R QTL 解析
ュ
2017.11.17
岩田洋佳
本 ュ R 用い QTL 解析 行う方法 い 明
定 例 利用
定 多環境試験 例 解析 行う 記 ウン
遺伝子型 :
http://www.genenetwork.org/genotypes/SXM.geno
表現型 :
http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/ggpages/SxM/phenotypes.html
表現型 様々 ウン ここ 収量 yield ウン
利用
定 こ ッ 品種 Steptoe×Morex 交配 得 150 倍加半数
体 doubled haploid DH 系統 含 い 遺伝子型 7 染色体
全体 布 218 含 収量 16 環境 計測さ 単
収量 t/ha 含 い
定 利用 R ッ
定 QTL 解析 qtl ッ GS 予測 qtl ッ kernlab ッ 用い
い R ッ ン 簡単 ウン ン 可能 あ
定 入力 準備
ウン R 込 こ 形式
作成
定 遺伝子型入力 以 手順 作成
定 ウン 区 Excel 表計算ソ 開く
定 28 行目 ッ 情報 削除
ウ 定 削除 後 残 選択 表計算ソ 行 列
入 え 転置 貼付け
定 入力 初 3 行 < <染色体番号 <染色体
置 順 並 い 必要 あ そこ 2 行目 先頭行 写
定 Locus id 変更 Chr cM 除く 空白
定 系統 SM### 1 〜 150 数 変更
定 測 示 − NA 一括変換
定 作業 行 CSV 形式 ここ geno.csv 保
定 表現型入力 作成 R qtl ッ 各列 系統 各行 形質 環
境 対応 形式 入力 準備 必要 あ い 列 系統 id
示 列 含 い 必要 あ こ 系統 id 遺伝子型 そ 一致 必要
あ ッ 入力 数
定 以 R 用い こ 述 う 形式 入力 作成 こ
こ 実 行 前 作 業 表 現 型
こ こ yield.dat 含 い 変 更
く必要 あ 実行 yield.csv 付け 出力さ
こ 引 続 行う解析 置い 表現型入力
定 QTL 解析 実行
定 こ こ R qtlAnalysis.R 手 順 QTL 解 析 行 う 以
qtlAnalysis.R 内 容 順 明 行 く qtl ッ 込
# read phenotype data
data <- scan("yield.dat", what = character())
n.env <- as.numeric(data[3]) # get the number of environments n.line <- as.numeric(data[4]) # get the number of lines yield <- matrix(NA, n.line, n.env) # prepare a data matrix for(i in 1:n.env) { # repeat n.env times
start <- 4 + (n.line + 1) * (i - 1) + 2 # start of the i-th env data end <- start + n.line - 1 # end of the i-th env data yield[, i] <- as.numeric(data[start:end]) # should convert to numeric }
yield <- cbind(1:n.line, yield) # add a data id column
colnames(yield) <- c("id", paste("Env", 1:n.env, sep = "")) # add names to columns write.csv(yield, "yield.csv", quote = F, row.names = F) # output data to a csv file
require(qtl) # R package for QTL mapping
準備 入力 込
実 記 通 入力 正 く 込 こ い F2 集団
認識さ こ qtl ッ DH 集団 直接扱うこ いこ 起因
そこ 遺伝子型入力 B い H 直 こ 戻 交
雑 back-cross BC 集団 込 実際 作業 Excel 表計算
ソ 用い geno.csv 開 B H 一括置換 geno_bc.csv 保
BC 集団 保 さ 込 染色体 置 全く 遺伝
子 あ jittermap 関数 こ 遺伝子 間 小さ 隙間 く さ
種々 plot 関数 使 連鎖地図 測値 表現型 表示
R 図 PDF 直接出力 ン 実行 連鎖地図等
描 PDF 出力さ
# Read an input file
cross <- read.cross(format = "csvs", genfile = "geno.csv", phefile = "yield.csv")
# again, read the input file
cross <- read.cross(format = "csvs", genfile = "geno_bc.csv", phefile = "yield.csv")
# add a small distance between markers at the same position cross <- jittermap(cross)
plot.map(cross) # show the linkage map plot.missing(cross) # show missing data
plot.pheno(cross) # show a histogram of phenotype. With this command, just id is shown plot.pheno(cross, pheno.col = 2) # show phenotype data in the second column
# data from the 1st environment is shown
# output to a pdf file
pdf("cross_summary.pdf") # set the name of pdf file plot.map(cross)
plot.missing(cross) for(i in 2:nphe(cross)) {
plot.pheno(cross, pheno.col = i) }
dev.off() # should close the file at the end
QTL 解析 染色体 等間隔 置 pseudo marker
け 遺伝子型 確率 計算 く ここ 2 cM 間隔 pseudo marker 配置
単純 ン ッ ン simple interval mapping SIM 行う ここ
16 環境 計測さ 収量 う 16 番目 env.id = 16 解析 こ R
qtl ッ いく 方法 ン ッ ン 行うこ ここ
EM 基 く方法 em Haley and Knott 回帰 基 く方法 hk 測
遺伝子型 QTL 遺伝子型 補完 行う方法 imp 3 試 qtl ッ 含
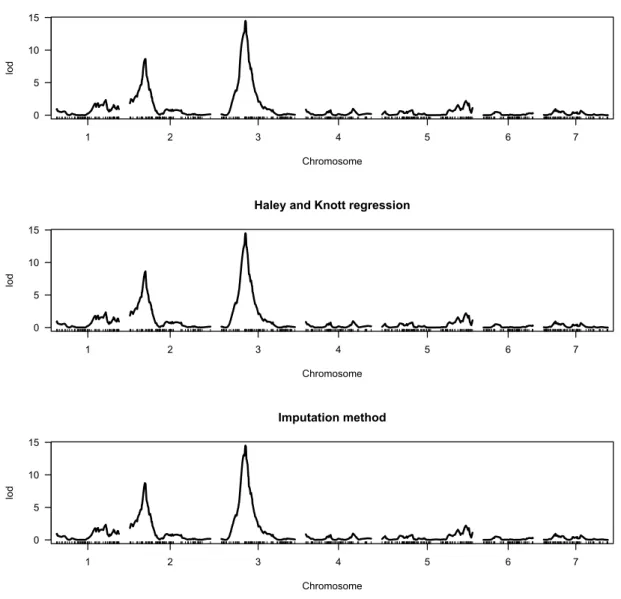
scanone いう関数 用い SIM 行う
3 方法 結果 ほ あ Fig. 1 こ こ 高密
配置さ い 間 在 QTL 計算方法 違う 計算
3 手法 違い 出 考え そこ こ 以降 計算 3 手法 中
計算速 速い hk 用い 解析 行う
# calculate the probabilities of genotypes at equal-spaced potisions on the map interval <- 2 # 2 cM intervals
cross <- calc.genoprob(cross, step = interval)
# preparation for the imputation method. it takes some time cross <- sim.geno(cross, step = interval, n.draws = 1000)
# determine environment env.id <- 16
# interval mapping with the EM-algorithm
out.em <- scanone(cross, pheno.col = env.id + 1, method = "em") plot(out.em)
# large QTL are detected on the 2nd and 3rd chromosome
# interval mapping with the Haley and Knott regression
out.hk <- scanone(cross, pheno.col = env.id + 1, method = "hk") plot(out.hk)
# interval mapping with the imputation method
out.imp <- scanone(cross, pheno.col = env.id + 1, method = "imp") plot(out.imp)
par(mfrow = c(3,1)) # plot 3 figures simultaneously to make comparison plot(out.em, main = "EM-algorithm")
plot(out.hk, main = "Haley and Knott regression") plot(out.imp, main = "Imputation method")
# difference between methods is quite small
par(mfrow = c(1,1)) # reset the number of figures plotted simultaneously to 1
Fig. 1. 3 異 手法 単純 ン ッ ン 結果 SIM 横軸 第 〜7染
色体 置 縦軸 LOD 値 大 いほ そ 場所 QTL あ 可能性 高い こ
手法間 違い ほ 見 い
LOD 値 大 さ 基 QTL 検出 い値 決 い値
決 前 QTL 表示 LOD 値 断さ QTL
表示さ い値 決 並べ え検 permutation test 行う 並べ
え検 表現型 無作 並び え QTL 解析 繰 返 行う 無作 並
び え こ 遺 伝 子 型 表 現 型 対 応 関 係 撹 乱 さ 本 来
い QTL 関 情報 消失 う 逆 見 並び え 行 検
出さ う LOD 値 偽物 QTL 偽陽性 起因 考え こ
0 5 10 15
EM-algorithm
Chromosome
lod
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0 5 10 15
Haley and Knott regression
Chromosome
lod
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0 5 10 15
Imputation method
Chromosome
lod
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
う 基 並び え 毎 QTL 解析 行い 染色体全域 中 LOD 大
値 記録 こ 複数回 例え 1,000 回 繰 返 こ QTL 無
い場合 LOD 値 布 経験的帰無 布 求 い値 例え こう 得
経験的帰無 布 5% 等 設 例え 5% 設 QTL 無い
誤 偽 QTL 検出 う確率 ノ 全体 5% う 設 さ こう
求 い値 LOD 値 う 意 求 こ 場合
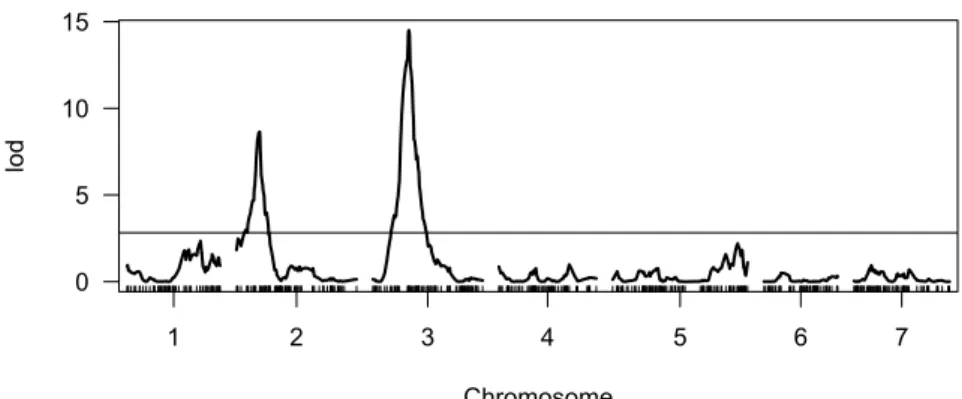
2 QTL 領域 検出さ Fig. 2
Fig. 2. 単純 ン ッ ン SIM 結果 線 並べ え検 求 LOD
値 LOD 値 線 あ 置 QTL 在 考え 領域
0 5 10 15
Chromosome
lod
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
# show the list of QTL detected by the hk regression summary(out.hk)
# perform a permutation test to get a threshold for LOD score to detemine QTL regions operm.hk <- scanone(cross, pheno.col = env.id + 1, method = "hk", n.perm = 1000)
# show the threshold obtained from the permtation test summary(operm.hk, alpha = 0.05)
# with this threshold, it is expected to detect non-QTL as QTL at the 5% probability
# show the QTL result figure with the threshold plot(out.em)
abline(h = summary(operm.hk, alpha = 0.05))
# close up one chromosome chr.id <- c(2,3)
plot(out.em, chr = chr.id)
abline(h = summary(operm.hk, alpha = 0.05))
# show the list of QTL detected with the threshold summary(out.hk, perms = operm.hk, alpha = 0.05)
検出さ QTL 効果 推 行 う makeqtl 関数 検出さ QTL 置
遺 伝 子 型 抜 出 そ 独 立 変 数 明 変 数 表 現 型 従 属 変 数 被 明
変数 回帰 述 い値 従う 2 QTL 検出さ Fig. 3 こ
QTL 効果 誤差 比べ そ 大 さ あ 大 く無く 回帰 析 け F 検 結果
意 い
Fig. 3. 単純 ン ッ ン SIM 検出さ 2 QTL
200
150
100
50
0
Chromosome
L o ca ti o n (cM)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Genetic map
Q1
Q2
# estimate QTL effects
temp <- summary(out.hk, perms = operm.hk, alpha = 0.05) # output the list of significant QTL qtl <- makeqtl(cross, chr = temp$chr, pos = temp$pos, what = "prob")
res <- fitqtl(cross, qtl = qtl, get.ests = T, method = "hk")
# show the result
plot(qtl) # plot the location(s) of QTL
summary(res) # summary of fitting significant QTL
# QTL effects are not so strong, and the result of F-test for QTL are not significant...
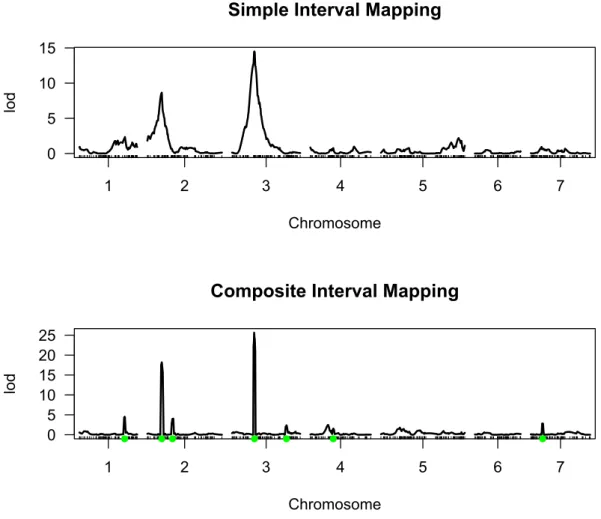
ン ッ ン ッ ン composite interval mapping CIM 行
う CIM 共変量 数 ここ 7 設 解析 窓 大 さ そ 窓 中
共変量 配置 い ここ 5 設 指 解析 行う必要 あ SIM
CIM 結果 図示 比較 前者 比べ後者 QTL 置 解像 高いこ
Fig. 4 こ CIM 共変量 用い こ 注目 い 場所以外 置 い
QTL 影響 込 こ そ 引 起こ 変動 押さえ込 こ 注
目 い 場所 あ QTL 明瞭 捉え う こ
SIM 様 並べ え検 行 決 い値 用 意 QTL 検出さ
い ここ 時間 節約 並び え 10 回 繰 返 い い 実際
100 回 繰 返 必要 あ
# perform the composite interval mapping with the Haley and Knott regression n.covar <- 7
window.size <- 5
outcim.hk <- cim(cross, pheno.col = env.id + 1, method = "hk", n.marcovar = n.covar, window = window.size)
# compare the results between SIM and CIM par(mfrow = c(2,1))
plot(out.hk, main = "Simple Interval Mapping") plot(outcim.hk, main = "Composite Interval Mapping") add.cim.covar(outcim.hk, col = "green")
par(mfrow = c(1,1))
# The resolution of CIM is much higher than SIM
# determine the threshold for QTL detection
opermcim.hk <- cim(cross, pheno.col = env.id + 1, method = "hk", n.marcovar = n.covar, window = window.size, n.perm = 10)
# With larger number of permutations, you can get a more accurate result.
# show the threshold obtained from the permutation test summary(opermcim.hk, alpha = 0.05)
# show the list of QTL detected with the threshold summary(outcim.hk, perms = opermcim.hk, alpha = 0.05)
# no QTL is significant...
Fig. 4. 単純 ン ッ ン SIM ン ッ ン ッ ン CIM
比較 CIM QTL 置 推 さ
後 単純 ン ッ ン 用い 複数 QTL 間 交互作用 検出
行 う ここ 2 QTL 間 scantwo 関数 索 並び え
検 結果 第 2 第 3 染色体 QTL 間 意 あ いう結果 得
2 QTL 時検出 場合 述 並べ え検 い値 決 こ
本 並べ え検 得 い値 基 く 第 2 び第 3 染
色体間 意 検出さ
0
5
10
15
Simple Interval Mapping
Chromosome
lo d
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0
5
10
15
20
25
Composite Interval Mapping
Chromosome
lo d
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
以 R 用い QTL 解析 方法 関 明 終わ あ ここ 2 番目 環境
い 解 析 行 異 環 境 計 測 さ 結 果 う 変 化
う env.id いう変数 2 以外 値 解析 繰 返 実行 解
析 設 例え CIM 際 共変量 数や窓 変化さ こ 得
結 果 変 化 示 少 変 更 解 析 行 い
い 発見 あ う
# scan two QTL interactions (epistasis)
out2.hk <- scantwo(cross, pheno.col = env.id + 1, method = "hk")
# show the result of the scanning plot(out2.hk)
## perform a permutation test to get a threshold for LOD score to determine epistasis operm2.hk <- scantwo(cross, method="hk", n.perm=100)
# show the threshold obtained from the permtation test summary(operm2.hk, alpha = 0.05)
# show the list of epistasis detected with the threshold summary(out2.hk, perms = operm2.hk, alpha = 0.05)
# one epistasis between the 2nd and 3rd chromosomes is significant