mg を投与する(投与 1 回目)。•
1 週間後、2000mg を 1 週間間隔で 7 回投与する(投与 2~8 回目)。•
4 週間後、2000mg を 4 週間間隔で 4 回投与する(投与 9~12 回目)。 2.2 投与方法 いずれの場合も、米国薬局方 0.9%塩化ナトリウム注射液 1000mL に希釈して調製する[「用法・ 用量」(2.5項)参照]。•
投与1 回目:3.6mg/時(12mL/時)の投与速度で点滴静注を開始する。•
投与2 回目:24mg/時(12mL/時)の投与速度で点滴静注を開始する。•
投与3~12 回目:50mg/時(25mL/時)の投与速度で点滴静注を開始する。 投与に伴う毒性が発現しなければ、表1 に示すとおり、投与速度を 30 分ごとに上げることができ る。表1 に示した投与速度を超えてはならない。 表1. ARZERRA の投与速度 投与開始後 の時間(分) 投与1 回目a (mL/時) 投与2 回目b (mL/時) 投与3~12 回目b (mL/時) 0-30 12 12 25 31-60 25 25 50 61-90 50 50 100 91-120 100 100 200 >120 200 200 400 a 投与 1 回目の用量 = 300mg(0.3mg/mL) b 投与 2 回目と投与 3~12 回目の用量 = 2000mg(2mg/mL) p. 2 Apr 19 2012 11:24:062.3 用量の調整