148 第22回 総 会抄録 Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 不 能 症 例 が10%か ら5%へ と,さ らに そ の 頻度 が減 少 して ゆ く努 力 が 必 要 で あ るが,こ の 目的 の た め 厳 重 な follow up studyが 最 重 要 で あ る と 結 論 さ れ そ うで あ る. 文 責 大 柴
シ ン ポ ジ ウ ムⅣ
Endoscopyと
映 像 診 断
― ERCPとUS,CT,RIを 中 心 に―司 会:武 内 俊彦 ・相 馬
智
1-1)膵 疾 患 のERCPとCT 順 天 堂 大学 消化 器 内科 ○ 島 口 晴 耕 ・有 山 裏 われ わ れ はERCPと 血 管 造 影 の組 み合 わ せ が 膵 疾 患 の診 断 に有効 で あ る こ とを報 告 して きた.1cm前 後 の小 膵 癌 の 診 断 が可 能 で,膵 癌 と膵 良性 疾 患 の 鑑 別 診 断 も高 率 にで き る.CTの 膵 疾 患 診 断能 にっ い て は す で に多数 の報告 が あ る.今 回,わ れ わ れ はERCPと 血 管造 影 で 診 断 した膵 疾 患 の症 例 にCTス キ ャン を行 い,CTの 膵 疾患 診 断 にお け る有 効 性,限 界 お よ び位 置 づ け につ い て 検討 した. 対 象 と方 法 過 去2年 間 にERCP,血 管 造 影,CTを 行 い,手 術 ま た は剖 検 で組 織 学 的 に確 か め た膵疾 患22例 を対 象 と し た.そ の 内 訳 は 膵 癌7例,膵 嚢 胞5例,膵 石 例8例,慢 性 膵 炎2例 で あ る.膵 癌7例 中,切 除 可 能 で あ っ たの は 4例 で あ った. 方 法 は最 初 にERCPを 行 い,つ ぎに 血 管 造 影 お よび CTを 施 行 して3つ の 検 査 法 か らえ られ る診 断 情 報 を組 織 所 見 と対 比 した.CTはEMI5005を 使 用 した. 結 果 1.膵 癌 ERCPで 膵 癌7例 全 例 の 存在 診 断 が で きた.し か し癌 の大 き さ,伸 展 範 囲,切 除 可 否 の決 定 は で きな か っ た. 血 管 造 影 で は 全 例 に膵 癌 の大 き さ,伸 展 範 囲,切 除 可 否 の決 定 が 術 前 に 正確 に で きた.CTは7例 中6例 に 膵 癌 の 存在 診 断 が可 能 で あ った.膵 被膜 内 に限局 し,膵 の変 形 を来 た さな か った1.3×1.2×1.2cmの 体 部 癌 はCT 画 像 で膵 が 明 瞭 に輪 郭 され た に もか か わ らず,存 在 診 断 もで きなか った.CTで は膵 癌 の 腸 間膜 根 部,肝 十 二 指 腸 靱 帯 へ の直 接 浸 潤 の 診 断が 困難 な例 が あ った. 2.膵 嚢 胞 ERCPで は 膵嚢 胞5例 中2例 が診 断 で きた.血 管造 影,CTで は全 例 診 断可 能 で あ っ たが,CT画 像 の方 が 嚢 胞 と周 囲臓 器 の関 係 が 明 瞭 に認 め られ た.膵 嚢 胞 の術 後 の経 過 をみ るの にはCTが もっ と も適 して い た. 3.膵 石 症 ERCPで は膵 石症8例 中6例 が 診 断 で きた.CTで は 腹部 単 純X線 像,ERCPで 認 め られ なか った 膵 石 ま で 全例,診 断 で きた.膵 石 に合 併 す る癌 の 除 外 診 断 に は血 管造 影 が もっ と も有 効 で あ った. 4.慢 性 膵 炎 膵 石 の ない慢 性 膵 炎 の 確定 診 断 は3つ の 検 査法 と も困 難 で あ った.膵 管 の 形 態異 常 の診 断 に はERCPが 優 れ, 癌 の除 外 診 断 に は血 管 造影 が有 効 で あ った.CTで は診 断 に特 異 的 な所 見 はみ られ な か っ た. 結 論 ERCPは 膵 癌 の存 在 診 断 に も っ と も有 効 で,膵 良 性 疾 患 の 膵管 異 常 を診 断 す る目 的 に よい.ERCP所 見 だ けか らは膵 疾 患 の確 定 診 断 を行 う こ とは困 難 な場 合 が あ る. CTは 膵 と周 囲 臓 器 の 関 係 を は っ き り させ るの に役 立 つ.膵 石 症 と膵 嚢 胞 の 診 断 に もっ と もよい.切 除不 能 な 大 きな膵癌 は容 易 に診 断 で き るが,切 除 可 能 な 小 さな膵 癌 は診 断 で きない.膵 癌 の直 接 浸 潤 の 診 断 も 困難 な場 合 が あ る. 血 管 造影 は膵 癌 の 大 き さ,伸 展 範 囲,切 除可 否 の決 定 に有効 で,小 さな膵 癌 も診 断 で き る.膵 癌 の 除外 診 断 も 高 率 に可 能 で あ る. 以上 の結 論 か ら表 に示 すdicisiontreeが 膵 疾 患 の 診 断 に も っ と も合 目的 で あ る と考 え られ る.Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 シ ン ポ ジ ウ ムⅣ 1483
Dicision Tree In Patient with Suspected Pancreatic Disease
ERCP, ANGIOGRAPHY AND COMPUTED TO-MOGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF PANCR-EATIC DISEASE
SEIKOH SHIMAGUCHI AND JOE ARIYAMA Department of Gastroenterology, Juntendo University, Tokyo, Japan
The relative efficacy of ERCP, angiography and computed tomography (CT) was studied in 22 pa-tients with proven pancreatic disease. Twenty-two patients include 7 patients with pancreatic carcinoma, 5 patients with pancreatic cyst, 8 patients with pancr-eatic calcification and 2 patients with chronic pancr-eatitis. Qualitative evaluation of the diagnostic effi-cacy of each modality revealed that ERCP was the most reliable method for detecting pancreatic carcino-ma. Even very small tumor was detected by ERCP. ERCP permitted to demonstrate fine abnormality of the pancreatic duct. It was difficult to assess extent of pancreatic disease with ERCP. CT was suited to demonstrate pancreatic calcification and cyst. Large unresectable pancreatic carcinoma was readily diagno-sed by CT. Small pancreatic carcinoma measuring
1.3•~1.2•~1.2cm was not detected with CT. Size of pancreatic carcinoma, its extent and resectability were
accurately defined by angiography. Angiography was also useful to exclude pancreatic carcinoma in patients with abnormal pancreatogram and/or computed to-mogram.
From these results diagnostic approach to pancre-atic disease has been evolved (Table).
1-2)ERCPとCT ― ERCPとCTを 中 心 に し て― 大 垣市 民病 院第2 内 科 ○ 綿引 元 ・中 野 哲 最 近,膵 ・胆道 疾患 の診 断 は,従 来 か らのERCP・ PTC等 に加 え,CT,US,RIの 普 及 に よ り,さ ら に 綜 合 的,合 目的 な診 断 が 可 能 に な って来 た.ま た,肝 疾 患, 特 に肝 悪 性 腫 瘍 等 の診 断 は,CTに よ り飛 躍 的 に 向上 し て来 た. わ れ わ れ は,昭 和53年4月 以 来,第Ⅲ 世 代GE製 CT/TXI,さ らにⅩⅡ を導 入 し,US,RⅠ と もど も 日常 診 療 に組 入 れ,肝 胆膵 疾 患 の綜 合 的 な 診 断 体 系 の 確 立 を はか って い る.今 回 は,CTの 診 断能 と限 界 を明 らか に し なが ら,臨 床 診 断 にお け るCTの 位置 づ け を明 らか に した. CTが 膵 胆 道 疾 患 の ス ク リー ニ ン グテ ス ト と して 有 用 か ど うか,閉 塞 性 黄 疸54例 につ い て検 討 した(Table). 肝 内胆 管 の 拡張,胆 嚢 の腫 大 ま た は緊 満,総 胆 管 の拡 張 な ど胆 道 の 閉 塞 を証 明 で きた もの90.7%,閉 塞 部 位 の 診 Table1閉 塞性 黄 疸 のCT診 断 Gastroenterological Endoscopy
1484 第22回 総会抄録 Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 Table2 膵 ・胆道 系 悪 性 腫 瘍 のCT診 断 Table3 CTな らび にERCPの 診 断 能 の 対 比 *内 視 鏡 お よ び 直 視 下 生 検 診 断 に も とづ く。 断 が で きた もの72.2%,さ らに,病 変 の存 在 診 断 が で き た もの は,75.9%で あ り,閉 塞 性黄 疸 か ど うか の診 断 に は 有 用 で あ っ た.し か し,中 に は,閉 塞 性 黄 疽 を呈 しな が ら,CT上 で は,明 らか な所 見 を認 め なか った膵 頭 部 癌 の 例 な ど もあ り,注 意 を要 した. 次 に,膵 ・胆 道 系 悪 性腫 瘍 につ い て,CTが 質 的診 断 に どの 程度 役 立 つ か 検 討 し た(Table2).胆 管 癌14例 で は,CT診 断 の確 診 例35.7%,疑 診 例14.3%で あ り, 胆 管癌 切 除例 で は28.6%に す ぎな か っ た.し か し,上 部 胆 管癌 に限 れ ば,50.0%の 確 診 が え られ た.胆 嚢 癌24 例 で は,確 診 例62.5%,疑 診 例25.%%と 比 較 的 良好 な 診 断能 を示 し,切 除例 で も50.0%の 確 診 例 が存 在 して い た.膵 癌20例 で は,確 診 例 は55.0%で あ った が,切 除 例 で の確 診 例 は存 在 しな か った.乳 頭 部 癌6例 で は,確 診 例 は な く,閉 塞 部 位 の診 断 が で きた だ けの 疑 診 例 が 66.7%に 認 め られ た.以 上 の ご と く,CT診 断 は,膵 ・ 胆 道 系 悪 性腫 瘍 の うち,胆 嚢 癌,上 部 胆 管 癌 、膵癌 の診 断 に は比較 的有 用 で あ ったが,切 除 例 の診 断 能 はお と っ て い た. さら に,CTの 診 断能 をERCPと 比 較 し て み る と (Table3).胆 嚢癌 で は,ERCPの 正 診 率 は48.3%と 低 く,,CTの 診 断率 の ほ うが す ぐれ て い た.胆 管癌,膵 癌 は,い ず れ もERCPの 診 断 能 が 高 く,そ れ ぞ れ,76.0 %,78.1%で あ った.な お,乳 頭 部 癌 で は,FRCPは 不 可 能 に近 いが,内 視 鏡 診 断 ま た は 直 視 下 生 検 に よ り, 全 例診 断 可 能 で あ った. さ らに,肝 内結 石,膵 嚢 胞,膵 石 症 な どの 良性 の膵 ・ 胆道 系疾 患 の 診 断 に もCTは 有 用 で あ り,い ず れ も全 例 診 断可 能 で あ った.す な わ ち,肝 内結 石6例 で は,全 例, 肝 内胆 管 の嚢 状拡 張 とその 中 に結 石 を示 すhighdensity 像 を証 明 した.膵 嚢 胞 で は,ERCPや 臨床 診 断 にて 疑 わ れ な が ら,確 診 ま で至 って い な い症 例 で,CTに よ り確 認 されて い る. 肝 内病 変 で は,特 に肝 悪 性 腫 瘍 の 診 断 が,CTに よ り 飛 躍 的 に向 上 し,3.5×3.8cmの 切 除 可 能 で あ った肝 細 胞 癌 をは じめ として悪 性 腫 瘍 の検 出率 は約94%に 及 ん だ. そ の ほか,肝 嚢胞 や 脂 肪肝 等 の 診 断 に も有 用 で あ った. 以上,CTは,肝 細胞 癌,転 移 性 肝癌,肝 内胆 管癌 な どの肝 悪 性腫 瘍,肝 内結 石,脂 肪 肝 な ど肝 内病 変 の 形 態 学 的診 断 の有 力 な手 段 とな りえた.膵 胆 道 系 疾 患 で は, 膵 嚢 胞,膵 石 症 の 診 断 に有 力 で あ り,膵 ・胆 道 系 悪 性腫 瘍 に つ いて み る と,胆 嚢癌 で,ERCPに 比 べ 明 らか に診 断 能 が す ぐれ て いた の み で あ り,他 の悪 性 腫 瘍 の診 断能 は ERCPに お よ ばな か った.ま た,各 悪 性 腫 瘍 の末 期 例 で は,CTに よ る質 的診 断 が可 能 な症 例 が 多 く,患 者 へ の 侵 襲 も少 ない 利点 が あ るが,早 期 診 断 へ の 糸 口を 見 出す こ とは不 可 能 に近 く,'他 の検 査 法 と組 合 せ 綜 合 的 に診 断 して行 く必 要 が あ る. 文 献 1) 中野 哲 他:肝 悪 性 腫瘍 診 断 の た め のCTの 診 断 的意 義 と限 界.臨 床 放 射 線,25,55∼61,1980
DIAGNOSTIC UTILITY OF CT AND ERCP HAJIME WATAHIKI AND SATORU NAKANO 2nd clinic of Internal Medicine (Department of Gastro-enterology) Ogaki Municipal Hospital
Computed tomography (CT), Ultrasonography (US) and Radioisotope examinations (RI) made a great progress in the diagnosis for the hepato-,
pancreato-Vol. 22(10), Oct. 1980 シ ン ポ ジ ウ ムIV 1485
biliary diseases in addition to conventional
examina-tions as ERCP and PTC.
This study is to clarify
the ability and limitation of the diagnosis for these
diseases by CT comparing with ERCP or PTC.
I. Diagnosis by CT (3rd Generat GE CT/ T)
a.
Of fifty four cases with obstructive jaundice,
the dilatation of the intrahepatic
duct and
some-times of the common bile duct with enlarged gall
bladder were detected in 90.7% by CT.
Thus, CT was useful for the differential diagnosis
of the jaundice, obstructive or not.
b.
A correct and suspicious diagnosis in 14 cases
with carcinoma of the bile duct were made in 35.7%
and 28.6% respectively.
As for the resected cases, it decreased to 28.6%.
The malignancy in the upper part of the biliary
tract was more easier to be diagnosed than other
parts showing 50.0% in correct diagnosis.
In twenty four cases with carcinoma of the gall
bladder, correct and suspicious diagnosis were
es-tablished in 62.5% and 25.0% respectively.
Even in the resected cases, the correct diagnosis
was obtained in a half of them.
In twenty cases with carcinoma of the pancreas,
correct diagnosis was made in 55.0%, but all of
them were in unresectable stages.
All of six cases with papillary cancer remained
in suspicious diagnosis.
As mentioned above,
dia-gnosis for the malignancies
of pancreato-biliary
system by CT were useful but it was difficult to
make a correct diagnosis in the early, resectable
stages.
c.
CT was also useful for the diagnosis of the
intrahepatic stones, pancreatolithiases
and cystic
le-sions as liver cyst and pancreatic cyst. In all six
cases with intrahepatic stones, the cystic dilatation
of the introhepatic
biliary tree with high density
area were observed.
CT demonstrated clearly the
lesion in the cases with pancreatic cyst even though
diagnosis remained suspicious by ERCP.
Hepatic
lesions including liver cyst, fatty liver and
malig-nant tumors became more detectable by CT.
A correct diagnosis was established in 94.0% of
3 cases with liver malignancies.
‡U
. Comparison of the diagnostic value between CT and ERCP.
For the diagnosis of the cases with carcinoma of the gall bladder, CT was superior to ERCP.
(Co-rrect diagnosis; 62.5%, 48.3% respectively)
On the contrary, ERCP was superior to CT in the cases with carcinoma of the biliary tract and the pancreas. (Correct diagnosis; 76.0%, 50.% re-spectively for the former, 78.1%, 55.0% respectively for the latter)
Endoscopic observation and biopsy were useful for the diagnosis of papillary cancer.
Conclusion:
Diagnostic usefulness of CT was confirmed in such cases as liver cyst, fatty liver, intrahepatic stones and liver malignancies including hepato-cellular carcinoma and metastatic liver cancer.
As for pancreato-biliary diseases, pancreatolithiases and pancreatic cyst became detectable more easily by CT and ERCP was superior to CT in the diagnosis for carcinoma of those organs except for carcinoma of the gall bladder.
As CT is non-invasive examination, it is reasona-ble to undergo in the patient, lying in end stages of
malignancies and can make a great progress in the correct diagnosis by combination of conventional exam-inations though early diagnosis in the resectable cases of malignancies is no promising.
2-1)リ
ニ ア 電 子 ス キ ャ ン 超 音 波 検
査 法 に よ る 膵 疾 患 の 診 断 能
―特 に,ERCPと
の 対 比 に よ
る 検 討―
千 葉 大 学 医学 部 第1内 科 ○ 税 所 宏 光 ・唐 沢 英 偉 超 音 波 検 査 は患 者 に苦 痛 を与 えず,簡 便 に行 な え る安 全 な検 査 法 で あ る.中 で も,リ ニ ア電 子 ス キ ャ ン超 音 波 検 査法(以 下,US)は 連 続 的 に短 時 間 で 目的部 位 を隈 な く観察 で き る利 点 を も ち,膵 管 と膵 実 質 の 両面 か ら膵 の 変 化 を診 断 す るこ とが可 能 な優 れ た検 査 法 とい え る.そ こで,本 法 によ る膵 疾 患 の超 音 波像 を 明 らか に し,診 断能 につ いて,内 視 鏡 的膵 管 造 影 法(以 下,ERCP)と 比較 Gastroenterological Endoscopy1486 第22回 総会抄録 Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 検 討 す る. 対 象:1.対 照 例87例,膵 癌51例,慢 性 膵 炎31例 に つ いて 膵 管 と膵実 質 のUS像 を検討 した.2.USと ERCP両 者 の行 な わ れ た93例 にお いて 両 検査 法 の診 断 能 を比 較 し た. 方 法:超 音 波 検 査 は3.5MHzの 探 触 子 を用 い,東 芝 製 リニ ア電 子 走 査 型 超 音 波診 断 装 置(SAL10Aま た は 20A)に て 行 な っ た.ERCPは オ リ ンパ ス製JF-B型 を 用 い,通 常 の 方 法 で行 な った. 成 績:1.対 照 例 の 膵 超音 波像:膵 管像 は84%に 認 め られ,内 腔 径 は0,5士0.2mm(M±SD)で,正 常 径 は1 mm未 満 と され た.形 状 は頭 部 が 最 も厚 く大 きい 勾 玉 状 を呈 し,内 部 エ コ ーは均 一 で肝 とほぼ 同等 か や や増 強 し て い た.60歳 以上 の高 齢 者 に 内部 エ コーの 増 強 を示 す頻 度 が高 か っ た.2.膵 疾 患 例 の 膵 超音 波 像:a)膵 管 像. 内腔 径1mm以 上 の拡 張 膵 管 像 は平 滑 拡 張,じ ゅず状 拡 張 お よ び不 整 拡 張 の3型 に分 類 され た.じ ゅず状 拡 張 を 示 した21例 中20例 が 膵 頭 部癌 で あ った.ま た,不 整 拡 張 を示 した18例 中12例 は慢 性膵 炎 で あ った.じ ゅず 状 拡 張 は膵 頭 部 癌,不 整 拡 張 は慢 性 膵 炎 に特 徴 的所 見 とい えた.b)膵 実 質 像.形 状 の変 化 と して,全 体 腫 大,局 所 腫 大,の う胞 が み られ た.局 所 腫 大 を呈 した45例 中43 例 は膵 癌 で あ った.実 質 の 異常 内 部 エ コー像 は点 状 型, 斑 状型,お よ び局 所 減 弱型 に分 け られ た.点 状 型 を呈 し た18例 中16例 は慢 性膵 炎,斑 状 型 を呈 した21例 全 例 と局所 減 弱 型 の24例 中21例 は膵 癌 で あ った.即 ち,点 状 型 は慢 性 膵 炎,斑 状 と局 所 減 弱型 は膵 癌 に特 徴 的 所 見 で あ った.3.USに よ る膵 疾 患診 断 能:慢 性 膵 炎31例 申 18例(58%)と 膵癌51例 中48例(94%)は 各 々 の疾 患 に特 徴 的 な超音 波所 見 を有 し,質 的診 断 が 可 能 で あ った, ま た,慢 性 膵 炎 の87%,膵 癌 で は100%に 超 音 波所 見 の 上 で異 常 が み られ た(Table1).4.ERCPと の診 断 能 の比 較:a)膵 頭 部 癌20例 の中,ERCPで は造 影 不 成 功 が9例 あ り,更 に,1例 に異 常 所 見 が 得 られ な か っ た. 一 方 ,USで は全 例 に異 常 が 診 断 し得 た(Table2).体 尾 部癌6例 で は両 検 査 と も全 例 に異常 所 見 を得 たが,膵 の う胞 との鑑 別 に はUSが 優 れ た.b)乳 頭 部 癌4例 で はUSで 膵 管 の拡 張 所 見 か ら全例 に 異常 が 指 摘 され た が,乳 頭 部 の 内 視鏡 所 見 と生 検 が可 能 で あ るERCPが 確 診 に有 効 で あ った.c)慢 性 膵 炎22例 で はERCPで 1例,USで3例 に異常 所 見 が 得 られ なか った.前 者 の 1例 はUSで,後 者 の3例 はERCPで 異 常 所 見 が得 ら れ,両 者 を組 み合 わせ る と,全 例 に異 常 が 指 摘 で き た (Table3).d)乳 頭 部癌 を含 めて 膵 疾 患 群54例 をま と め る とERCPで は13例(24%)に 造 影不 成功 あ るい は 異 常 所 見 が指 摘 で きな か ったが,USで は 検 査 の無 効 が 4例(7%)に と どま ってお り,ERCPと 比 較 して, USの 膵診 断法 として の 優秀 性 が 示 され た. 結 語:USは 慢 性 膵 炎 の一 部 を 除 いて,膵 病 変 の 存 在 を明 らか に し,確 診 す るこ とが可 能 で あ る.本 法 でな お Table1慢 性膵炎と膵癌の特徴的超音波所見
Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 シ ン ポ ジ ウ ムIV 147 Tabie2内 視 鏡 的膵 管 造 影(ERCP)所 見 と超 音 波 検 査 (US)所 見 膵 頭 部 癌20例 Table3内 視 鏡 的 膵 管 造 影(ERCP)所 見 と超 音 波 検 査 (US)所 見 慢 性 膵 炎22例 不 明 の場 合,ERCPの 適 応 とな るこ とを述 べ た・
REAL-TIME ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN PANCRE-A TIC DIAGNOSIS •\COMPARATIVE APPRAI-SAL WITH ENDOSCOPIC RETROGRADE CHO-LANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY•\
HIROMITSU SAISHO AND Eli KARASAWA The First Department of Internal Medicine
Ultrasonography of he panrcreas was performed in 169 patients including 51 with pancreatic carcinoma, 31 with chronic pancreatitis and 87 with normal pan-creas. Commercially available linear-array real-time ultrasound equipment with 3.5 MHz transducer was employed for the examination. Based on the results of these patients, ultrasound diagnosis of the pan-creas was assessed. Furthermore, both ultrasonogra-phy (US) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancr-eatography (ERCP) were performed in 93 patients;
both studies were always done within one week of each other. In these patients, US was compared with ERCP for the pancreatic evaluation.
The sonographic features of chronic pancreatitis
and pancreatic carcinoma were analyzed concerning to pancreatic duct dilatation, pancreatic size and shape,
and pancreatic tissue echo pattern. Beaded dilatation of the pancreatic duct, partial enlargement of the pancreas, nodular tissue echopattern and focal decrease of echogenicity were the chararteristic sonographic signs of pancreatic carcinoma. In all of the 51 pa-tients with pancreatic carcinoma, US showed pan-creatic abnormality. Especially, 48 patients (94°0) had the characteristic signs. Irregular dilatation of the pancreatic duct and echogenic heterogenous echo pattern with scattered strong echo spots were the characteristic sonographic signs of chronic panrceati-tis. In 27 (87°0) of 31 patients with chronic pan-creatitis, abnormal sonographic findings were shown. Among them, 18 patients had the characteristic signs.
In the 93 patients who underwent both US and ERCP, the results of US were compared with those of ERCP. Of the 26 patients with pancreatic carci noma, 9 ERCP studies failed in cannulation and oth-er one failed to provide abnormality. In contrast, US could provide diagnostic information in all of the pa-tients with pancreatic carcinoma. Additionally, US was superior to ERCP for the differentiation of pseu-docysts from solid tumors. In the 22 patients with
chronic pancreatitis, false negative diagnosis was pro-vided in 3 US studies and in one ERCP study; in every patient, however, either of both studies could show abnormality. In the patients with ampullary carcinoma, ERCP including duodenoscopy could provi-de the provi-definite diagnosis, while pancreatic duct dilata-tion was shown by US.
It is concluded that US is a very reliable screening and diagnostic technique for the pancreas, so that the complementary use of US and ERCP constituted pow-erful diagnostic combination for the patients suspected of pancreatic disease. 2-2)肝 ・胆 ・膵 疾 患 診 断 に お け る ERCPとUS 名 古 屋 大学 第2内 科 ○木 本 英 三 中 沢 三 郎 肝 ・胆 ・膵 疾 患 を疑 ってERCPとUSを 共 に施 行 し Gastroentexological Endoscopy
1488 第22回 総会抄録 Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 Figure1疾 患 別 の 診 断 能 の 対 比 た257例 を対 象 と して,診 断能,得 られ る情 報 内 容 の対 比 を行 な い,Figure1の 成 績 を得 た. 肝 内 占拠 性 病変25例 で は,ERCで は圧 排 偏 位 よ り16 %に 占拠 性 病 変 を指 摘 で きた に過 ぎな い の に比 し,USで は100%に 存 在 診 断 可 能 で,嚢 胞,充 実 性 腫 瘍,膿 瘍 の 鑑 別 も可 能 で あ っ た. 胆 石 症 で は,肝 内結 石7例 で は両 者 と も71%の 正 診 率 だ った が,ERCで は拡 張 胆 管 内 の透 亮 像,胆 管 の 閉塞 像 と共 に胆 管 硬 化 像 が 得 られ た が,総 胆 管 の結 石 の為 肝 内 まで 造 影 し得 ない 例 が2例 存在 した.USで はbistabl の2例 で 診 断不 能 だ った.USで は非 造影 部 の情 報 も得 られ る と共 に,USガ イ ドで の選 択 的PTCに も応 用 で きた.胆 管 結 石24例 で は,ERCで96%に 正 診 した の に対 し,USで は正 診33%,胆 管 拡 張 の み58%で あ り, 胆 管 拡 張 の ス ク リー ニ ン グ法 に位 置 す る と い え る.胆 嚢 結 石61例 で は,ERCで 正 診40%,胆 嚢 不 影27%で あ っ たが,USで は93%に 正 診 す る と共 に,adenomyoma-tosis,empyema等 も診 断 で きた. 胆 道 癌 で は,胆 嚢癌7例 で,ERCで57%に 正 診,US で86%に 正 診 した が,小 病 変 は無 か った.胆 管 癌7例 で は,ERCで72%に 正 診 した が,USで は29%の 正 診 率 で,閉 塞 レベ ル の 診 断 に と どま る例 が 多 か った. 先天 性胆 道 拡 張 症16例 で は,USで81%に 肝 外 胆 管 の 嚢腫 状拡 張 を描 出 す る と共 に,合 併病 変8病 変 を全 て 正 診 した.膵 胆 管合 流 異常 はERCPで88%に 証 明 し得 た が,合 併 病変 は3病 変 を診 断 した に過 ぎな か った. 膵 嚢胞13例 で は,ERPで 造 影 剤 貯 溜38%,膵 管 閉 塞 31%,圧 排23%で あ り,膵 管 との交 通 の有 無 の 検索 に不
Vol22(10),Oct.1980 シ ン ポ ジ ウ ムⅣ 1489 Figure2膵 体 部 癌切 除 例 Figure3同 症 例 のERCP 可 欠 だ った.USで は100%に 嚢 胞 像 そ の もの が得 られ, 内腔 の 変 化 も識 る こ とが で き,し か も,偶 発 症 の 心 配 の 無 い利 点 も有 して い た. 膵 炎 非 石 化群39例 で は,USで 腫 大 や膵 管 拡 張 像 に よ り72%を チ ェ ック で きた.ECRPで も72%に 狭 窄,拡 張 や辺 縁 硬化 像 を認 め た.主 膵 管 の変 化 の軽 い もの は, US像 が 正 常 で あ る例 に 多 か った.膵 石 症11例 で は,US で91%に 膵 石 エ コ ーを示 す こ とが で きた.ERCPで は 82%に 膵 管 像 を得 た が,造 影 剤 の過 剰注 入 へ の 注 意 を要 し た.限 局 性 膵 炎 で は膵 癌 との 鑑別 が重 要 だが,而 検 査 所 見 を併 せ る こ とに よ り鑑 別 し得 た例 もあ り,鑑 別 困難 な 例 もあ った. 膵癌36例 で は,ERCPで は主 膵 管 の 閉像,狭 窄像, 辺 縁 不 整 像,造 影 剤 不整 貯 溜像 に よ り81%に 正 診 した. USで は,限 局 性 腫 大,減 衰 を伴 な う腫 大,不 整 内 部 エ コ ー を もつ 腫 大,膵 影 内 の低 エ コ ー レベ ル域 等 に よ り, 89%に 正 診 で きた.ま たERPで 膵 管 像 の得 られ な い頭 部 癌 では,USガ イ ドに尾 側拡 張 膵 管 を穿 刺 造 影 す る方 法 が 有 効 で あ る こ と も認 め た.USは 無 侵 襲 に行 な え る 点 で ス ク リー ニ ン グ法 と して最 適 とい え る. 癌 腫 以 外 の 膵 腫 瘍4例 の う ち,2例 は 出 血性 嚢胞 を形 成 して い たが,細 網 肉腫 の1例 は 膵 管 の圧 排 像 とUSで の 特 異 な腫 瘍 像,膵A細 胞 癌 の!例 で は不 整 貯 溜 を伴 な う膵 管 圧排 像 と,一 部 大 小 多 発 の 嚢胞 像 を もつ 混合 性 腫 〓に よ り,い ず れ も膵 癌 とは 異 な る腫 瘍 との 診 断 が可 能 で あ った, 以 上 の如 く,USは 肝 ・胆 ・膵 の ス ク リー ニ ム グ検 査 と して最 適 で あ る と共 に,腫 瘤 の 直 接 像,ERCPで の非 造 影 部 の 情 報 が 得 られ る利 点 を持 っ.他 方,ERCPは, 胆管,膵 管 の よ り詳 細 な所 見 が得 られ,USで の胆 管像 や 膵 管 像 で も って それ にか え る こ とは で きな い と い え る.
ENDOSCOPIC RETROGRADE CHOLANGIOPAN-CREATOGRAPHY AND ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF HEPATOBILIARY AND PANCREATIC DISEASES.
EIZO KIMOTO AND SABURO NAKAZAWA The second department of internal medicine, Nagoya University, school of medicine, Nagoya, Japan.
Comparison between endoscopic cholangiopancreato-graphy (ERCP) and ultrasonography was made in 257 patients with suspected hepatobiliary or pancreatic diseases, in whom both ERCP and ultrasonography were performed.
In 25 cases of space occupying lesion (SOL) of the liver ERC could point out SOLs only in 16%. While, ultrasonography could not only detect them in 100%, but also differentiate solid tumor, cyst and abscess from each other.
In 7 cases of intrahepatic biliary calculi, the diag-nostic accuracy of ERC was 71%, and that of ultra-sonography was also 71%. ERC revealed obstruction of any of the intrahepatic bile ducts or biliary calculi themselves, and rigidity of the contour of bile ducts
1496 第22回 総会抄録 Vol.22(10),pct.1980
Ultrasonography
delineated strong echoes
accompany-ing acoustic shadows in the liver. In one of the cases,
ultrasonically-guided
percutaneous transhepatic
chol-angiography proved to be of great value. In 24 cases
of choledocholithiasis,
ERC correctly diagnosed in
96°0. Ultrasonography,
however, could diagnose only
in 33%.
In 58%, it revealed biliary dilatation but
failed to find any calculous. In 61 cases of gall stone,
the accuracy of ERC was 40%, and that of
ultra-sonography reached 93%.
ERC correctly diagnosed 57% of 7 cases of
gallbla-dder carcinoma, and ultrasonography did 86°0 of them.
However, all of them were far advanced.
In the
diagnosis of bile duct carcinoma, ERC was superior
to ultrasonography.
In 16 cases of choledochal cyst ultrasonography
well delineated cystic dilatation of extrahepatic bile
duct in 81% of them, but abnormal
cholangio-pan-creatico anastomoses were demonstrated only by ERCP.
Investigation
of concomitant lesions, such as biliary
calculi and carcinoma, were successfully accomplished
by ultrasonography.
In patients with pancreatic diseases, both ERCP
and ultrasonography
proved to be efficacious
diagno-stic tools.
In all of 13 cases of cyst of the pancreas,
ultrason-ography made it possible to visualize cyst itself. ERP
demonstrated obstruction of the pancreatic duct,
pool-ing o contrast
media within the cyst or pressure
effect to the pancreatic duct. It should be investigated
by ERP whether the pancreatic duct communicated
with the cyst or not.
It was possible to investigate the inflammatory
proc-ess of the pancreas both with ERCP and
ultrasonog-raphy.
Pancreatic calculi were also visualized by
ultrasono-graphy.
It was difficult, however, to differentiate
localized pacreatitis from carcinoma. Aspiration biopsy
was regarded to be useful in this respect.
In 36 patients with carcinoma of the pancreas. ERCP
revealed obstruction or stenosis of the main pancreatic
duct with or without irregular pooling of contrast
media within the gland, and obstruction or stenosis
of the bile duct.
The overall accuracy with ERCP
was 81%. Ultrasonography demonstrated localized-enlargement of the pancreas with or without attenua tion, localized enlargement with central echoes or low-echo level area within the gland, and its overall accu-racy was 89%. It was considered that some difficul-ty existed in detecting smaller lesions and in differe-ntiating from localized pancreatitis.
Both ERCP and ultrasonography gave usefull in-fomations in diagnosing pancreatic tumors other than carcinoma.
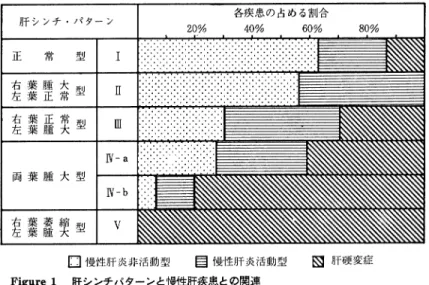
It might well be concluded that ultrasonography was best suited for investigation of hepatobiliary and pan-creatic diseases because of its noninvasiveness and relative diagnostic accuracy. Frequently it offered valuable informations which ERCP failed to. On the other hand, only ERCP made it possible to appreciate more detailed changes of bile and pancreatic duct. Thus, both modalities should be employed in conbina-tion in the diagnosis of hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases. 3-1)Endoscopyと 映 像 診 断 ― ERCPとRI― 大 阪 市 立 大学 第3内 科 ○ 辰 己 駿一 小 林 絢 三 scintigraphyは 最 近 器 械 の 進 歩 と,使 用 す るisotope の 開発 な ど に よ りそ の診 断 能 が 向上 した こ と,簡 単 で 苦 痛 の な い検 査 法 で あ るた め繁 用 され るよ うに な った ・肝 ・胆 道 ・膵 にお い てscintigraphyとERCPを 対 比 して そ の診 断 能 とその 限界 にっ き比 較 検討 した. (1)肝 臓;び まん 性肝 疾 患 にお い てscintigraphyに よ って描 画 され る肝 形 態 を1型 ∼V型 に分 類 し(Fig-ure1),組 織 学 的 に診 断 され た慢 性 肝 炎,肝 硬 変 が 示 す scintigramの 肝形 態 を調 べ た.1型,豆 型 で は慢 性 肝 炎 が94%を 占 め,皿 型,W型 で は肝 硬 変 が60%と 増 加 し, V型 で は す べ て肝 硬 変 で あ った.ま た,肝 形 態 の変 化 以 外 に病 態 の進 展 に伴 う肝 描 画 能 の低 下,脾 の 大 き さ,脾 ・骨 髄 像 の描 画 状 態 も加 え,病 態 の正 確 な把 握 が可 能 と い え る.一 方ERCPに よ る肝 内 胆 管 像 は慢 性 肝 炎 で は 末 梢 胆 管 で の 限局 的 な狭 窄 を示 し,肝 硬 変 で は分 枝 の少 ない 先 細 りよ うの胆 管 像 を示 す場 合,胆 管 の 狭 窄 ・偏 位 と末 梢胆 管 が淡 く描 出 され る場 合 が あ った.し か し通常 のERCPで 診 断 可 能 な肝 内胆 管 描 出像 を示 す もの は肝
Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 シ ン ポ ジ ウ ムⅣ 1491
Figure1 肝 シ ンチ パ タ ー ン と慢 性 肝 疾 患 と の関 連
Figure 2 COMPARISON between PANCREATO-SCINTIGRAM and ERCP
内 胆 管 ま で描 出 され た症 例 の45%と 少 な く,ERCPの 診 断 能 に問題 が残 されて い る.肝 の 限局 的 な疾 患 にお け るscintigraphyで は陰 影 欠 損 の大 き さ ・数,そ の 質 的診 断 まで 可 能 とな って い る.一.方ERCPで は肝 癌7例 の うち5例 は肝 門部 の狭 窄 所 見 を,2例 は腫 瘤 に よ る胆 管 の 閉 塞,延 長 と偏 位 が み とめ られ た.ま た左 葉 欠 損 症例 のERCPで は胆 道 系 の 奇 形 の併 存 も証 明 され,右 葉 ・ 左 葉 の 萎 縮変 形 肝 で は特 異 な胆 管 が得 られ た.以 上 よ り 肝 にお け るscintigraphyに よ り質 的診 断 な らび に病態 把 握 も可 能 で あ るが,ERCPは 補 助 的診 断 にす ぎな い. (2)胆 道:scintigraphyで 従 来 の 排 泄性 胆 道 造 影 で描 出 され な い症 例(T-Bi15mgdl以 上,ALP20K・A・u 以 上),50例 中30例(60%)に 胆道 の描 画 が 得 られ た. 本 検 査 はisotopeの 肝 → 胆 道 → 腸 管 へ の移 行 と胆 管 の拡 張 の 有 無 の 診 断 に有 用 で あ る.一 方ERCPは 黄 疸 の有 無 にか か わ らず胆 道 が 描 出 され,し か も鮮 明 で そ の 質 的 診 断 ま で も可 能 で あ る.choledochalcystに お い て ERCPは その 存 在診 断 に加 え膵 胆 合 流部 形 式 の情 報 を 提 供 す る こ とで優 れ た検 査 法 で あ るが 全胆 道 が描 出 され な い こ と もあ り,肝 内病 変 の 検 索 にscintigraphyの 併 用 も必 要 とな る.以 上 よ りscintigraphyは 胆 道 の拡 張 所 見 と胆 汁 の排 泄 障 害 の把 握 に は優 れ た 検 査法 で あ るが, そ の 質 的診 断 に はERCPな ど直 接胆 道 造 影 が必 要 とな る. (3)膵 臓: ERCA, scintigraphy両 者 を施 行 した181 例 中scintigraphyで 膵 描 画 の あ った もの126例,部 分 的 欠 損29例,全 体 欠 損26例 で あ った.膵 描 画 陽 性 症 例 で 描画 状 態 を不 影,希 薄化,描 画 軽 度 低下,正 常 の 四段 階 に分 け,ERCPの 膵 管 像(normal, slightly; moder-ate; severe)の 変 化 と対 比 したが 膵 の 描画 状 態 と膵 管 像 とは ほ ぼ平 衡状 態 に あ った(Figure2).scintigraphyに お い て 正 常群 で は膵 管 異常 は み とめず,反 対 にERCP で 膵 管変 化軽 度 に もか か わ らず急 性 膵 炎 や 糖 尿 病 で scintigraphyで 描 画 能 の低 下 を み と めた もの が あ った. scintigraphyで 欠 損 描 画,描 画 陰 性 を示 した55例 中60 %と 高率 に膵 癌 が 存 在 した.ま た膵 癌 にお い て は経 過 を 追 求 し得 た症 例 で はそ の描 画 能 が 経 時 約 に低 下 した.膵 の う胞19例 に お いて は,陽 性 描 画 され た1例 がscinti-graphyで 診 断 された.欠 損 例,描 画 低 下 例 で は他 の疾 患 との 鑑 別 を要 した.ERCPで は11例 に大 ・小 の の う 胞 が 描 出 され た.Pleural effusionを 呈 した2症 例 にお いて,scintigraphyで は膵 体尾 部 の欠 損,膵 体 部 の欠 損 として 描画 され,ERCPに よ り主 膵 管 に起 因す るfistel との う胞 が証 明 され た.以 上 よ りscintigraphyで の描 画 Gastroenterological Endoscopy
1492 第22回 総会抄録 Vol.22(10),Oct.1980
欠 損,描 画 陰 性 例 は 膵癌 を想 定 し たERCP検 査 を施 行 す る こ とが 膵 疾 患 の 診 断 を向上 させ る もの と考 え る.
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF E. R. C. P. AND SCINTIGRAPHY WITH REFERENCE TO LIVER, BILIARY AND PANCREATIC DISEASE
SHUNICHI TATSUMI AND KENZO KOBAYASHI
3rd Dept. of Internal Medicine, Osaka City University Medical School
We discussed about the diagnostic value of scinti-graphy and endoscopic retrograde choledochopancrea-tography (ERCP) in disease of the liver, the biliary tract or the pancreas.
(1) The liver
We approached the liver shape obtained by liver scan in diffuse liver disease such as chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis which was diagnosed histologically.
As the result, chronic hepatitis was revealed in 94% of patients indicated normal liver shape or enlarge-ment of the right lobe. Liver cirrhosis was revealed in 60% of patients indicated enlargement of the left
or both lobe and in all patients indicated atrophy of the right lobe. The varying liver shape in liver scan was often associated with the progress of the liver disease. In addition, when the disease was advanced the liver scintigram indicated diffuse decrease together with increased radioactivity in the spleen and bone marrow of the spine.
On the other hand, in ERCP performed patients with chronic hepatitis it showed local narrowing of the peripheral hepatic duct. In liver cirrhosis it
show-ed either the few-branched and tapered hepatic duct or displacement and narrowing of the hepatic duct and a faint visualization of the peripheral hepatic duct. In localized liver disease such as hepatoma, metas-tatic liver tumor or abscess, the liver scintigram show-ed focal defect of the activity, and it was possible to differentiate hepatoma from other malignant lesions and benign lesions. We examined ERCP in 7 pa-tients with hepatoma. 5 patients indicated stenosis of the common hepatic duct. 2 patients indicated obstruc-tion, elongation or displacement due to tumor of the liver.
(2) The biliary tract
99mTC-PI
, 99mTC-HIDA has been used in
scintig-aphic examination of the biliary tract. These isotopes
transfer speedily from the liver to the biliary tract
and its image is sharp. So they provide the imf
orma-tion about dilataorma-tion of the bile duct.
In addition,
it is possible to examine the contruction of the gall
bladder used egg. The diagnosis of biliary
obstruc-tion can be performed if the radioactivity has
appear-ed not in the gut but in the kidney. We obtainappear-ed the
biliary tree in 60% of 70 patients with the impared
hepatic function
(it is over both 2.0mg/dl
in total
bilirubin and 20 K.A.
units in alkaliphosphatase).
In such cases, it was possible to differentiate whether
intrahepatic or extrahepatic cholestasis and to admit
dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct in patients with
extrahepatic obstruction such as stones or tumor.
On the other hand. ERCP provides the distinct
imformation of obstruction, stenosis or filling defect
in the biliary tract.
So it leed to accurate diagnosis
about biliary disease.
In choledochal cyst both biliary scan and ERCP
are usefull examination.
Our 11 patients showed
cystic dilatation of the biliary tract in biliary scan.
9 of these patients was diagnosed by ERCP in
addi-tion to the informaaddi-tion
of choledocho-pancreatic
com-munication.
(3) The pancreas
We examined both scintigraphy and ERCP in 180
patients. 126 patients had pancreatic visualization in
pancreatic scan. In those cases, the decreased
radio-activity in pancreatic scan was proportionate to
abnor-mality of the pancreatic duct in ERCP.
Patients
with glucose intolerance or acute pancreatitis revealed
more decreased pancreatic view than abnormality
of
the pancreatic duct.
Residual patients revealed
pa-rtial visualization
(21 patients)
and complete
non-visualization (34 patients) in pancreatic scan.
They
contained pancreatic cancer in 60%. Pancreatic cancer
was diagnosed by ERCP as obstruction (14 patients),
stenosis (7 patients) or cystic formation (2 patients).
40°o were chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cyst.
In 21 patients with pancreatic cyst, 1 patient had
Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 シ ン ポ ジ ウ ムⅣ 1493
decreased visualization (10 patients) and partial visua-lization (5 patients) and complete nonvisualization (5
patients). ERCP obtained visualization of cyst in 11 patients. Especially, in 2 patients of chronic pan-creatitis with pleural effusion ERCP was usefull pro-cedure to prove pancreatic fistel or pancreatic large cyst throughout esophageal hiatus to pleural cavity.
3-2)ERCPと
映 像 診 断
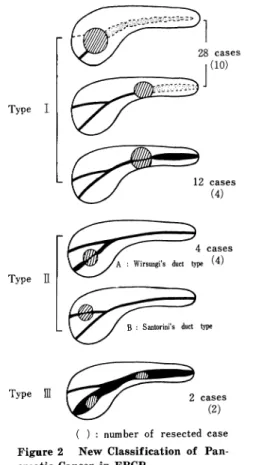
癌 研 究 会 附 属 病 院 内 科 ○ 大 橋 計 彦 同 外 科 高 木 国 夫 ERCPは 高 木,大 井 に よ り開 発 さ れ て 以 来,10年 で 膵 疾 患 診 断 の 中 心 的 役 割 を 果 す よ う に な っ た.今 だ に 胃, 大 腸 に 比 べ 膵 癌 の 早 期 発 見 例 が 少 な い の は ど ん な 患 者 に ERCPを 施 行 す るか,と い う問 題 が 未 解 決 の た め で あ る.こ の シ ン ポ ジ ウ ム の 主 題 で あ る 映 像 診 断,す な わ ち US,CT,RIは 患 者 へ の 苦 痛 が 少 な い と い う点 でscreen-ingfilterに な り う る と い う期 待 が あ る.し か しscreen-ingfilterの 重 要 な 要 素 で あ る そ れ ぞ れ の 検 査 の 「診 断 能 」 に つ い て は ま だ 充 分 な 討 論 が な さ れ な い.そ こ で わ れ わ れ に 課 せ られ た 主 題,ERCPとRI(膵 シ ン チ),CT と の 診 断 能 を 比 較 し て,そ れ ぞ れ の 検 査 体 系 に お け る位 置 づ け を 検 討 した.症 例 は1975年 か ら1979年 の5年 間 に行 な わ れ た509例 のERCP施 行 患 者 で あ る.膵 シ ン チ は509例 中99例,約20%に 行 な わ れ て い た.膵 シ ン チ の 診 断 能 はFigure1に 示 され て い る.膵 シ ン チ の 利 点 と さ れ たtrue negative率,つ ま り膵 シ ン チ で 正 常 な ら ば 膵 病 変 は 否 定 で き る率 は80%で あ っ た.true pos-itiveは40%で,false negativeす な わ ち 膵 シ ン チ で 見 逃 さ れ た の が5例 あ り3例 は 膵 癌,2例 は 乳 頭 部 癌 で あ っ た.ま た 膵 シ ン チ で 異 常 が あ っ た がERCPを し て 異 常 が な か っ たfalse positiveが50%も あ っ た.こ の 結 果 を み る とtrue negativeが 予 想 以 上 に 低 く,false po-sitiveが 高 か っ た の が 注 目 さ れ る.そ の う え 膵 シ ン チ に 使 用 さ れ る核 種 の 半 減 期 の 長 さ,costの 高 さ を 考 え る と 膵 シ ン チ はscreening filterと し て は 不 適 当 で あ る と思 わ れ る.次 にCT診 断 の 現 状 よ りERCPの 問 題 点 を 検 討 し た.最 近1年 間 で 切 除 が 可 能 でCT検 査 が 行 わ れ た の が8例 あ っ た.最 小 は8×8mmの 体 部 癌 で あ っ た.こ れ ら8例 のCT像 で 大 動 脈,下 大 静 脈,上 腸 間 膜 動,静 脈 の 描 出 が 可 能 で 癌 と こ れ ら大 血 管 の 位 置 関 係 か ら,血 管 造 影 ほ ど で は な い が,お お よ そ の 切 除 可 能 性 が 推 測 で き る.膵 癌 の 直 接 所 見 で あ るirregular contour,Figure 1 Result of Pancreatic Scintigram
Figure 2 New Classification of Pan-creatic Cancer in ERCP
enlargement low densityと 関接 所 見 と も言 うべ き閉 塞 部 よ り尾 側 の膵 管 の拡 張,実 質 の 萎縮 とに は所 見 出現 に 解 離 が あ り,直 接所 見 の みで は小 膵癌 の 発 見 は む ず か し く更 に症 例 を重 ね て所 見 の解 析 が 要求 され る と ころ で あ る.事 実,膵 管 拡 張 の著 明 で な い 切 除 可 能 膵癌 が4例 あ り,こ れ らの症 例 の検 討 か ら映像 診断 に 適 し た 膵 癌 の ERCP分 類 を して み た.Figure 2はERPの 得 られ た46 例 の膵 癌 の 癌 占 居部 位 を膵 管 所 見 よ り分 類 した もの で あ
1494 第22回 総 会抄録 Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 る.TypeⅠ は主 膵 管 の 狭 窄 が あ り,そ の 尾側 の膵 管 の 狭 窄 が あ り,そ の 尾 側 の膵 管 の 拡 張,実 質 の 萎縮 の み ら れ る型 で最 も頻 度 が高 い.こ の 型 はUS,CTで はtumor の直 接 所 見 と関接 所 見 の両 方 か ら診 断 で き る.TypeⅡ はWirsungi管 また はSantorini管 の い ず れ か一 方 が 癌 に浸潤 され,他 の一 方 が 開存 して い るた め 癌 よ り尾 側 の 膵 管 の拡 張 や実 質 萎 縮 の な い もの で あ る.Wirsungi 管 だ けが浸 潤 され た例 が4例 あ りいず れ も切 除可 能 で あ った.Santorini管 だ け の閉 塞 例 は現 在 ま だ な いが,膵 頭 部 癌 の初 期像 はTypeⅡ で あ る と考 え てい る・ この 型 はUS,CTで はtumorそ の もの を捕 え る他 に診 断 の 手 が か りは な くERCPが 決 め手 とな る.TypeⅢ は び慢 性 に著 明 な膵 管 拡 張 が あ り,そ の膵 管 内 に隆起 性 の 癌 の あ る特 殊 例 で,2例 あ りい ずれ も切 除 可 能 で あ っ た. この型 はUS,CTで 拡 張 した膵 管 を と らえ,そ の中 に tumorを 見 出す こ とで診 断 で きる.こ の他 にERCPで 主 膵 管 に異常 の な いTypeⅣ と も言 うべ き膵 野 欠 損 型 が あ る.こ の 型 分 類 はUS,CTを 膵 疾 患 のscreeningと して 行 うと き に有 用 でTypeⅠ,TypeⅢ は 従来 の概 念 で よ いがTypeⅡ の癌 の発 見 は現 在 の 方 法論 の延 長 で は 困難 で あ り,ど うして もERCPが 必 要 で あ る.つ ま り US,CTで は主 膵 管 に変 化 の こな い初 期 の膵 癌 の 発 見 は 困難 で あ り,現 段 階 で はERCPは 不 可 欠 な 検 査 で あ る.
ERCP AND IMAGING DIAGNOSIS OF
PANCRA-TIC CANCER
KAZUHIKO OHHASHI*
AND KUNIO TAKAGI**
*Department of Internal Medicine
**Department of Surgery , Cancer Institute Hospital,
Tokyo, Japan.
In spite of the development of diagnostic modalities
for pancreatic cancer, the surgical resectability and
prognosis of pancreatic cancer have remained
disco-uraging.
Small pancreatic cancers are hardly
detct-able firstly because the clinical symptoms are
com-moly so vague that careful attention cannot be paid
to the pancreas and secondly because ERCP could
not have been performed in all but a few rare cases.
Therefore, we need to urgently find out the
non-invasive screening filter for pancreatic cancer.
Body
imaging technigues
such as ultrasonography,
com-puted tomography or pancreatic scintigraphy seem to
be suitable for this purpose.
In this paper, a diagnostic acuracy of pancreatic
scintigraphy was evaluated in comparion with the re-sults of ERCP and CT findings of resectable pancreatic cancer were analyzed to approach an early detection of pancreatic cancer. ERCP has been perormed in 509 patients in the past five years and pancreatic scintigraphy has been performed in about 20% of them. As shown in Figure 1, the true negative rate of pancreatic scintigraphy was about 80%, while the true positive rate was 40%. Pancreatic scintigraphy failed to detect 5 pancreatic cancers with a false neg-ative rate of 10% and the false positive rate (50%) was unexpectedly high. In view of high cost of panc-reatic scintigraphy and a long half life of radiopharm-aceutical, the diagnostic results of scintigraphy are not satisfactory.
13 patients have been found to have resectable panc-reatic cancer in the past 12 months, and computed tomography has been carried out in 8 of them. There was no pathognomonic CT findings for small resec-table pancreatic cancer, but computed tomography dis-played useful information on surgical resectability by visualizing large vessels around the pancreas (aorta, inferior vena cava, superior mesenteric artery and su-perior mesenteric vein). The direct CT findings of pancreatic cancer such as irregular contour enlarge-ment and low density were rarely visualized in cases of small resectable pancreatic cancer, but the indirect CT findings such as dilatation of the main pancreatic duct or parenchymal atrophy distal to the tumor were demonstrated.
46 cases of pancreatic cancer with abnormal pancre-atogram were divided into 3 types based on the site of tumor and appearance of pancreatic duct as shown in Figure 2. Type I is the commonest type of pancr-eatic cancer with marked dilatation of the main pan-creatic duct and parenchymal atrophy. This type of pancreatic cancer may be detected by imaging tech-niques for both direct and indirect findings. Type ‡U is very rarely seen but this type could be an early appearance of so called cancer of the pancreas head. In this type, either Wirsungi's or Santorini's duct is only involved and indirect findings cannot be seen. ERCP must be only the diagnostic modality to pick-up this type of pancreatic cancer. Type ‡V is a
spe-Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 シ ンポ ジ ウ ムⅣ 1495
cial form of pancreatic cancer with polypoid tumor inside the dilated main pancreatic duct. This type may be detected by imaging techniques.
Thus, Type II pancreatic cancer can be only detect-ed by ERCP and it must be indispensable as a screen-ing filter at the moment.
4-1)膵 胆 道 疾 患 の 診 断 に お け る ERCP,US,CT,RIの 位 置 づ け 愛知 県が ん ゼ ン ター 第1内 科 ○ 久 野 信 義 同 放 射 線 診 断 部 木 戸 長 一 郎 Ⅰ.対 象 ERCP,US,CT,RIの 二 者 以 上 で診 断 され,手 術 ま た は剖 検 にて 確認 され た膵 癌22例,慢 性 膵 炎3例,胆 道 系 腫 瘍5例,胆 道 系結 石21例 に対 す る各 検 査 法 の 診 断 能,特 徴,及 び診断 体 系 な ど を検 討 した. Ⅱ.診 断 基 準 諸 家 の報 告 に基 づ い たERCP,US,CT,RIの 各 疾 患 に対 す る診 断 基 準 に よ り,確 診,疑 診,診 断 不 能 に分 け, 各 検 査法 の診 断 率 をみ た. Ⅲ.成 績 1.膵 癌 22例,各 検 査法 に よ る診 断 率 は,Table1上 段 の如 く で,確 診 率 はERCP,CTに お い て高 か った が,疑 診 を 含 め た診 断率 は 何 の検 査 法 で も80%前 後 で あ った.黄 疸 を有 す る膵癌 の各 検 査 法 の 診 断率 は80∼100%で,四 検 査 法 と も黄 疸 の有 無 に拘 らず 有効 で あ っ た.殊 にUS, CTな どにお い て胆 嚢,肝 内胆 管 の拡 張 な ど所 謂 間接 所 見 は,そ れ ぞれ6例 中4例,10例 中8例 に み られ た.本 シ リー ズ22例 は 四検 査 法 何 れ か の方 法 で 全 例拾 い上 げ られ た.即 ち相 補 的診 断率 は100%で あ った.22例 中切 除例 は4例 の みで あ った が,そ の4例 に於 け る各 検 査法 の 診 断率 はTable1下 段 の 如 くで,ERCPで 全 例確 診 され た.そ の 中2例 術後 不 幸 に して 腹 水,肝 転 移 な ど を みた こ と を,CTに て 追 跡 出来 た. 2.慢 性膵 炎 対象 を現 在 の膵 研 試 案 で確 診 と され た もの に限 った た め,何 れ も高 度 の もの で,各 検 査 法 に よ りほ とん ど確 診 で きた. 3.胆 道 系腫 瘍 胆 嚢 癌 は,確 診 の み で み る とERCPは3例 中1例 と 弱 いが,胆 管 癌 に な る と,直 接 撮 影 法 で あ るERCPで 2例 と も確 診 出来 た. 4.胆 道 系 結 石(Table2) 胆 嚢結 石 にお い て は,ERCPで もな お胆 嚢 が 造 影 され ず 疑診 に止 る もの が 多 か ったが,CTに よ り低 濃度 の胆 嚢 内 に高 濃 度 の影 像 を認 め た り,CE後 胆 嚢 内 に低 濃度 の 陰 影 を認 め,確 診 を得 る こ とが 多 く13例 あ った ・胆 嚢 胆 管 結石1例,胆 管 結 石2例 は,ERCPに よ り確 診 が得 られ た. Ⅳ.考 案 並 び に纒 め 膵 癌 にお け る確 診 率 は,ERCP,CTが 高 い が,疑 診 も含 めれ ばERCP,US,CT,RI何 れ も80%前 後 の 診 断 率 で,ま た何 れか で 拾 い上 げ る相補 的診 断 率 は100% で あ る.黄 疸 を有 す る例 で もUS,CTな どは 所 謂 間 接 所 Table1各 種 検 査 法 に よ る 膵 癌 の 診 断率 各種検査法 による膵癌(切 除 例)の 診断率 Gastroenterological Endoscopy
1496 第22回 総会抄録 Vol.22(10),Oct.1980
Table2各 種検査法 による胆道 系結石 の診断率
Table3膵 癌 のDecision tree
見 か ら も有 効 で,ま た 四 検 査法 と も黄 疽 の有 無 に 拘 らず 実 施 出来 る.経 過 を追 った り,他 臓 器 との 関係 を み るの にCTは 有力 で あ る.併 し現 況 で は 膵癌 は進 行 例 が多 く,切 除可 能 な もの は少 な い.切 除 可 能 例 の 確 診 率 は ERCPが 高 か った.従 って現 佐 の処,切 除可 能 な例 を 如 何 に してERCPや 血 管 撮 影 迄 もって 行 くか とい う捨 い上 げの方 法 が 最 も問題 とな る.新 しい 捨 い上 げの方 法 の 開発 と共 に,ERCP,US,CT,RIに 就 い て も新 た な 工 夫 が 為 され て い る.即 ち血 管 撮 影 下 のCT,サ ブ トラ ク シ ョン を行 うRI,ERCPに お け る直 接 拡 大撮 影 な ど で あ る.現 在 の処 の 膵 癌 の 診 断体 系 は,Table3上 段 の 如 くな ろ う.慢 性 膵 炎 に就 いて は,現 在 の 膵 研試 案 確 診 例 は高 度 の ものが 多 く,四 検 査 法 何 れ で も殆 ど確 診 出来 た.胆 嚢癌 は矢 張 り早 期 の捨 い上 げ法 が 問題 とな る・ 胆 管 癌,胆 管結 石 は,ERCPな ど直接 造 影 法 が,現 況 で は 有 力 で あ る.排 泄 性胆 道 造 影 法 で胆 嚢 が 造 影 され な い胆 嚢 結 石 は,ERCPに て もな お 胆 嚢造 影 陰 性 の こ とが 多 い が,CT,USに て確 診 され る こ とが あ る.胆 石 症 にお け る診 断体 系 を例 示 す る とTable3下 段 の 如 くな ろ う.
ASSESSMENTS
OF ERCP, US, CT AND RI IN
THE DIAGNOSIS
OF PANCREATICOBILIARY
DISEASES
NOBUYOSHI KUNO AND CHOICHIRO
KIDO
Departments of Iniernal Medicine, and Radiology,
Aichi Cancer Center Hospital, Nagoya, Japan
Assessments of the diagnostic value of 4 tests in
51 patients with proven carcinoma of the pancreas
(22 patients)
chronic pancreatitis
(3), carinoma of
the biliary tracts (5), and calculi of the biliary tracts
(21) were made.
ERCP, US, CT and RI were judged as correct,
suspicious and undiagnostic according to the criteria
discribed previously by us and others.
ERCP and CT were most sensitive in diagnosing
patients with pancreatic cancer (77.3°0, 72.2°0,
re-spectively).
These 4 tests offered complementary
corrert
or
suspicious information in the evaluation of pancreatic
cancer.
An indirect sign on US and CT is dilatation of
intrahepatic biliary tree.
All 4 tests are useful in
patients with or without jaundice.
Most of tumors are not diagnosed at a resectable
stage.
In this series only 4 patients had resectable
pancreatic cancer.
ERCP gave the correct diagnosis
in these 4 patients.
ERCP is the best means of
dia-gnosing resectable tumors.
Most patients, however,
experienced vague, nonspecific symptoms at an early
stage in the disease process. If an effecive diagnostic
Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 シ シ ポ ジ ウ ムⅣ 1497
procedure were used at this earlier stage, not only would the prognosis after resection be improved, but also a further group of patients who would otherwise progress to non-resctable disease could be identified and offered radical surgical treatment. We proposed decision tree for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
The diagnosis of pancreatitis was accepted follow-ing the criterion of Japan panreatic disease society. In all 3 patients with chronic pancreatitis, almost of all 4 tests gave the correct diagnosis.
Despite many efforts, our detection of resectable tumor of the gallbladder by 4 tests was not effective.
In 2 patients with carcinoma of the bile duct and in 3 patients with choledochocholelithiasis or choledo-cholithiasis, the ERCP diagnosis was definite and correct.
In 10 of 18 patients with cholelithiasis, the ERCP diagnosis was suspicous, because the gallbladder could not be visualized in spite of sufficient opacification of the intrahepatic bile duct. In many of these pat-ients, CT showed a high density in the area of the gallbladder or a low density in the area of the ga-llbladder with contrast enhancement.
A more sensitive diagnostic modality for the correct diagnosis of pancreatico-biliary diseases remains to be established. CT associated with angiography, RI with subtraction and direct magnification during ERCP are under investigation.
References
1) Kuno, N., Kasugai, T., Oguri, T.' Matsuura, A., Fujiwara, K. and Kato, O.: Endoscopic diagnosis of pancreatic diseases. Gendai Igaku 24:24, 1977 (In Japanese).
2) Doust, B. D.: The use of ultrasound in the diagnosis of gastroenterological disease. Gastroenterology 70: 602, 1976.
3) stanley, R. J., Sagel, S. S., and Levitt, R. G.: Com-puted tomography evaluation of the pancreas. Radiology 124 : 715, 1977.
4) Uno, K., Uchiyama, A., Hotta, T., and Kuniyasu, Y.: The diagnosis of the pancreatic cancer on pancreatic scintigram. Naika 43 : 782, 1979 (in Japanese).
4-2)ERCP,CT,US,RIに よ る 膵 胆 道 系 疾 患 診 断 能 の 検 討 岡 山大 学 第2内 科 〇 三 島 邦 基 武 田 正 彦 Ⅰ.目 的:膵 胆 道 系 疾 患 に つ い て,ERCP,CT,US, RIの 診 断 能 を比較 す る と共 に,そ れ ぞ れ の検 査 法 の 利 点 と限界 を検 討 した. Ⅱ.対 象:対 象 は乳 頭 膨 大部 癌4例,膵 癌21例,膵 石 症14例,非 石 灰 化 慢 性 膵 炎13例,膵 嚢 胞7例,胆 嚢 結 石38例,胆 管 結 石7例,胆 嚢癌4例,胆 管 癌5例,肝 癌 7例,正 常37例 の計157例 で あ る. Ⅲ.方 法:ERCPと 同時 にCT,US,RIを 行 った 上 記 対 象157例 につ い て,そ れ ぞ れ の 検 査法 に よ る 「診 断 」 を正 診 ・疑 診 ・診 断 不 能 に分 け診 断率false positive率 を検 討 した.正 診 は病 変 の 存 在 ・部 位 ・大 き さ ・数 ・良 悪 全 て 診 断 し得 た もの,疑 診 は1項 目 で も欠 けた もの, 診 断 不 能 は 全 く診 断 で き なか った もの で あ る.ま た,い か な る疾 患 ・病 変 に対 して は どの検 査法 が 秀 れ て い るか 或 い は限界 が あ るか を検 討 した. Ⅳ結 果:Table1の 通 りで あ る Ⅴ.考 察:(1)膨 大部 癌:ERCPが:最 も良 く診 断す る. (2)膵癌:こ こで の膵 癌 は1例 を除 き全 て 手 術摘 除不 能 例 で あ るた めCTで の正 診 率 が 高 く な って い るが,全 分 枝 迄 充 分 造 影 され たERCPで は,部 位 ・大 き さ ・浸 潤 範 囲迄 診 断 可 能 でCT,US,RIに 勝 る.ERCP疑 診7 例 の 内訳 は,主 膵癌 閉塞 像 の た め大 き さ,性 状 の不 明 な もの3例,分 枝 像 の読 影 が で きず 浸潤 範 囲 の不 明 な もの 3例,膵 管 に変 化 が乏 し く読 影 困 難 な もの1例 で あ る. CT,US,RIで の疑 診 例 は腫 瘤 陰 影 の 悪 性 の 有無 が診 断 で きな い もの で あ る.(3)膵 石 症:膵 石 症 と の 診 断 は, CT,USが 簡 単 で あ る.ERCPで は造 影 で きれ ば,結 石 の数 ・大 き さ ・部 位 ・膵 管 との 関 係;膵 管 の 性 状 が読 影 で き,operability手 術方 法 迄 診 断 可 能 で,CT,USに 勝 る診 断 能 を発揮 す る.(4)非 石 灰 化 慢 性 膵 炎:こ こで の 症 例 は 全 て進 展 例 で は な い.比 較 的mildな 慢 性 膵炎 の 診 断 はCT,USで は困難 で あ る.(5)膵 嚢胞:CT,US
がERCPに 勝 る.ERCPで はcystに 造 影 剤 が 入 った
1例 とcystを 膵 管 が 取 り巻 く1例 の み正 診,膵 管 中断 像 の2例 は疑 診,慢 性 膵 炎像 の み でcystの 存 在 す ら読 影 で きな か っ た3例 は診 断不 能 で あ った ・(6)胆嚢 結石: USが 最 も有 用 で あ る.ERCPは 造影 で きれ ば最 も秀 れ た 診 断 能 を発 揮 す るが,そ の成 功 率 は75∼85%で あ る. こ こで のERCP疑 診 例 は胆 嚢 管 の 中 断像 を呈 した 症例 で あ る.CTで の診 断 不 能65%は,slice間 隔8∼10mm Gastroenterological Endoscopy
1498 第22回 総会抄録 Vol.22(10).Oct.1980
Table1 各 種 膵 胆 道 系疾 患 に 対 す るERCP・CT・US・RIの 診 断 能
Vol.22(10),Oct.1980 シ ン ポ ジ ウ ムⅣ 1499 Table3 CT・USが:FRCPよ り勝 って い る場 合 X線 透 過 結 石 に起 因 す る所 が 大 で あ る.(7)胆管 結 石:US で の診 断 不 能2例29%は 初 期 の技 術 的未 熟 さに よ る も の で,そ れ を考 慮 す れ ばERCPUSは ほ ぼ 同等 の診 断 能 を有 す る.CTは 胆 管 を横 断 面 でsliceす るた め不 利 で,USERCPに 劣 る.(8ン胆 嚢癌:こ こでの 症 例 は全 て 治 癒切 除 で きた 早 期 の もの で あ る.ERCPは 造 影 で きれ ば最 も秀 れ た 診 断 能 を発 揮 す る.USは 簡 単 に腫 瘤 陰 影 を描 出す るが,良 悪 の判 定 は困 難 な こ とが多 く,こ こで の3例 は全 て 疑 診 に届 った.(9)胆 管 癌:ERCPが 最 も秀 れ て い る.CTUSで は胆 管拡 張 像 を 捕 えた の み で,癌 腫 を診 断 で きなか った.(10)肝癌:ERCPで は 全領 域 を造 影 す る こ とが 難 しい こ と,space taking lesionの 質 的診 断 が 困難 な こ とか ら正 診 例 が な い.(11)False Positive: ERCP false positiveは 主 膵 管 閉 塞 像 を膵 癌 と誤 った も
の1例,胆 管 末 端 部 陰影 欠 損 を膨 大 部 癌 と誤 った もの1
例 で あ る.CTで は膵 腫瘤 と誤 った もの4例 ・ 膵 嚢腫 と
誤 った もの1例 の計5例,USで は膵 腫 瘤 と誤 った もの
1例 で あ る.CTUSで は胆道 系 に対 す るfalse posi-tiveは0%で あ るが,そ れ は誤 って診 断 す る程 詳 細 明 瞭 な像 が 得 られ な い た めで あろ う. Ⅳ.結 論:(Table2・3参 照)病 変 の解 析力 以 外 に・ 簡 便 さ ・患 者 に対 す る苦 痛,利 点 と限 界 を考 慮 し,こ れ らの 検 査 は相 補 わ れ るべ きで あ る. CORRELATIVE EVALUATION OF FRCP, CT SCANNING, ULTRASOUND SONOGRAPHY, AND RADIO-ISOTOPE SCANNING IN DIAGNOSIS OF
PANCREATIC AND HEPATO-BILIARY
DIS-EASES.
KUNIKI MISHIMA AND MASAHIKO TAKEDA. Second Department of Int. Med., Okayama Uninersity Medical School, Okayama, Japan
Correlative evaluation of ERCP, CT, US, and RI in
the diagnosis of pancreatic and hepato-biliary diseases was performed in order to disclose the usefulness of each diagnostic procedures. Materials consist of 4 cases of ampullary cancer, 21 cases of pancreatic
can-cer, 14 cases of calcifying chronic pancreatitis, 13 cas-es of non-calcifying chronic pancreatitis, 7 cases of pancreatic pseudocyst, 38 cases of cholecystolithiasis, 7 cases of choledocholithiasis, 4 cases of cancer of the gallbladder, 5 cases of cancer of the common bile duct, 7 cases of hepatoma, and 37 cases of normal controls. Diagnostic efficiency was categorized into three: definite, suspect, and non-diagnostic. "Definite" means that the findings obtained are diagnostic in terms of 1) presence of lesions; 2) location of the lesions; 3) size of the lesions; 4) number of the le-sions; 5) malignancy of the lesions.
"Suspect" means that the findings obtained are diag-nostic in terms of only some of the above items.
Diagnostic accuracy and efficiency of each procedure were evaluated according to lesions.
Results and comments: 1) ERCP was definite in all cases of ampullary cancer; CT was suspect in 2 cases and non-diagnostic in 2; US was non-diagnostic in all. ERCP is the best procedure for the diagnosis of ampullary cancer. 2) In pancreatic cancer, ERCP was definite in 62% and suspect in 33%; CT was definite in 86% and suspect in 7%; US was definite in 57% and suspect in 36%; RI was definite in none and suspect in 88%. ERCP was interpreted as sus-pect in 33% due to the lack of convincing evidence of malignancy and inability to disclose the extent of a space-taking lesion. One case showed extrapan-creatic growth which was disclosed only by CT and US. US and RI were interpreted as suspect mostly due to the lack of convincing evidence of malignancy of a lesion. 3) In pancreatolithiasis, ERCP was def-inite in 86% and suspect in 7%; US and CT were definite in all; RI was suspect in all.
ERCP, when satisfactorily opacified, gives the best information in terms of an indication for operation as well as diagnosis. 4) In non-calcifying chronic pancreatitis, ERCP was definite in 92% and suspect in 8%; CT was definite in 8% and non-diagnostic in 92%; US was non-diagnostic in all. ERCP in the