Subjective thermal sensation effect of cool feeling compression stocking for patients with lower limb lymphedema: a preliminary pre-post study
全文
(2) Conclusion: This preliminary study indicated that compression stockings made from Cupro coated with xylitol made patients with lower limb lymphedema feel cooler immediately after putting the stockings on without any skin problems. Key Words:lower extremity lymphedema, compression therapy, clothing comfort, thermal comfort, hot environment no present report was found to resolve this clinical. Introduction. problem for patients with lymphedema.. Compression therapy is essential in lymphedema 1). To overcome this problem, we developed a new. management and has been known as an effective. compression stocking that provides a cool feeling,. treatment for improving edema condition2); however,. made of cuprammonium rayon(Cupro, Asahi Kasei. most of the patients have concerns on wearing. Fibers Corp., Tokyo)coated with xylitol. Cupro is a. 3). compression stockings due to heat during summer .. regenerated cellulose fiber made from cotton waste.. Then, we developed the contact cooling stocking for. Xylitol(C5H12O5)is a sugar alcohol extracted from. patients with lymphedema to overcome this clinical. Betula. Since both Cupro and xylitol may reduce heat. issue. This is a preliminary study for the evaluation of. from objects with which they come into contact with,. this product, which has a new concept for application. a combination of two materials is expected to improve. to hot environment.. contact thermal sensation of patients. This was the. Lymphedema is defined as an accumulation of. first time that these materials had been used for. protein-rich fluid in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. patients with lymphedema as a compression device.. 2). due to insufficient lymph circulation . To improve. Therefore, we conducted this preliminary study as a. lymph circulation, compression therapy with a. first step.. low-stretch elastic compression product, such as. The hypotheses of this study were as follows:(1). stockings and bandages, is required for lymphedema. the prototype of the cool feeling stocking would make. management 4)5). The International Society of. the patients feel cooler than conventional stockings. Lymphology(ISL)recommended that patients with. immediately after they put it on;(2)subjective. moderate severity should wear compression stocking. thermal sensation would show no difference between. 5)6). . Actually,. the cool feeling and conventional stocking when. a previous study reported the high acceptance. removing them; and(3)the patient would have no. rate(96.1%)of wearing compression stocking in. skin problems by wearing the cool feeling stocking.. at daytime throughout their lives. 7). lymphedema management .. Aim. To generate a constant and uniform compression level(20-60 mmHg), the stocking is generally made. This study aimed to evaluate subject thermal. 2)4)5). sensation, effect, and safety of cool feeling compression. of dense nylon fabric knitted urethane rubber. ,. which leads to patients’ discomfort due to stuffiness in. stocking for patients with lower limb lymphedema.. hot and humid conditions in midsummer. A previous. Methods. study reported that 76.5% in patients with lower limb lymphedema have experiences of some concerns. 1. Cool Feeling Compression Stocking. while wearing compression stockings during the. The prototype of cool feeling compression stocking. summer. Especially, warm feeling was reported in. was manufactured by Yoshida Tsukasa Corp. (Ishikawa,. 3). 70.4% of patients . Clothing and thermal comfort in. Japan). To be effective as lymphedema compression. the hot environment have been focused for sports. therapy and improve the contact thermal sensation of. 8)-11). . Despite problems that. patients, two conditions were required: compression. cannot be overlooked for lymphedema patients as well,. of ≥ 20 mmHg and a maximum rate of heat flow. athletes and workers. ― 11 ―.
(3) Journal of Japanese Society Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Management, Vol. 25, No. 1, 2021. (Qmax)of ≥ 0.2 W/cm2. Compression was preliminarily. On the first investigation day as pre-intervention,. ®. measured by Pico Press (Microlab, Padua, Italy). participants wore conventional stocking as usual and. in three healthy volunteers, and the results were 32. answered questionnaires. Cool feeling compression. mmHg, 30 mmHg, and 28 mmHg. The Q max of the. stocking was worn on the next day as post-intervention;. cooling stocking, an indicator for the heat absorption. then, the same questionnaire was answered. The. properties of fabric, was measured using Thermal. stocking and questionnaires were sent back to the. Property-Measuring Instrument(KES-F7 Thermo Lab. researcher by post. After the investigations, adverse. 2. II, Kato Tech, Kyoto, Japan)at 0.244 W/cm . As it was 2. events, such as skin problems(e.g., redness, feeling of. > 0.2 W/cm , this prototype had the required property. heat, itching, pain, and wound)and some symptoms of. of contact thermal sensation. According to these data,. exacerbation of edema-like heaviness and skin tension. this prototype, called cool feeling compression stocking,. by wearing stockings, were confirmed on the phone.. met the requirements for compression therapy with. 5. Contact thermal sensation. contact thermal sensation.. Contact thermal sensation as the outcome was. 2. Study Design and Setting. assessed according to the scale of the American. This preliminary pre-post study was conducted at a. Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning. lymphedema specialized clinic. Intervention comprised. Engineers(ASHRAE), in which thermal sensation. wearing of the prototype cool feeling compression. was scored as follows: -3, cold; -2, cool; -1, slightly cool;. stocking, and the control comprised the wearing of. 12) 0, neutral; +1, slightly warm; +2, warm; and +3, hot .. a conventional stocking which participants usually. The respondents were asked to select their scores. use. All participants wore both stockings at home. All. immediately after putting the stockings on and when. protocols were performed between April and June. removing them.. 2016, in consideration of safety of the skin, which is. 6. Individual and Lymphedema Characteristics. absence of redness, feeling of heat, itching, pain, and. Individual and lymphedema characteristics. wound. This period was in early summer, in which. were collected from the medical records including. the temperature and humidity were not as high as the. details such as age, sex, body mass index(BMI),. Japanese midsummer season.. lymphedema site, cause of lymphedema(primary. 3. Participants. or secondary), history of cancer therapy(radiation. We recruited patients diagnosed with lower. t h e r a p y a n d / o r c h e m o t h e r a p y ), d u r a t i o n o f. limb lymphedema with moderate stage, which was. lymphedema, history of cellulitis, lymphedema. 2). indicated in the ISL classification as stage II or late II.. management, and period of compression stocking use.. The inclusion criteria were as follows: understanding. 7. Analysis. of skin problems(e.g., redness, feeling of heat, itching,. We compared thermal sensation and wearing. pain, and wound)in lymphedema by standard. time between cool feeling compression stocking. education from medical professions, using compression. and conventional stocking. Descriptive data were. pantyhose, and visiting the lymphedema clinic. expressed as N(%)for categorical variables and. regularly for lymphedema treatment. The exclusion. median(interquartile range)for continuous variables.. criteria were as follows: active neoplastic disease and. Statistical analysis was performed using Wilcoxon. arteriosclerosis confirmed on physician’s diagnosis.. signed-rank test to compare thermal subjective. 4. Procedure. sensation of pre- and post-intervention. A P-value < 0.05. Participants were recruited and provided written. indicated statistical significance. We used Stata/SE. informed consent to a physician and nurse in a. 14.2 software for statistical analysis.. lymphedema clinic. A researcher then explained the. 8. Ethical Considerations. schedule and contents of the study on the phone to. This study was approved by the Medical Ethical. the participants. Subsequently, questionnaires and cool. Committee of Kanazawa University(#586). Written. feeling compression stockings were sent to them.. informed consent was obtained from all participants.. ― 12 ―.
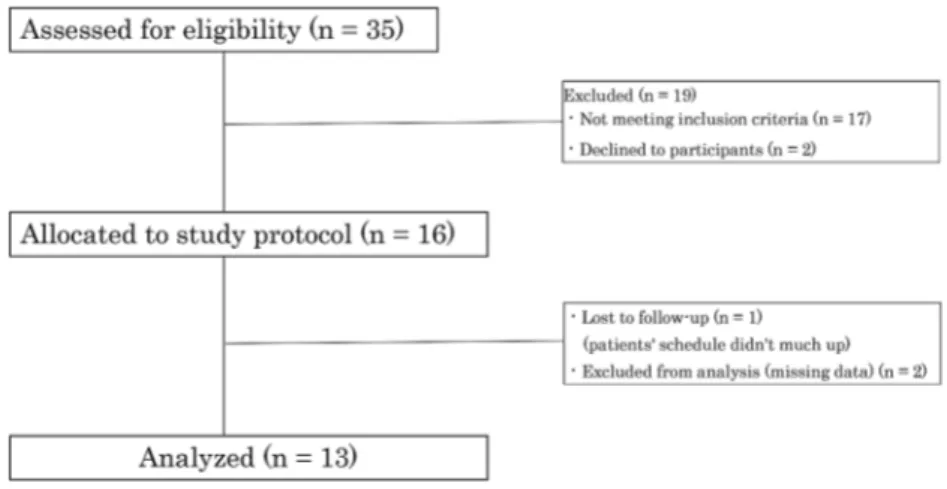
(4) Figure 1 Flowchart of patients in this study. Table 1 Individual characteristics (n=13) Age. (years). Body mass index. (kg/m2). 62 (60 - 71) 21.6 (20.4 - 23.5). Type of gynecologic cancer Cervical cancer. 11 (84.6). Ovarian cancer. 2 (15.4). Cancer treatment Radiation therapy. 4 (30.8). Chemotherapy. 7 (53.9). Data are expressed as numbers(%)for categorical variables and median(interquartile range)for continuous variables.. A researcher explained that participants could remove the prototype stocking if they felt any discomfort.. The median lymphedema duration was 8 years (IQR, 7-11 years). Of all patients, 46.2% were ISL II and 53.8% were ISL late II. They used compression. Results. pantyhose stocking for 7.5 years(5.5-9.5 years).. In this study, 35 patients were eligible, 16 were. Conventional stockings were standard commercial. allocated, and finally, 13 were analyzed(Fig. 1).. products made from nylon and polyurethane, and. Thirteen patients completed the protocol in this. 53.9% also used elastic bandages for treatment the. preliminary study, which included intervention and. night after, removing the compression stockings(Table. control days. No side effects, such as skin problems,. 2).. e.g., redness, feeling of heat, itching, pain, and wound,. 2. Contact Subject Thermal Sensation(Fig. 2). and some symptoms of exacerbation of edema, such. Contact thermal sensation was scored by seven-. as heaviness and skin tension, were reported. The. stage ASHRAE subjectively. Figure 2 showed that 11. patients were diagnosed with leg lymphedema with. patients felt that post-intervention was cooler than pre-. ISL stage II or late II.. intervention immediately after putting the stockings. 1. Characteristics of Participants. on. The median ASHRAE score decreased from +. All participants were female, and the median age. 1(IQR, 0-2)to -1(-2--1)(P = 0.002). However, six. was 62 years(IQR, 60-71 years)and BMI was 21.6. patients felt that the post-investigation was cooler than. 2. 2. kg/m (IQR, 20.4-23.5 kg/m ). Participants had all. the pre-investigation when removing the stocking, and. secondary leg lymphedema after surgery for cervical (n. ASHRAE score was 0(IQR, 0-2)to 0(-2--1) (P = 0.133).. = 11, 84.6 %)or ovarian cancer(n = 2, 15.4%) (Table 1).. ― 13 ―.
(5) Journal of Japanese Society Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Management, Vol. 25, No. 1, 2021. Table 2 Lymphedema characteristics (n=13) Characteristic Lymphedema site Both. 6 (46.2). Unilateral. 7 (53.8). Duration of lymphedema(years). 8 (7 - 11). International Society of Lymphology stage Stage II. 6 (46.2). Stage late II. 7 (53.8). History of cellulitis(yes). 4 (30.8). Lymphedema management(yes) Skin care. 13 (100.0). Manual lymphatic drainage. 13 (100.0). Elastic bandage. 7 (53.8). Exercise. 3 (23.1). Duration of wearing compression stocking(years). 7.5 (5.5 - 9.5). Data are expressed as numbers(%)for categorical variables and median(interquartile range)for continuous variables.. Figure 2 Effectiveness of thermal subjective sensation when patients put stockings on and remove them The line graph shows the change in ASHARE score for each patient. The median values before and after are indicated by black circles. There was a significant decrease before and after removing the stockings and no significant difference when removing them. The analysis was performed using Wilcoxon signed-rank test, and a P -value <0.05 indicated statistical significance.. stockings are expected to expand the options for. Discussion. selecting stockings in the summer for patients with. This preliminary study showed that compression. lower limb lymphedema with moderate severity.. stockings made from Cupro coated with xylitol were. Immediately after putting the cool feeling stockings. effective in improving subjective warmth and coldness. on, patients had a subjective thermal sensation. without skin problems. This concept is believed to. significantly cooler than that of the conventional. have been accepted, and cool feeling compression. stocking. This result supported our hypothesis as. ― 14 ―.
(6) to the potential of this material ‒ Cupro coated with. This study has several limitations. First, the setting. xylitol ‒ to have the effect of cool feeling when putting. of control stockings as similar products in all patients. them on. However, this effect did not last until they. was impossible because we aimed to compare this. remove them. Since the structure of the compression. prototype and actual compression stockings which. stocking was designed to make contact with the skin. patients used daily. Their stockings were selected. 10). , which is necessary for maintaining. for lymphedema management. The differences in. cool contact sensation, this was the limitation of the. components could possibly have affected this result. current material used for manufacturing the cool. even though their material and shape were common,. feeling compression stocking and improvement of this. which were pantyhose type and made from nylon and. property is expected.. polyethylene. We sought to minimize this effect by pre-. Although this effect was limited to a short period. post study design. Second, the intervention period was. during which patients wore the stocking, it is. only a day for cool feeling compression stocking for. extremely important for patients to feel cool when they. safety. For motivation, skin problems, or edema status,. put cool feeling compression stockings on to improve. long-term effect verification is required, because this. or maintain their motivation. Motivation is an essential. study cannot determine the effect under continuous. without airflow. 11). . Although self-. wearing of cool feeling compression stocking in the. management education is related to self-management. long term. Further research is expected after the. 13)14). .. improvement of the prototype. Finally, we investigated. Compression therapy is almost self-management in the. subjective thermal sensation via questionnaire, which. part of self-management behavior. behavior, it is ineffective without motivation 15). daily life of patients with lymphedema . The concept. is an indirect indicator of comfort or increasing. of a cool feeling compression stocking contributes to. motivation. Furthermore, individual characteristics. continuous compression therapy in patients with lower. and external environment, such as temperature,. limb lymphedema.. humidity, and activity level, might be related to. This study is the first trial to apply the cool feeling. thermal sensation. Additional investigation, which can. compression stocking for patients; therefore, we. evaluate clothing comfort and motivation with the. conducted it in the mild season, which was from. related variables, should be corrected. In the future,. April to June. The average temperature was 19.6℃. improvement of cool feeling stocking and further. -23℃, and the average humidity was 61.9%-74.5%. research are expected to verify the effectiveness of. in the investigation area, Tokushima Prefecture. this product.. in Japan(Japan Meteorological Agency records).. Conclusion. Therefore, the effect of the cool feeling stocking was evaluated under the condition that the participants. This preliminary study indicated that compression. did not feel constricted and overheated during. stockings made from Cupro coated with xylitol made. compression therapy. Even under such conditions,. patients with lower limb lymphedema feel subjective. most participants had a contact cooling sensation. thermal sensation immediately after putting them on. when they wore the cool feeling stocking, suggesting. without any skin problem.. that the cool feeling stocking improves subject thermal. Acknowledgment. sensation of patients during compression therapy. Furthermore, there were no side effects, such as skin. This study was funded by a grant from the. problems and deterioration of lymphedema, in wearing. Japanese Society of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence. compression stockings in this study. It is expected. Management.. that further studies under severe conditions(e.g., the. References. average temperature and humidity are 37℃ and 70%, respectively, in the midsummer in Japan)will show. 1)Moffatt C, Doherty D, Morgan P, et al. Treatment decisions. Best practice for the management. physiological and psychological effects.. ― 15 ―.
(7) Journal of Japanese Society Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Management, Vol. 25, No. 1, 2021. of lymphedema International Consensus, 15-21,. the ability of PMV model in predicting thermal. Medical Education Partnership Ltd, London, 2006.. sensation in naturally ventilated buildings in UK.. 2) International Society of Lymphology Executive. Proceedings of 7th Windsor Conference: The. Committee. The diagnosis and treatment of. changing context of comfort in an unpredictable. peripheral lymphedema: 2016 consensus document. world. Cumberland Lodge, Windsor, UK, Network. of the International Society of Lymphology.. for Comfort and Energy Use in Buildings, UK,. Lymphology 49: 170-184, 2016.. 2012.. 3) Dai M, Minematsu T, Nakagami G, et al.. 13) Choi S, Song M, Chang SJ, et al. Strategies for. Awareness and attitudes of lymphoedema patients. enhancing information, motivation, and skills for. toward compression stockings in the summer: a. self-management behavior changes: A qualitative. cross-sectional questionnaire survey. Journal of. study of diabetes care for older adults in Korea.. Lymphoedema 15: 49-53, 2020.. Patient Prefer Adherence 8: 219-226, 2014.. 4) Lasinski BB, Thrift KMK, Squire DC, et al. A. 14) Jung MJ, Jeong Y. Motivation and self-. Systematic Review of the Evidence for Complete. management behavior of the individuals with. Decongestive Therapy in the Treatment of. chronic low back pain. Orthop Nurs 35, 330-337,. Lymphedema From 2004 to 2011. PMR 4: 580-601,. 2016.. 2012.. 15) Douglass J, Graves P, Gordon S. Self-Care for. 5) Zasadzka E, Trzmiel T, Kleczewska M, et al.. Management of Secondary Lymphedema: A. Comparison of the effectiveness of complex. Systematic Review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10: 1-20,. decongestive therapy and compression bandaging. 2016.. as a method of treatment of lymphedema in the elderly. Clin Interv Aging 13: 929-934, 2018. 6) MacGregor L, Mortimer P, Partsch H. Role of hosiery in lower limb lymphoedema. Compression Hosiery in Lymphedema, 10-21, Medical Education Partnership Ltd, London, 2006. 7) Dai M, Nakagami G, Sugama J, et al. The prevalence and functional impact of chronic edema and lymphedema in Japan: LIMPRINT study. Lymphat Research Biol 17: 195-201, 2019. 8) Zwolinska M. Thermal subjective sensations of motorcyclists. Accid Anal Prev 50: 1211-1220, 2013. 9) Rijal HB, Humphreys M, Nicol F. Adaptive thermal comfort in Japanese houses during the summer season: Behavioral Adaptation and the Effect of Humidity. Buildings 5: 1037-1054, 2015. 10) Lim J, Choi H, Roh EK, et al. Assessment of airflow and microclimate for the running wear jacket with slits using CFD simulation. Fashion and Textiles 2: 1-13, 2015. 11) Tsujimura H, Taoda K, Katahara T. A Field Study on the Physiological Workload of Garbage Collectors in the Japanese Summer. Ind Health 50: 556-566, 2012. 12) Beizaee A, Vadodaria K, Loveday D. Assessing. ― 16 ―.
(8) 下肢リンパ浮腫患者に対する接触冷感弾性ストッキングの 主観的温冷感効果:前後比較プレリミナリースタディ 臺 美佐子 1) 峰松 健夫 1)2) 小川 佳宏 3) 高西 裕子 3) 須釜 淳子 4) 真田 弘美 2)5). 東京大学大学院医学系研究科社会連携講座スキンケアサイエンス 1) 東京大学大学院医学系研究科グローバルナーシングリサーチセンター 2) 医療法人リムズ徳島クリニック 3) 金沢大学新学術創成研究機構先端的ヘルスケアサイエンスユニット 4) 東京大学大学院医学系研究科老年看護学/創傷看護学 5). 要 旨 目的:弾性ストッキングは主要なリンパ浮腫管理方法である。しかし、高温多湿な夏季には、装着継続のモチベーショ ン維持に困難感を生じさせる。そこでわれわれは、この問題を解決すべくキシリトール加工したキュプラ繊維を用い た接触冷感弾性ストッキングを開発した。本研究の目的は、プロトタイプによる下肢リンパ浮腫患者への接触温冷感 の効果および安全性を検証することである。 方法:本研究は前後比較試験で、下肢リンパ浮腫患者をリクルートし、対象者は介入前(従来型)と介入後(接触 冷感弾性ストッキング)を各 1 日自宅で装着して過ごした。アウトカムは、主観的な接触温冷感として ASHARE スコ アである 7 点法スケール質問紙に、装着直後と脱着時に回答した。その後、電話にて皮膚トラブルと浮腫状態につい てインタビューし回答を得た。 結果:分析対象となった者は下肢リンパ浮腫患者の女性 13 名で、接触冷感弾性ストッキングによる有害事象が発生 した者はいなかった。接触温冷感の評価では、11 名が装着直後では介入前より介入後のほうが冷たいと感じ、中央値 +1(やや温かい)から -1(やや冷たい)へ有意に減少した(P= 0.002) 。一方、脱着時には両グループに前後で有意な 差は見られなかった(P=0.133) 。また、皮膚トラブルや浮腫増悪の生じた者はいなかった。 結論:キシリトール加工したキュプラ繊維を用いた接触冷感弾性ストッキングは、下肢リンパ浮腫患者に対して皮 膚トラブルや浮腫悪化なく接触冷感を感じさせる可能性があると示唆された。 キーワード:下肢リンパ浮腫、圧迫療法、衣服快適性、温熱感快適性、暑熱環境. ― 17 ―.
(9)
図

関連したドキュメント
Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography, oral cancer, oropharyngeal cancer, sentinel lymph node, Sonazoid TM , Superb Microvascular
According to multi- variate analysis, expression of CD42b, a platelet marker, in our biopsy specimens from advanced gastric cancer with preoperative DCS therapy was
compared to standard laparoscopic cystectomy in women with a dermoid
Based on this experience, we conclude that acute correction with focal dome osteotomy is suitable for segments without limb length discrepancy, while for segments with limb length
patient with apraxia of speech -A preliminary case report-, Annual Bulletin, RILP, Univ.. J.: Apraxia of speech in patients with Broca's aphasia ; A
In this work, we have theoretically studied the effect of thermal radiation and thermal diffusion on unsteady MHD free convection heat and mass transfer flow of an
This problem becomes more interesting in the case of a fractional differential equation where it closely resembles a boundary value problem, in the sense that the initial value
The group acts on this space by right translation of functions; the implied representation is smooth... We want to compute the cocy-