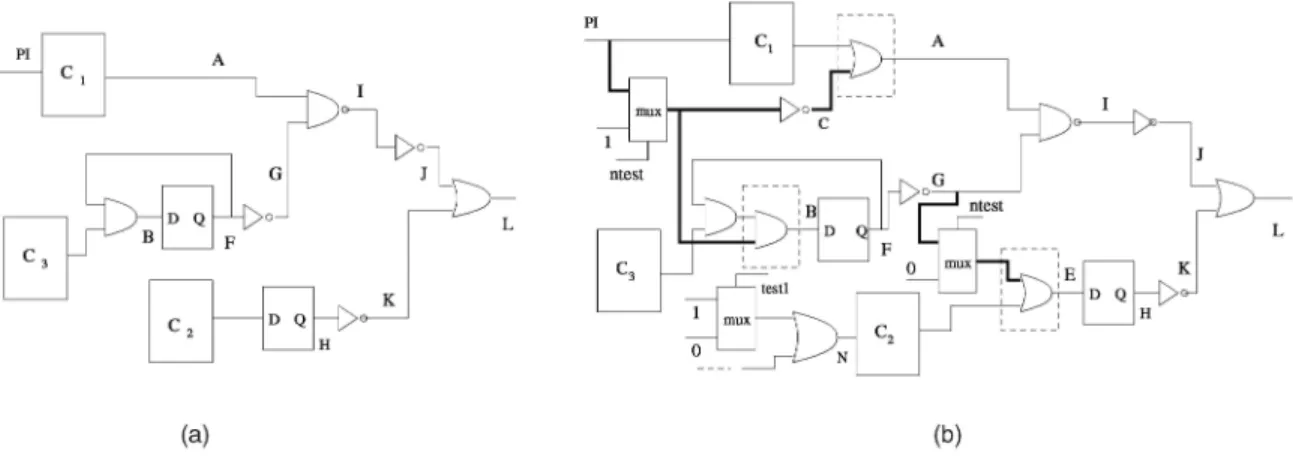
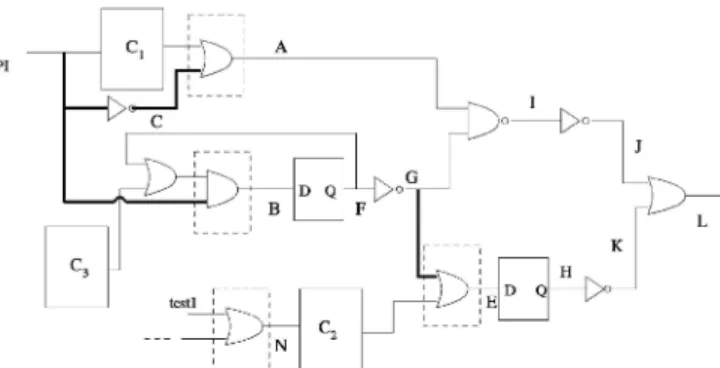
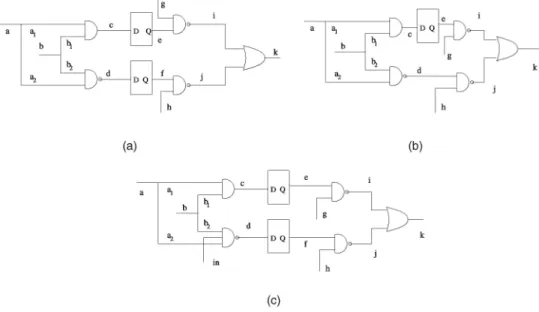
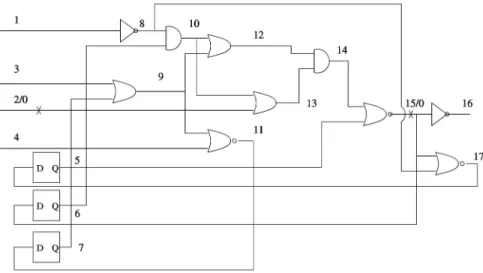
J105 e IEEE TC 2003 8
全文
図


関連したドキュメント
In the second computation, we use a fine equidistant grid within the isotropic borehole region and an optimal grid coarsening in the x direction in the outer, anisotropic,
As explained above, the main step is to reduce the problem of estimating the prob- ability of δ − layers to estimating the probability of wasted δ − excursions. It is easy to see
It turns out that the symbol which is defined in a probabilistic way coincides with the analytic (in the sense of pseudo-differential operators) symbol for the class of Feller
In addition to the basic facts just stated on existence and uniqueness of solutions for our problems, the analysis of the approximation scheme, based on a minimization of the
This paper presents an investigation into the mechanics of this specific problem and develops an analytical approach that accounts for the effects of geometrical and material data on
While conducting an experiment regarding fetal move- ments as a result of Pulsed Wave Doppler (PWD) ultrasound, [8] we encountered the severe artifacts in the acquired image2.
The scattering structure is assumed to be buried in the fluid seabed bellow a water waveguide and is a circular elastic shell filled with a fluid that may have different properties
According to the divide and conquer method under equivalence relation and tolerance relation, the abstract process for knowledge reduction in rough set theory based on the divide