Case
Report
Allergic
contact
dermatitis
caused
by
titanium
screws
and
dental
implants
Maki
Hosoki
DDS,
PhD
a,
Keisuke
Nishigawa
DDS,
PhD
a,
Youji
Miyamoto
DDS,
PhD
b,
Go
Ohe
DDS,
PhD
b,
Yoshizo
Matsuka
DDS,
PhD
a,*
aDepartmentofStomatognathicFunctionandOcclusalReconstruction,InstituteofBiomedicalSciences,Tokushima
UniversityGraduateSchool,Tokushima,Japan
bDepartmentofOralSurgery,InstituteofHealthBiosciences,TokushimaUniversityGraduateSchool,Tokushima,
Japan
1.
Introduction
AnincreaseintheprevalenceofallergicdiseasesinJapanhas
beenreportedrecently[1–3].Thatis,3–4%ofthepopulation
hasthesymptomsofasthma,30%sufferfromallergicrhinitis,
and20%juniorhighschoolstudentshaveatopicdermatitis.In
general,allergicdiseaseisbenign,butthequalityoflifecan
decrease remarkably.Itisnotanoverstatementtosaythat
preventionofallergicdiseaseisapublic-healthissue.
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received12August2015
Receivedinrevisedform
28November2015
Accepted10December2015
Availableonline8January2016
Keywords: Titanium Dentalimplants Metalallergy Patchtesting Orthopedicsurgery
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
Patients: Titaniumhasbeenconsideredtobeanon-allergenicmaterial.However,several
studieshavereportedcasesofmetalallergycausedbytitanium-containingmaterials.We
describe a 69-year-old male for whom significant pathologic findings around dental
implantshadneverbeenobserved.Heexhibitedallergicsymptoms(eczema)after
ortho-pedicsurgery.Thetitaniumscrewsusedintheorthopedicsurgerythatheunderwentwere
removed 1yearlater, buttheeczemaremained.Afterremoval ofdentalimplants,the
eczemadisappearedcompletely.
Discussion: Titaniumisusednotonlyformedicalapplicationssuchasplasticsurgeryand/or
dentalimplants,butalsoforpaints,whitepigments,photocatalysts,andvarioustypesof
everydaygoods.Mostoftheusageoftitaniumisintheformoftitaniumdioxide.Thisrapid
expansionoftitanium-containingproductshasincreasedpercutaneousandpermucosal
exposureoftitaniumtothepopulation.
Conclusions: Ingeneral,allergicriskoftitaniummaterialissmallerthanthatofothermetal
materials.However,wesuggestthatpre-implantpatientsshouldbeaskedaboutahistoryof
hypersensitivityreactionstometals,andpatchtestingshouldberecommendedtopatients
whohaveexperiencedsuchreactions.
#2016JapanProsthodonticSociety.PublishedbyElsevierLtd.Thisisanopenaccessarticle
undertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
*Corresponding author at:Department of StomatognathicFunctionandOcclusal Reconstruction,Institute ofBiomedicalSciences,
TokushimaUniversityGraduateSchool,3-18-15Kuramoto-cho,Tokushima770-8504,Japan.Tel.:+81886337350;fax:+81886337391.
E-mailaddress:matsuka@tokushima-u.ac.jp(Y.Matsuka).
Available
online
at
www.sciencedirect.com
ScienceDirect
journalhomepage:www.elsevier.com/locate/jpor
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpor.2015.12.004
1883-1958/#2016JapanProsthodonticSociety.PublishedbyElsevierLtd.ThisisanopenaccessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense
Varioustypesofmetallicandorganicmaterialshavebeen
usedfordentalprostheses.Someofthesematerialshavebeen
reportedtohavepro-allergenicproperties.Ourresearchteam
has been engaged in the treatment of patients allergic to
dentalmaterials.Wehavereportedontheclinicalsurveillance
ofdental allergic hypersensitivity at Tokushima University
DentalHospital(Tokushima,Japan)andevaluatedtheextent
andseverityofadversereactionstodentalmaterialsamong
thesepatients[4].Allergicsymptomsfromthesematerialsare
notrestrictedtothemouth;theyarealsofoundonthehands,
legs and all the skin on the body [4–7]. Mercury, nickel,
chromium,palladiumandcobaltareclassicallergens[8–12].
Titaniumisknowntopossessgoodbiocompatibility[13,14],
soseveralproductscontainingtitanium havebeen usedin
plasticsurgeryanddentalimplants.However,recentstudies
havereportedcasesofallergicsymptomscausedby
titanium-based materials. The amount of titanium in products has
increased with advances in smelting technology, thereby
providingmoreopportunitiesforhumanstobesensitizedto
thismetal.Thomasetal.reportedapatientwhodeveloped
eczemaupontitanium-basedosteosynthesis[15].Egusaetal.
reportedfacialeczemainassociationwithatitaniumdental
implant [16]. In their review, Siddiqi et al. suggested that
titaniumcaninducehypersensitivityinsusceptiblepatients,
andcouldplayacriticalpartinimplantfailure[17].Whether
dental materials comprising titanium are associated with
allergicsymptomsiscontroversial.
Here,wedescribeapatientwhohaddentalimplantsand
exhibited allergic symptoms after undergoing orthopedic
surgery. Thedental implant was functioning satisfactorily,
butallergicsymptoms(eczema)wereshown.Moreover,patch
testsrevealedpositivereactionstomanyreagents(including
titanium).
2.
Outline
of
the
case
A 69-year-old male who had never experienced allergic
symptoms apart from rhinitis and a reaction to leather
productsisdescribed.Hehadnohistoryof
contact-hypersen-sitivity reactions to metals. In 2008, he had two dental
implants using Fixture MicroThreadTM (Astra Tech Dental,
Mo¨lndal,Sweden)andhaddisplayedgoodprogress.
In2010,hehadafractureofalowerlimbandunderwent
open reduction with titanium screws. Six months later,
nummulareczemadevelopedovertheskinsurface.Hewas
prescribedhistamine H1 antagonists,sodiumcromoglycate,
ascorbicacid,andcalciumpantothenate,buttheeczemadid
notimprove.Apatchtestat adermatologyclinicinOsaka
UniversityHospital(Osaka,Japan)revealedanallergy-positive
reactiontocobalt,tin,palladium,indium,andiridium,butalso
demonstratedafalse-positivereactiontocopperand
titani-um.Titaniumscrewswereplannedtoberemoved1-yearlater,
so medication and follow-up of allergic symptoms were
appliedatthattime.
In 2011, the titanium screws were removed from the
patient’slimbbytheplasticsurgeon.Aftertheneczemawas
recovered,butwasstillremained50%levelofthecondition
beforeremovingscrew.Sothedermatologistsuspecteddental
metal allergy and the patient for the previous dentist to
remove all metal prosthesis. After removing all metal
prosthesis exceptfordental implant andits abutment,the
patient’seczemawasrecovered30%levelbeforeremovingit,
butstillnotexhibitedcompleterecovery.
In2013,thepatientwasreferredtoourdentalmetalallergy
clinic. Fig. 1 shows a panoramic dental radiograph of the
patientathisfirstvisit.Thetwodentalimplantswereinthe
right mandibular molar area. No metallic restoration was
foundinthemouthapartfromtheabutmentsofthedental
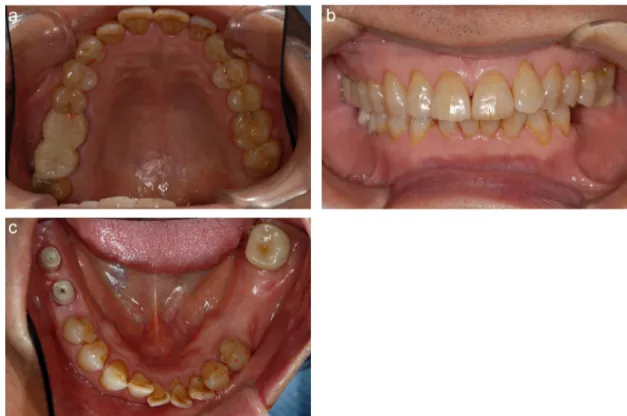
implants.Significantpathologicfindingsaroundtheimplants
werenotobserved(Fig.2).Theseimplantsdidnotexhibitany
signofperi-implantitisand/ormechanicalproblemssuchas
loose screwandsuperstructurefracture.Radiograph
exami-nationdidnotfindanyimagesofboneresorptionaroundthe
implantfixture.Theimplantsandabutmentsweremadewith
pure titanium (ASTM F-67, grade 4 (N20.05, C20.08,
H20.013,Fe20.5)).Atemporaryacryliccrownwasattached
ontothemaxillaryandmandibularrightmolars.Atemporary
acryliccrownwasplacedontheabutments.
We altered temporary cement from poly carboxylate
cement that contains allergy positivezinc componentsfor
zincfreeglassionomercement.After4-monthfollow-upwith
anti-allergic medicationsby the dermatologist, the eczema
remained. Patch testing with 17 patch-test metal reagents
(Patch Test Reagents; Torii Pharmaceutical Corporation,
Tokyo,Japan)and11custom-madereagentswasundertaken
atourclinic.Thesereagentswereattachedtotheskinonthe
back with an adhesive plaster (Patch Tester Torii; Torii
PharmaceuticalCorporation).Reactionstothetestwereread
accordingtocriteriasetbytheInternationalContact
Derma-titisResearchGroupatD2,D3andD7afterapplication.
Atthattime,hedemonstratedanallergy-positivereaction
againstcobalt,tin,palladium,indiumandiridium(thesameas
inthe previouspatchtest).Moreover, titanium,gold,
plati-num,zincandironalsoelicitedanallergy-positivereaction
(Table1)(Fig.3).
From these results in April 2014, the abutments were
removed.Onemonthafterremovingimplantabutment,the
patient didnotexhibited remarkableprogress. Thepatient
keptmedicationfromthedermatologistduringthisperiod.In
May2014,the dentalimplantfixtureswereremovedat the
Department of Oral Surgery within Tokushima University
Hospital.Animplant-retrievaltool(NobelBiocareUSA,Yorba
Fig.1–Panoramicdentalradiographofthepatientathis
initialvisit.
journalofprosthodonticresearch 60(2016) 213–219
214
Linda, CA, USA) that enabled a less invasive effect in
peripheral bone during removal of the osseointegrated
implantwasused(Figs.4and5).Implant-retrievaltoolwas
connectedinsidethreadgroovesoftheimplantfixture.Then
oral surgeon applied implant reverse torque with hand
wrench. This instrument did not give implant fixture any
destructiveaffectduringremoving.Afterremovingintraoral
metallicrestorations,allergicsymptomssometimesdevelop
Fig.2–(a)–(c)Intraoralphotographsattheinitialvisit.
Fig.3–Resultsofpatchtests.(a)Upperbackbeforepatchtesting.(b)Resultofpatchtestingat48h.(c)Resultofpatchtesting
moreseverebeforeremoving.Thiscounterallergicreaction
seemstobecausedbycutting dustofmetallic restoration.
Since chance of additional titanium contamination was
minimumduringthisremovingprocedure,allergicsymptoms
ofthispatientdidnotexhibitsuchimmediatereaction.The
extentofthe eczema reducedrapidly.One month later,he
stopped taking medication and the eczema disappeared
completely. Figs.6and7showahypogastric skincondition
before and 2 months after removal of the dental implant
fixtures. After 2-months follow-up, the patients underwent
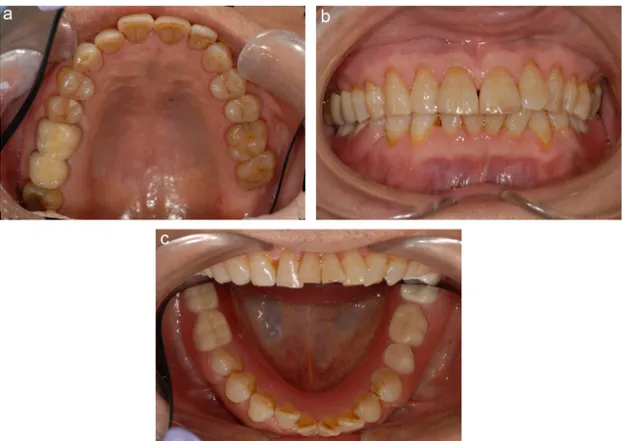
finalprosthetictreatmentwithzirconiafullveneercrownand
metalfreeremovabledenture.Fig.8showsintraoral
photo-graphsofthepatientafterprosthetictreatment.Fig.9showsthe
Table1–Patchtesting.
Metal-based allergen % Vehicle D2 D3 D7 1 CuSO4 1 aq ?+ + 2 PdCl2 1 aq ?+ + 3 K2Cr2O7 0.5 aq + + 4 NiSO4 5 aq 5a NiSO 4 2 aq 6 CoCl2 2 aq + + ++ 7a HgCl 2 0.1 aq + + 8 HgCl2 0.05 aq 9 SnCl4 1 aq + + + 10a CdSO 4 1 aq ?+ ?+ ?+ 11 HAuCl4 0.2 aq + + 12 H2PtCl6 0.5 aq 13 FeCl3 2 aq ?+ 14 InCl3 1 aq ?+ 15 IrCl4 1 aq + + 16a MoCl 5 1 aq ?+ + + 17 AgBr 2 pet 18a SbCl 3 1 pet 19 ZnCl2 2 pet ?+ + + 20 MnCl2 2 pet 21a BaCl 2 0.5 aq 22a BaCl 2 0.1 aq 23 CrSO4 2 aq 24 Al2O3 2 aq 25a TiO 2 30 pet 26a TiO 2 10 pet 27a TiCl 4 0.1 aq ?+ + 28a TiCl 4 0.05 aq ?+ +
aq,aqueous;pet,petroleum.
Patch-test reagents (Torii Pharmaceutical Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
a Custom-madereagents.
Fig.4–Animplant-retrievaltoolwiththeimplantbodyis
shown.
Fig.6–Symptomaticprogress.Beforeremovalofimplants.
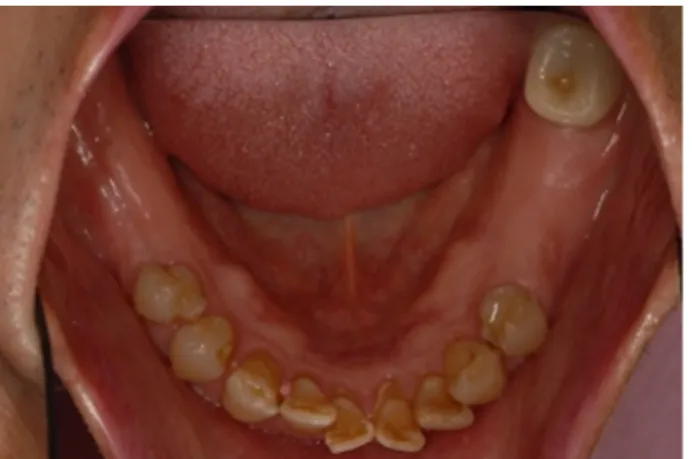
Fig.5–Intraoralphotograph2monthsafterremovalof
implants.
Fig.7–Symptomaticprogress.Twomonthsafterremoval
ofimplants(nomedication).
journalofprosthodonticresearch 60(2016) 213–219
216
hypogastricskincondition1yearafterremovaloftheimplants.
Severerecurrenceofeczemahasnotbeenobserved.
3.
Discussion
Wereportapatientwithallergiccontactdermatitiswhohad
dentalimplantprosthesesandwhoexhibitedallergic
symp-tomsafterorthopedicsurgery.Dentalimplantprosthesesand
screwfixationdidnotresultinspecificproblemsinalocalarea
ofthebody.Allergicsymptomsappearedonthegeneralskin
surface,andremovaloftitaniumscrewsdidnotreducethe
extent of skin eruptions. He clearly exhibited an
allergy-positivereactionforatitaniumreagent,andthesesymptoms
disappearedafterremovalofdentalimplantfixtures.
Our patient may have become sensitized to titanium
becauseofthetitaniumscrewsusedinorthopedicsurgery,
and presented symptoms simultaneously.Alternatively, he
might have presented allergic symptoms for the dental
implantsthathehadreceivedpreviously.Anotheroptionis
thathebecamesensitizedtotitaniumupondental
implanta-tionandsubsequentlydevelopedallergicsymptomsbecause
ofthetitaniumscrewsusedinorthopedicsurgery.
Hissymptomsremainedwhilehehaddentalimplantsand
aftertheremovaloftitaniumscrews.Thispatientdeveloped
eczema1yearafterorthopedicsurgery,sotheprimarycauseof
allergicsymptomsseemedtobetitaniumscrewsinthelower
limb. Nevertheless, the titanium component in the dental
implantwasthemostsuspiciouscauseofallergicsymptoms.
Some medicalstudies and dentalstudies have reported
casesoftitaniumallergy,and ourresearchteam, indental
metal allergy clinics, has documented suspicious cases of
titaniumallergy.Studieshaveshownthatmostinstancesof
titaniumallergyappearascontactdermatitisaroundtitanium
products[15,16,18].However,ourpatientdeveloped
dermati-tissymptomsonthegeneralskinsurface.
Osseointegrateddentalimplantsworkwell,butremovalof
such implants is notconsidered easy or free ofrisk. If an
osseointegratedimplantmustberemoved,thenan
implant-retrievaltoolisveryusefulbecauseitenablesalessinvasive
effectinperipheralbone.
Fig.8–(a)–(c)Intraoralphotographsofthepatientafterprosthetictreatment.
Fig.9–Symptomaticprogress.Oneyearafterremovalof
In the 1980s, dental implants became one of the major
choicesforthetreatmentofmissingteeth.Titaniumwasused
asamaterialfordentalimplantsataveryearlystageofthe
developmentofdentalimplants[19,20].Thehigh
biocompati-bilityofthismetalsuggestedthattitaniumwasanallergy-free
material,andseveralreportssupportedthesafetyoftitanium
[21–24].Today,titaniumisusedformedicalapplicationssuchas
plastic surgery,but also for paints, white pigments,
photo-catalysts,andvarioustypesofeverydaygoods[25].Mostofthe
usageoftitaniumisastitaniumdioxide.Thisrapidexpansionof
titanium-containingproductshasincreasedthepercutaneous
andpermucosalexposureoftitaniumtothepopulation.
However,thepatch-testreagentfortitaniumhasnotbeen
standardized worldwide.Nakajima examined theformand
densityofpatch-testreagentsfortitanium[26].Hereported
that reagents composed of pure titanium powder and the
petroleum jelly Vaseline (Unilever, Rotterdam, the
Netherlands)wasnotpreferablebecauseitwasastimulant
inthisform.Hesuggestedthattitaniumtetrachloride(0.1%)is
preferable as a patch-test reagent for titanium, and we
followedhisadvice.
Prevalence ofallergy-positive reactionsagainst titanium
reagentsisfarlowerthanthatfor‘‘risky’’materialssuchas
chromium, mercury, palladium and nickel. Nopatient has
exhibited an allergy-positive reaction only for a titanium
reagent. Hence, one could conclude that titanium is a
relativelysafematerialthatcausesallergicsymptomsrarely.
Thedetailedmechanismofactionofallergyand
hypersensi-tivitywithmetalmaterialsisnotknown,butwespeculatethat
thetotalamountofexposuretospecificmetallicionsisan
important parameter. Theextent ofexposure to
titanium-basedmaterialsineverydaylifeandmedicalapplicationsis
increasing,sothenumberofthetitanium-allergicpatientswill
probablyincreaseinthenearfuture.
4.
Conclusions
Wereportapatientwithallergiccontactdermatitiswhohad
dentalimplantprosthesesandwhoexhibitedallergic
symp-tomsafterorthopedicsurgery.Theallergicriskfortitaniumwas
lowerthanthatforothermetalmaterials.However,wesuggest
thatpre-implantpatientsshouldbeaskedaboutahistoryof
hypersensitivityreactionstometals,andpatchtestingshould
be recommended to patients who have experienced such
reactions.
Ethical
approval
This experimental protocol was approved by the Ethics
CommitteeofTokushima ClinicalTrialCenter for
Develop-mentalTherapeutics(number1036).
Source
of
funding
Thisresearch wassupportedbyaGrant-In-Aid((C)number
25463003)forScientificResearchfromtheMinistryof
Educa-tion,ScienceandCultureofJapan.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarethattheyhavenoconflictsofinterest.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Professor Emeritus
EiichiBando.Moreover,manythanksgotoMr.OsamuIshida
(dentaltechnicianinTokushimaUniversityHospital)forhis
assistanceincreatingprostheticappliances.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
[1] KawadaT.Riskfactorsandprevalenceofasthmaoratopic dermatitisinyoungchildrenbyaquestionnairesurvey.J NipponMedSch2004;71:167–71.
[2] MutoT,HsiehSD,SakuraiY,YoshinagaH,SutoH, OkumuraK,etal.Prevalenceofatopicdermatitisin Japaneseadults.BrJDermatol2003;148:117–21.
[3] OzasaK,HamaT,DejimaK,WatanabeY,HyoS,TeradaT, etal.A13-yearstudyofJapanesecedarpollinosisin Japaneseschoolchildren.AllergolInt2008;57:175–80.
[4] HosokiM,BandoE,AsaokaK,TakeuchiH,NishigawaK. Assessmentofallergichypersensitivitytodentalmaterials. BiomedMaterEng2009;19:53–61.
[5] GawkrodgerDJ.Investigationofreactionstodental materials.BrJDermatol2005;153:479–85.
[6] HosokiM,NishigawaK.Dentalmetalallergy. In:RoYS, editor.ContactDermatitis.Croatia:InTech;2011.p.119–38.
[7] YanagiT,ShimizuT,AbeR,ShimizuH.Zincdental fillingsandpalmoplantarpustulosis.Lancet2005; 366:1050.
[8] BlumenthalF,JaffeK.AmalgamplombenalsUrsachevon Quecksilberdermatitis.DtschMedWochenScher 1929;55:1720.
[9] FleischmannP.ZurFragederGefa¨hrlichkeitKleinster Quecksilbermengen.DtschMedWochenScher1928;54:304.
[10] HublerJrWR,HublerSrWR.Dermatitisfromachromium dentalplate.ContactDermat1983;9:377–83.
[11] LundstromIM.Allergyandcorrosionofdentalmaterials inpatientswithorallichenplanus.IntJOralSurg 1984;13:16–24.
[12] MagnussonB,BergmanM,BergmanB,SoremarkR.Nickel allergyandnickel-containingdentalalloys.ScandJDent Res1982;90:163–7.
[13] GarauV,MasalaMG,CortisMC,PittauR.Contactstomatitis duetopalladiumindentalalloys:aclinicalreport.J ProsthetDent2005;93:318–20.
[14] Hensten-PettersenA.Castingalloys:side-effects.AdvDent Res1992;6:38–43.
[15] ThomasP,BandlWD,MaierS,SummerB,PrzybillaB. Hypersensitivitytotitaniumosteosynthesiswithimpaired fracturehealing,eczema,andT-cellhyperresponsiveness invitro:casereportandreviewoftheliterature.Contact Dermat2006;55:199–202.
[16] EgusaH,KoN,ShimazuT,YataniH.Suspected associationofanallergicreactionwithtitaniumdental implants:aclinicalreport.JProsthetDent2008;100: 344–7.
[17] SiddiqiA,PayneAG,ZafarS.Bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosisofthejaw:amedicalenigma?OralSurgOral MedOralPatholOralRadiolEndod2009;108:e1–8.
journalofprosthodonticresearch 60(2016) 213–219
218
[18] PetersMS,SchroeterAL,vanHaleHM,BroadbentJC. Pacemakercontactsensitivity.ContactDermat 1984;11:214–8.
[19] BranemarkPI,AdellR,AlbrektssonT,LekholmU,Lundkvist S,RocklerB.Osseointegratedtitaniumfixturesinthe treatmentofedentulousness.Biomaterials1983;4:25–8.
[20] BreineU,BranemarkPI.Reconstructionofalveolarjaw bone.Anexperimentalandclinicalstudyofimmediateand preformedautologousbonegraftsincombinationwith osseointegratedimplants.ScandJPlastReconstrSurg 1980;14:23–48.
[21] MosseriM,TamariI,PlichM,HasinY,BrizinesM, FrimermanA,etal.Short-andlong-termoutcomesofthe titanium-NOstentregistry.CardiovascRevascMed 2005;6:2–6.
[22] WatahaJC,HanksCT,SunZ.Effectofcelllineoninvitro metalioncytotoxicity.DentMater1994;10:156–61.
[23] YamamotoA,HonmaR,SumitaM.Cytotoxicityevaluation of43metalsaltsusingmurinefibroblastsandosteoblastic cells.JBiomedMaterRes1998;39:331–40.
[24] HoshiN,NegishiH,OkadaS,NonamiT,KimotoK. Responseofhumanfibroblaststoimplantsurfacecoated withtitaniumdioxidephotocatalyticfilms.JProsthodont Res2010;54:185–91.
[25] SomiS,ObaidY,BenjaminWG,ThomasL,MichaelN. Titanium:industrialbase,pricetrends,and
technologyinitiatives.SantaMonica:RandCorporation; 2009:7–34.p.73–82.
[26] NakajimaK.[Studyonpatchtestreagentfortitanium]. KokubyoGakkaiZasshi2007;74:92–8.